Abstract
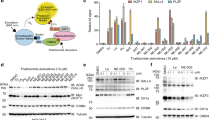
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is critical for B-cell receptor signaling and related to many types of human cancers. However, the drug resistance and off-_target effect of present traditional BTK inhibitors occurred over time. As a new strategy for drug development, the proteolysis _targeting chimera (PROTAC) has been proved to _target varieties of proteins. Here SPB5208 (4-(2-(2-(2-(2-(3-(4-amino-3-(4-phenoxy phenyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)-2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione) was synthesized as a new PROTAC degradation agent of BTK by linking Ibrutinib and Thalidomide. In vitro study indicated that SPB5208 reduced the BTK enzyme activity with high selectivity and inhibited effectively cancer cell proliferation. More than that, SPB5208 induced BTK protein degradation through a proteasome- and CRBN- dependent manner in JeKo-1 cells. In addition, SPB5208 was also confirmed to induce significantly BTK protein degradation in vivo. Thus, this study provides a new pharmacological tool for further study of new BTK PROTAC and their mechanism of action in physiological environment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PROTAC:
-
Proteolysis _targeting chimera
- BTK:
-
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase
References
Bender AT, Gardberg A, Pereira A, Johnson T, Wu Y, Grenningloh R (2017) Ability of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors to sequester y551 and prevent phosphorylation determines potency for inhibition of fc receptor but not B-cell receptor signaling. Mol Pharm 91(3):208–219
Cheng WZ, Xiao RX, Xiao BY, Bin J, Jin J (2018) Proteolysis _targeting chimeras (protacs) of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). Eur J Med Chem 150:301–314
George VD, Qing S, Qing JL, Douglas GB, Myra BB, Rick R, Arvind M, Lorell D, Celia DA, Jun D, Mary O, Rodney V, Ying RZ, Zheng Y, Punit M, Andrew JT, Jodi K, Chiehying JC, Hui PZ, Kathleen G, Tracy T, Mark AP, Stacey S, Daniel WK, Kim WM, Luisa SC, Aberra F, James RB, Joel CB, Percy HC, Joseph AT (2016) Small molecule reversible inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). J Med Chem 59(3):7915–7935
Gadd MS, Testa A, Lucas X, Chan KH, Chen W, Lamont DJ (2017) Structural basis of PROTAC cooperative recognition for selective protein degradation. Nat Chem Biol 13(5):514–521
Huang HT, Dobrovolsky D, Paulk J, Yang G, Gray NS (2017) A chemo proteomic approach to query the degradable kineme using a multi-kinase degrader. Cell Chem Biol 25(1):88–97
Jing JW, Christina L, Tsui ST, Dong L (2016) Second-generation inhibitors of Bruton tyrosine kinase. J Clin Hematol Oncol 9(1):80–91
Khan WN (2001) Regulation of B lymphocyte development and activation by bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Immunol Res 23(2–3):147–156
Kim HO (2019) Development of BTK inhibitors for the treatment of B-cell malignancies. Arch Pharmacal Res 3:171–181
Lai AC, Crews CM (2016) Induced protein degradation: an emerging drug discovery paradigm. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(2):101–114
Michael L, Brad S, Ranjana H, Michael E, Jorge E (2013) _targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma. Boston Med Surg J 369(6):507–516
Miao X, Hou Y, Sheng L, Peng J (2013) Therapeutic effects of thalidomide in hematologic disorders: a review. Front Med 7(3):290–300
Matyskiela ME, Lu G, Ito T, Pagadian B, Lu CC, Miller K (2016) A novel cereblon modulator recruits GSPT1 to the CRL4CRBN ubiquitin ligase. Nature 535(7611):252–7
Ottis P, Crews CM (2017) Proteolysis-_targeting chimeras: induced protein degradation as a therapeutic strategy. ACS Chem Biol 12(4):892–898
Olson CM, Jiang B, Erb MA, Liang Y, Doctor ZM, Zhang Z (2017) Pharmacological perturbation of cdk9 using selective CDK9 inhibition or degradation. Nat Chem Biol 14(2):163–170
Qian K, Bori ID, Chen CH, Huang L, Lee KH (2012) Anti-aids agents 90. novel c-28 modified bevirimat analogues as potent hiv maturation inhibitors. J Med Chem 55(18):8128–8136
Radford J, Davies A, Cartron G, Morschhauser F, Vitolo U (2013) Obinutuzumab (GA101) plus CHOP or FC in relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma: results of the GAUDI study (BO21000). Blood 122(7):390–400
Ravichandiran P, Jegan A, Premnath D, Periasamy VS, Muthusubramanian S, Vasanthkumar S (2014) Synthesis, molecular docking and cytotoxicity evaluation of novel 2-(4-amino-benzosulfonyl)-5h-benzo[b]carbazole-6,11-dione derivatives as histone deacetylase (HDAC8) inhibitors. Bioorg Chem 53(4):24–36
Ravichandiran P, Jegan A, Premnath D, Periasamy VS, Vasanthkumar S (2014) Design, synthesis, molecular docking as histone deacetylase (HDAC8) inhibitors, cytotoxicity and antibacterial evaluation of novel 6-(4-(4-aminophenylsulfonyl) phenylamino)-5h-benzo[a]Phenoxazine-5-one derivatives. Med Chem Res 24(1):197–208
Ravichandiran P, Athinarayanan J, Premnath D, Periasamy VS, Alshatwi AA, Vasanthkumar S (2015) Synthesis, molecular docking and biological evaluation of novel 6-(4-(4-aminophenylsulfonyl) phenylamino)-5h-benzo[a]phenothiazin-5-one derivative. Spectrochim Acta, Part A 139(1):477–487
Sachdeva M, Dhingra S (2015) Obinutuzumab: an FDA approved monoclonal antibody in the treatment of untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int J Appl Basic Med Res 5(1):54–57
Satterthwaite AB, Witte ON (2000) The role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B-cell development and function: a genetic perspective. Immunol Rev 175:120–127
Sakamoto KM, Kim KB, Kumagai A, Mercurio F, Crews CM, Deshaies RJ (2001) Protacs: chimeric molecules that _target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(15):8554–8559
Sehn LH, Gascoyne RD (2015) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: optimizing outcome in the context of clinical and biologic heterogeneity. Blood 125(1):22–32
Xin YL, Bin S, Yu T, Yu C, Hui ZY, Jiu RL, Lian JW, Si YH, Qi DY, Hua X (2019) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 2-phenyl pyrimidine derivatives as potent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors. MedChemComm 10:421–428
Yong HS, Xing WZ, Ning D, Hong YG, Yue W, Yi QY (2018) Protac-induced BTK degradation as a novel therapy for mutated BTK c481s induced ibrutinib-resistant B-cell malignancies. Cell Res 28(7):779–781
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP11961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Da, Y., Wang, F. et al. _targeted selective degradation of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase by PROTACs. Med Chem Res 29, 802–808 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02526-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02526-3