Abstract
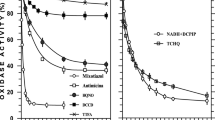
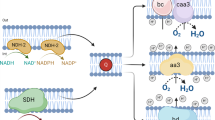
Seven strains of bacteria belonging to the Beggiatoa-Vitreoscilla group were studied for their respiratory activity and for the presence of electron transport conponents. All strains tested oxidized [1-14C] and [2-14C] acetate to 14CO2 at relatively high rates. All strains tested were N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylphenylenediamine (TMPD)-oxidase positive and contained spectra representing a-type and carbon monoxide-binding cytochromes. Most of the strains also contained spectra representing c-type and b-type cytochromes. Beggiatoa alba B18LD contained b-type, a-type, c-type and CO-binding cytochromes, the latter two being located in the 144,000 x g soluble fraction. B. alba also contained ubiquinone-8 as its only detectable quinone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSS:
-
basal salts solution
- BH:
-
Beggiatoa heterotrophic medium
- BSO:
-
Beggiatoa sulfide oxidation medium
- TMPD:
-
N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylphenylenediamine
- Q8:
-
ubiquinone-8
References
Burton SD, Morita RY (1964) Effect of catalase and cultural conditions on growth of Beggiatoa. J Bacteriol 88:1755–1761
Burton SD, Morita RY, Miller M (1966) Utilization of acetate by Beggiatoa. J Bacteriol 91:1192–1200
Cannon GC, Strohl WR, Larkin JM, Shively JM (1979) Cytochromes in Beggiatoa alba. Curr Microbiol 2:263–266
Carr NG, Exell G, Flynn V, Hallaway M, Talukdar S (1967) Minor quinones of some Myxophyceae. Arch Biochem Biophys 120:503–507
DiSpirito AA, Loh W H-T, Tuovinen OH (1983) A novel method for the isolation of bacterial quinones and its application to appraise the ubiquinone composition of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Arch Microbiol 135:77–80
Güde H, Strohl WR, Larkin JM (1981) Mixotrophic and heterotrophic growth of Beggiatoa alba in continuous culture. Arch Microbiol 129:357–360
Kelly DP (1982) Biochemistry of the chemolithotrophic oxidation of inorganic sulphur. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 298:499–528
Kowallik U, Pringsheim EG (1966) The oxidation of hydrogen sulfide by Beggiatoa. Am J Bot 53:801–806
Kuenen JG, Beudecker RF (1982) Microbiology of thiobacilli and other sulphur-oxidizing autotrophs, mixotrophs and heterotrophs. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 298:473–497
Larkin JM, Strohl WR (1983) Beggiatoa, Thiothrix, and Thioploca. Annu Rev Microbiol 37:341–367
Mayfield DC, Kester AS (1975) Nutrition of Vitreoscilla stercoraria. Can J Microbiol 21:1947–1951
Mezzino MJ, Strohl WR, Larkin JM (1984) Characterization of Beggiatoa alba. Arch Microbiol 137:139–144
Minges CG, Titus JA, Strohl WR (1983) Plasmid DNA in colorless filamentous gliding bacteria. Arch Microbiol 134:38–44
Nelson DC, Castenholz RW (1981) Use of reduced sulfur compounds by Beggiatoa sp. J Bacteriol 1947:140–154
Nelson DC, Jannasch HW (1983) Chemoautotrophic growth of a marine Beggiatoa in sulfide-gradient cultures. Arch Microbiol 136:262–269
Pringsheim EG (1964) Heterotrophism and species concepts in Beggiatoa. Am J Bot 51:893–913
Pringsheim EG (1967) Die Mixotrophie von Beggiatoa. Arch Mikrobiol 59:247–254
Schmidt TM, Vinci VA, Strohl WR (1986) Protein synthesis by Beggiatoa alba in the presence and absence of sulfide. Arch Microbiol 144:158–162
Scotten HL, Stokes JL (1962) Isolation and properties of Beggiatoa. Arck Mikrobiol 42:353–368
Strohl WR, Larkin JM (1978) Enumeration, isolation, and characterization of Beggiatoa from freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 36:755–770
Strohl WR, Schmidt TM (1984) Mixotrophy in Beggiatoa and Thiothrix. In: Strohl WR, Tuovinen OH (eds) Microbial chemoautotrophy. The Ohio State University Press, Columbus, pp 79–95
Strohl WR, Cannon GC, Shively JM, Güde H, Hook LA, Lane CH, Larkin JM (1981) Heterotrophic carbon metabolism by Beggiatoa alba. J Bacteriol 148:572–583
Strohl WR, Schmidt TM, Lawry NH, Mezzino MJ, Larkin JM (1986) Characterization of Vitreoscilla beggiatoides and V. filiformis sp. nov., nom. rev., and comparison to V. stercoraria and Beggiatoa. Internat J Syst Bacteriol (in press)
Vargas A, Strohl WR (1985a) Ammonium assimilation by Beggiatoa alba. Arch Microbiol 142:275–278
Vargas A, Strohl WR (1985b) Utilization of, nitrate by Beggiatoa alba. Arch Microbiol 142:279–284
Webster DA, Hackett P (1966) Respiratory chain of colorless algae. II. Cyanophyta. Plant Physiol 41:599–605
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strohl, W.R., Schmidt, T.M., Vinci, V.A. et al. Electron transport and respiration in Beggiatoa and Vitreoscilla . Arch. Microbiol. 145, 71–75 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413029
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413029