Abstract
Purpose
Phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) tadalafil administration in men with erectile dysfunction is associated with increased testosterone/estradiol ratio, leading to hypothesize a potential increased effect of androgen action on _target tissues. We aimed to characterize, in a cellular model system in vitro, the potential modulation of aromatase and sex steroid hormone receptors upon exposure to tadalafil (TAD).
Methods
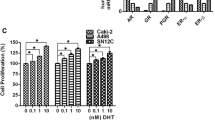
Human osteoblast-like cells SAOS-2 were chosen as an in vitro model system since osteoblasts are _target of steroid hormones. Cells were tested for viability upon TAD exposure, which increased cell proliferation. Then, cells were treated with/without TAD for several times to evaluate potential modulation in PDE5, aromatase (ARO), androgen (AR) and estrogen (ER) receptor expression.
Results
Osteoblasts express significant levels of both PDE5 mRNA and protein. Exposure of cells to increasing concentrations of TAD (10−8–10−7 M) decreased PDE5 mRNA and protein expression. Also, TAD inhibited ARO mRNA and protein expression leading to an increase in testosterone levels in the supernatants. Interestingly, TAD increased total AR mRNA and protein expression and decreased ERα, with an increased ratio of AR/ER, suggesting preferential androgenic vs estrogenic pathway activation.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate for the first time that TAD decreases ARO expression and increases AR protein expression in human SAOS-2, strongly suggesting a new control of steroid hormones pathway by PDE5i. These findings might represent the first evidence of translational actions of PDE5i on AR, which leads to hypothesize a growing relevance of this molecule in men with prostate cancer long-term treated with TAD for sexual rehabilitation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Francis SH, Busch JL, Corbin JD, Sibley D (2010) cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phophodiesterases in nitric oxide and cGMP action. Pharmacol Rev 62:525–563. doi:10.1124/pr.110.002907
Bruzziches R, Francomano D, Gareri P, Lenzi A, Aversa A (2013) An update on pharmacological treatment of erectile dysfunction with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. Expert Opin Pharmacother 14:1333–1344
Morelli A, Filippi S, Mancina R et al (2004) Androgens regulate phosphodiesterase type-5 expression and functional activity in corpora cavernosa. Endocrinology 145:2253–2263
Ahlström M, Lamberg-Allardt C (2000) Inactivation of atrial natriuretic factor-stimulated cyclic guanosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (cGMP) in UMR-106 osteoblast-like cells. Biochem Pharmacol 59(9):1133–1139
Gong Y, Xu CY, Wang JR, Hu XH, Hong D, Ji X, Shi W, Chen HX, Wang HB, Wu XM (2014) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 5 reduces bone mass by suppression of canonical Wnt signaling. Cell Death Dis 5:e1544. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.510
Carosa E, Martini P, Brandetti F, Di Stasi SM, Lombardo F, Lenzi A, Jannini EA (2004) Type V phosphodiesterase inhibitor treatments for erectile dysfunction increase testosterone levels. Clin Endocrinol Oxf 61:382–386
Greco EA, Pili M, Bruzziches R, Corona G, Spera G, Aversa A (2006) Testosterone : estradiol ratio changes associated with long-term tadalafil administration: a pilot study. J Sex Med 3:716–722
Aversa A, Caprio M, Antelmi A et al (2011) Exposure to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors stimulates aromatase expression in human adipocytes in vitro. J Sex Med 8:696–704
Andric SA, Janjic MM, Stojkov NJ, Kostic TS (2010) Sildenafil treatment in vivo stimulates Leydig cell steroidogenesis via the cAMP/cGMP signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299:E544–E550
Janjic MM, Stojkov NJ, Bjelic MM, Mihajlovic AI, Andric SA, Kostic TS (2012) Transient rise of serum testosterone level after single sildenafil treatment of adult male rats. J Sex Med 9:2534–2543
Wannenes F, Caprio M, Gatta L, Fabbri A, Bonini S, Moretti C (2008) Androgen receptor expression during C2C12 skeletal muscle cell line differentiation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 292(1–2):11–19
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 25:402–408
Vidal O, Kindblom LG, Ohlsson C (1999) Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-beta in murine and human bone. J Bone Miner Res 14:923–929
Scipioni A, Stefanini S, Santone R, Giorgi M (2005) Immunohistochemical localisation of PDE5 in Leydig and myoid cells of prepuberal and adult rat testis. Histochem Cell Biol 124:401–407
Middendorff R, Davidoff MS, Behrends S, Mewe M, Miethens A, Müller D (2000) Multiple roles of the messenger molecule cGMP in testicular function. Andrologia 32:55–59
Saraiva KL, Silva AK, Wanderley MI, De Araújo AA, De Souza JR, Peixoto CA (2009) Chronic treatment with sildenafil stimulates Leydig cell and testosterone secretion. Int J Exp Pathol 90:454–462
Behan LA, Amir E, Casper RF (2015) Aromatase inhibitors for prevention of breast cancer in postmenopausal women: a narrative review. Menopause 22:342–350
Laurent M, Gielen E, Claessens F, Boonen S, Vanderschueren D (2013) Osteoporosis in older men: recent advances in pathophysiology and treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 27:527–539
Lormeau C, Soudan B, d’Herbomez M, Pigny P, Duquesnoy B, Cortet B (2004) Sex hormone-binding globulin, estradiol, and bone turnover markers in male osteoporosis. Bone 34:933–939
Aversa A, Bruzziches R, Francomano D, Greco EA, Fornari R, Di Luigi L, Lenzi A, Migliaccio S (2012) Effects of long-acting testosterone undecanoate on bone mineral density in middle-aged men with late-onset hypogonadism and metabolic syndrome: results from a 36 months controlled study. Aging Male 15:96–102
Miki Y, Suzuki T, Hatori M, Igarashi K, Aisaki KI, Kanno J, Nakamura Y, Uzuki M, Sawai T, Sasano H (2007) Effects of aromatase inhibitors on human osteoblast and osteoblast-like cells: a possible androgenic bone protective effects induced by exemestane. Bone 40:876–887
Chen R, Cui J, Wang Q, Li P, Liu X, Hu H, Wei W (2015) Antiproliferative effects of anastrozole on MCF–7 human breast cancer cells in vitro are significantly enhanced by combined treatment with testosterone undecanoate. Mol Med Rep. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.3427
Santen RJ, Petroni GR, Fisch MJ, Myers CE, Theodorescu D, Cohen RB (2001) Use of the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole in the treatment of patients with advanced prostate carcinoma. Cancer 92:2095–2101
Smith MR, Kaufman D, George D et al (2002) Selective aromatase inhibition for patients with androgen-independent prostate carcinoma. Cancer 95:1864–1868
Acknowledgments
Research was funded by PRIN 2011 052013 to SM, PON 01_00829 to AL. FW is supported by an ELI Lilly grant. LiSa laboratories are a Joint-Venture between Eli Lilly Firenze and Sapienza University of Rome, Department of Experimental Medicine, Section of Medical Pathophysiology, Endocrinology and Nutrition, Sapienza University of Rome. AA designed the study, analyzed the in vitro data, contributed to the interpretation, wrote the manuscript, contributed to the discussion; FW, VMB, SF, VP designed the study, produced and analyzed the in vitro data, contributed to the interpretation; DF, EAG, CC contributed to the interpretation of the data and discussion, revised the manuscript; AL designed the study, reviewed the manuscript; SM, designed the study, analyzed the in vitro data, contributed to the interpretation and discussion, wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study in object has been approved by the local ethical committee of Sapienza University of Rome; Compliant with the Ethical standards.
Informed consent
Each subject signed a complete and detailed informed consent before entering the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aversa, A., Fittipaldi, S., Bimonte, V.M. et al. Tadalafil modulates aromatase activity and androgen receptor expression in a human osteoblastic cell in vitro model. J Endocrinol Invest 39, 199–205 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0344-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0344-1