Dasatinib inhibits the growth of prostate cancer in bone and provides additional protection from osteolysis
- PMID: 19603032
- PMCID: PMC2720213
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605178
Dasatinib inhibits the growth of prostate cancer in bone and provides additional protection from osteolysis
Abstract
Background: Dasatinib is a small molecule kinase inhibitor that has recently been shown to inhibit Src family kinases (SFK) and also has activity against CaP. Of importance to metastatic CaP, which frequently metastasises to bone, SFK are also vital to the regulation of bone remodelling. We sought to determine the ability of dasatinib to inhibit growth of CaP in bone.
Methods: C4-2B CaP cells were injected into tibiae of SCID mice and treated with dasatinib, alone or in combination with docetaxel. Serum prostate-specific antigen levels, bone mineral density, radiographs and histology were analysed.
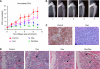
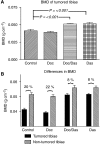
Results: Treatment with dasatinib alone significantly lowered sacrifice serum prostate-specific antigen levels compared to control, 2.3+/-0.4 vs 9.2+/-2.1 (P=0.004). Combination therapy improved efficacy over dasatinib alone (P=0.010). Dasatinib increased bone mineral density in tumoured tibiae by 25% over control tumoured tibiae (P<0.001).
Conclusion: Dasatinib inhibits growth of C4-2B cells in bone with improved efficacy when combined with docetaxel. Additionally, dasatinib inhibits osteolysis associated with CaP. These data support further study of dasatinib in clinical trials for men with CaP bone metastases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dasatinib combined with docetaxel for castration-resistant prostate cancer: results from a phase 1-2 study.Cancer. 2012 Jan 1;118(1):63-71. doi: 10.1002/cncr.26204. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21976132 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized phase II study of cediranib alone versus cediranib in combination with dasatinib in docetaxel resistant, castration resistant prostate cancer patients.Invest New Drugs. 2014 Oct;32(5):1005-16. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0106-5. Epub 2014 May 3. Invest New Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24788563 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Increased serum insulin-like growth factor-1 levels are associated with prolonged response to dasatinib-based regimens in metastatic prostate cancer.Prostate. 2013 Jun;73(9):979-85. doi: 10.1002/pros.22645. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Prostate. 2013. PMID: 23371521 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SRC family kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases by dasatinib: possible combinations in solid tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Sep 1;17(17):5546-52. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2616. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21670084 Review.
-
Dasatinib: a potent SRC inhibitor in clinical development for the treatment of solid tumors.Cancer Treat Rev. 2010 Oct;36(6):492-500. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.02.015. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010. PMID: 20226597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bone metastasis in prostate cancer: emerging therapeutic strategies.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011 Jun;8(6):357-68. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.67. Epub 2011 May 10. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21556025 Review.
-
Src signaling pathways in prostate cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014 Sep;33(2-3):595-606. doi: 10.1007/s10555-013-9481-1. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014. PMID: 24522479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathobiology and management of prostate cancer-induced bone pain: recent insights and future treatments.Inflammopharmacology. 2013 Oct;21(5):339-63. doi: 10.1007/s10787-013-0183-7. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Inflammopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23918298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK phosphorylation disrupts the intramolecular interaction of capicua to promote cytoplasmic translocation of capicua and tumor growth.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 22;9:1030725. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1030725. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36619173 Free PMC article.
-
Dasatinib combined with docetaxel for castration-resistant prostate cancer: results from a phase 1-2 study.Cancer. 2012 Jan 1;118(1):63-71. doi: 10.1002/cncr.26204. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21976132 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Brubaker KD, Vessella RL, Brown LG, Corey E (2003) Prostate cancer expression of runt-domain transcription factor Runx2, a key regulator of osteoblast differentiation and function. Prostate 56: 13–22, doi: 10.1002/pros.10233 - PubMed
-
- Corey E, Quinn JE, Bladou F, Brown LG, Roudier MP, Brown JM, Buhler KR, Vessella RL (2002) Establishment and characterization of osseous prostate cancer models: intra-tibial injection of human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 52: 20–33, doi: 10.1002/pros.10091 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

