Antisense properties of tricyclo-DNA
- PMID: 12087157
- PMCID: PMC117067
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf412
Antisense properties of tricyclo-DNA
Abstract
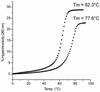
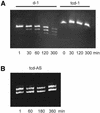
Tricyclo (tc)-DNA belongs to the class of conformationally constrained DNA analogs that show enhanced binding properties to DNA and RNA. We prepared tc-oligonucleotides up to 17 nt in length, and evaluated their binding efficiency and selectivity towards complementary RNA, their biological stability in serum, their RNase H inducing potential and their antisense activity in a cellular assay. Relative to RNA or 2'-O-Me-phosphorothioate (PS)-RNA, fully modified tc-oligodeoxynucleotides, 10-17 nt in length, show enhanced selectivity and enhanced thermal stability by approximately 1 degrees C/modification in binding to RNA _targets. Tricyclodeoxyoligonucleotides are completely stable in heat-deactivated fetal calf serum at 37 degree C. Moreover, tc-DNA-RNA duplexes are not substrates for RNase H. To test for antisense effects in vivo, we used HeLa cell lines stably expressing the human beta-globin gene with two different point mutations in the second intron. These mutations lead to the inclusion of an aberrant exon in beta-globin mRNA. Lipofectamine-mediated delivery of a 17mer tc-oligodeoxynucleotide complementary to the 3'-cryptic splice site results in correction of aberrant splicing already at nanomolar concentrations with up to 100-fold enhanced efficiency relative to a 2'-O-Me-PS-RNA oligonucleotide of the same length and sequence. In contrast to 2'-O-Me-PS-RNA, tc-DNA shows antisense activity even in the absence of lipofectamine, albeit only at much higher oligonucleotide concentrations.
Figures
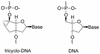
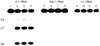

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the RNase H cleavage kinetics and blood serum stability of the north-conformationally constrained and 2'-alkoxy modified oligonucleotides.Biochemistry. 2007 May 15;46(19):5635-46. doi: 10.1021/bi0620205. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17411072
-
Mixed backbone antisense oligonucleotides: design, biochemical and biological properties of oligonucleotides containing 2'-5'-ribo- and 3'-5'-deoxyribonucleotide segments.Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Jan 15;25(2):370-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.2.370. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997. PMID: 9016567 Free PMC article.
-
2'β-Fluoro-Tricyclo Nucleic Acids (2'F-tc-ANA): Thermal Duplex Stability, Structural Studies, and RNase H Activation.Chemistry. 2017 Aug 1;23(43):10310-10318. doi: 10.1002/chem.201701476. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28477335
-
Locked nucleic acids: a promising molecular family for gene-function analysis and antisense drug development.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2001 Jun;3(3):239-43. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11497347 Review.
-
2'-carbohydrate modifications in antisense oligonucleotide therapy: importance of conformation, configuration and conjugation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Dec 10;1489(1):117-30. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(99)00138-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10807002 Review.
Cited by
-
The bench to bedside journey of tricyclo-DNA antisense oligonucleotides for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Jul 19;15(9):3017-3025. doi: 10.1039/d4md00394b. eCollection 2024 Sep 19. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39309360 Review.
-
Towards combining backbone and sugar constraint in 3'-3' bis-phosphonate tethered 2'-4' bridged LNA oligonucleotide trimers.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 26;14(33):23583-23591. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04277h. eCollection 2024 Jul 26. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39070250 Free PMC article.
-
A Convenient Oligonucleotide Conjugation via Tandem Staudinger Reaction and Amide Bond Formation at the Internucleotidic Phosphate Position.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 7;25(4):2007. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042007. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396686 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Chemically Modified Nucleic Acid Analogues for Splice Switching Application.ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 11;8(51):48650-48661. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07618. eCollection 2023 Dec 26. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38162739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Therapeutic Delivery with DG9, a Versatile Cell-Penetrating Peptide.Cells. 2023 Oct 2;12(19):2395. doi: 10.3390/cells12192395. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Taylor M.F., Wiederholt,K. and Sverdrup,F. (1999) Antisense oligonucleotides: a systematic high-throughput approach to _target validation and gene function determination. Drug Discov. Today, 4, 562–567. - PubMed
-
- Uhlmann E. (2000) Recent advances in the medicinal chemistry of antisense oligonucleotides. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev., 3, 203–213. - PubMed
-
- Levin A.A. (1999) A review of the issues in the pharmacokinetics and toxicology of phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1489, 69–84. - PubMed
-
- Baker B.F. and Monia,B.P. (1999) Novel mechanisms for antisense-mediated regulation of gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1489, 3–18. - PubMed
-
- Crooke S.T. (1999) Molecular mechanism of action of antisense drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1489, 31–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

