Abstract
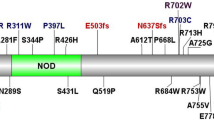
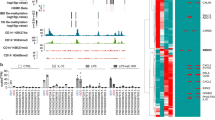
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, which is thought to result from the effect of environmental factors in a genetically predisposed host. A gene location in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 16, IBD1, that contributes to susceptibility to Crohn's disease has been established through multiple linkage studies1,2,3,4,5,6, but the specific gene(s) has not been identified. NOD2, a gene that encodes a protein with homology to plant disease resistance gene products is located in the peak region of linkage on chromosome 16 (ref. 7). Here we show, by using the transmission disequilibium test and case-control analysis, that a frameshift mutation caused by a cytosine insertion, 3020insC, which is expected to encode a truncated NOD2 protein, is associated with Crohn's disease. Wild-type NOD2 activates nuclear factor NF-κB, making it responsive to bacterial lipopolysaccharides; however, this induction was deficient in mutant NOD2. These results implicate NOD2 in susceptibility to Crohn's disease, and suggest a link between an innate immune response to bacterial components and development of disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hugot, J. P. et al. Mapping of a susceptibility locus for Crohn's disease on chromosome 16. Nature 379, 821–823 (1996).
Ohmen, J. D. et al. Susceptibility locus for inflammatory bowel disease on chromosome 16 has a role in Crohn's disease, but not in ulcerative colitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 5, 1679–1683 (1996).
Curran, M. E. et al. Genetic analysis of inflammatory bowel disease in a large European cohort supports linkage to chromosomes 12 and 16. Gastroenterology 115, 1066–1071 (1998).
Cavanaugh, J. A. et al. Analysis of Australian Crohn's disease pedigrees refines the localization for susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease on chromosome 16. Ann. Hum. Genet. 62, 291–298 (1998).
Cho, J. H. et al. Identification of novel susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease on chromosomes1p, 3q, and 4q: evidence for epistasis between 1p and IBD1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7502–7507 (1998).
Annese, V. et al. Genetic analysis in Italian families with inflammatory bowel disease supports linkage to the IBD1 locus—a GISC study. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 7, 567–573 (1999).
Ogura, Y., Inohara, N., Benito, A., Chen, F. F. & Nuñez, G. Nod2, a Nod1/Apaf-1 family member that is restricted to monocytes and activates NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 4812–4818 (2001).
Loftus, E. V. Jr et al. Crohn's disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1940–1993: incidence, prevalence, and survival. Gastroenterology 114, 1161–1168 (1998).
Kyle, J. Crohn's disease in the northeastern and northern Isles of Scotland: an epidemiological review. Gastroenterology 103, 392–399 (1992).
Fiocchi, C. Inflammatory bowel disease: etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 115, 182–205 (1998).
Binder, V. Genetic epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Digest. Dis. 16, 351–355 (1998).
Inohara, N., Ogura, Y., Chen, F. F., Muto, A. & Nuñez, G. Human Nod1 confers responsiveness to bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 2551–2554 (2001).
Parniske, M. et al. Novel disease resistance specificities result from sequence exchange between tandemly repeated genes at the Cf-4/9 locus of tomato. Cell 91, 821–832 (1997).
Ellis, J. G., Lawrence, G. J., Luck, J. E. & Dodds, P. N. Identification of regions in alleles of the flax rust resistance gene L that determine differences in gene-for-gene specificity. Plant Cell. 11, 495–506 (1999).
Dixon, M. S., Golstein, C., Thomas, C. M., van Der Biezen, E. A. & Jones, J. D. Genetic complexity of pathogen perception by plants: the example of Rcr3, a tomato gene required specifically by Cf-2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 8807–8814 (2000).
Aderem, A. & Ulevitch. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 406, 782–787 (2000).
Arbour, N. C. et al. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nature Genet. 25, 187–191 (2000).
Moore, K. W. et al. Interleukin-10. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 11, 165–190 (1993).
Berg, D. J. et al. Enterocolitis and colon cancer in interleukin-10-deficient mice are associated with aberrant cytokine production and CD4+ TH1-like responses. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 1010–1020 (1996).
Spielman, R. S. & Ewens, W. J. The TDT and other family-based tests for linkage disequilibrium and association. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 59, 983–989 (1996).
Risch, N. & Merikangas, K. The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science 273, 1516–1517 (1996).
Han, C. S. et al. Construction of a BAC contig map of chromosome 16q by two-dimensional overgo hybridization. Genome Res. 10, 714–721 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families that participated in this study. We acknowledge the contributions of J. B. Kirsner and M. Boyer. We thank T. Ross. P. Lucas and L. McAllister-Lucas for critically reading the manuscript; and A. Moran and M. Apicella for LPS samples. The work was supported by grants from the NIH (G.N. and J.H.C.), the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of American (J.H.C.), the Reva and David Logan Foundation (J.H.C.) and the Gastrointestinal Research Foundation (J.H.C). Y.O. was supported by funds from Tokushima University, Japan. G.N. and J.H.C. contributed equally to this work and share senior authorship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogura, Y., Bonen, D., Inohara, N. et al. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn's disease. Nature 411, 603–606 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35079114
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35079114
This article is cited by
-
Understanding the molecular mechanism of pathogenic variants of BIR2 domain in XIAP-deficient inflammatory bowel disease
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
The Genetics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2024)
-
Platelet/Albumin ratio and plateletcrit levels are potential new biomarkers for assessing endoscopic inflammatory bowel disease severity
BMC Gastroenterology (2023)
-
Engineered live bacteria as disease detection and diagnosis tools
Journal of Biological Engineering (2023)
-
Molecular mechanisms in colitis-associated colorectal cancer
Oncogenesis (2023)