Locked nucleic acid (LNA) mediated improvements in siRNA stability and functionality
- PMID: 15653644
- PMCID: PMC546170
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki193
Locked nucleic acid (LNA) mediated improvements in siRNA stability and functionality
Abstract
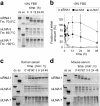
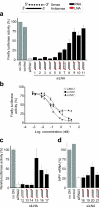
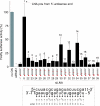
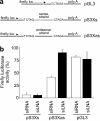
Therapeutic application of the recently discovered small interfering RNA (siRNA) gene silencing phenomenon will be dependent on improvements in molecule bio-stability, specificity and delivery. To address these issues, we have systematically modified siRNA with the synthetic RNA-like high affinity nucleotide analogue, Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA). Here, we show that incorporation of LNA substantially enhances serum half-life of siRNA's, which is a key requirement for therapeutic use. Moreover, we provide evidence that LNA is compatible with the intracellular siRNA machinery and can be used to reduce undesired, sequence-related off-_target effects. LNA-modified siRNAs _targeting the emerging disease SARS, show improved efficiency over unmodified siRNA on certain RNA motifs. The results from this study emphasize LNA's promise in converting siRNA from a functional genomics technology to a therapeutic platform.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LNA incorporated siRNAs exhibit lower off-_target effects compared to 2'-OMethoxy in cell phenotypic assays and microarray analysis.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2008;(52):25-6. doi: 10.1093/nass/nrn013. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2008. PMID: 18776235
-
Application of small interfering RNAs modified by unlocked nucleic acid (UNA) to inhibit the heart-pathogenic coxsackievirus B3.FEBS Lett. 2010 Feb 5;584(3):591-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.12.007. Epub 2010 Jan 13. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20005874
-
LNA-antisense rivals siRNA for gene silencing.Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2004 Mar;7(2):188-94. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2004. PMID: 15603252 Review.
-
Structure and sequence motifs of siRNA linked with in vitro down-regulation of morbillivirus gene expression.Antiviral Res. 2008 Jul;79(1):37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.01.159. Epub 2008 Mar 11. Antiviral Res. 2008. PMID: 18394725
-
Locked nucleic acids: promising nucleic acid analogs for therapeutic applications.Chem Biodivers. 2010 Mar;7(3):536-42. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200900343. Chem Biodivers. 2010. PMID: 20232325 Review.
Cited by
-
The beauty of symmetry: siRNA phosphorodithioate modifications reduce stereocomplexity, ease analysis, and can improve in vivo potency.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Sep 10;35(4):102336. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102336. eCollection 2024 Dec 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39391764 Free PMC article.
-
Next generation APOBEC3 inhibitors: Optimally designed for potency and nuclease stability.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 6:2024.09.05.611238. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.05.611238. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39282427 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Principle, application and challenges of development siRNA-based therapeutics against bacterial and viral infections: a comprehensive review.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 13;15:1393646. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1393646. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38939184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembling the RNA therapeutics toolbox.Med Rev (2021). 2024 Mar 20;4(2):110-128. doi: 10.1515/mr-2023-0062. eCollection 2024 Apr. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 38680684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA nanostructures for _targeted drug delivery and imaging.RNA Biol. 2024 Jan;21(1):1-19. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2328440. Epub 2024 Mar 31. RNA Biol. 2024. PMID: 38555519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elbashir S.M., Harborth J., Lendeckel W., Yalcin A., Weber K., Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498. - PubMed
-
- Fire A., Xu S., Montgomery M.K., Kostas S.A., Driver S.E., Mello C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton A.J., Baulcombe D.C. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286:950–952. - PubMed
-
- Zamore P.D., Tuschl T., Sharp P.A., Bartel D.P. RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell. 2000;101:25–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

