IL-1 family members and STAT activators induce cytokine production by Th2, Th17, and Th1 cells
- PMID: 19666510
- PMCID: PMC2726336
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0906988106
IL-1 family members and STAT activators induce cytokine production by Th2, Th17, and Th1 cells
Abstract
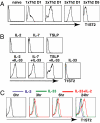
Expression of T1ST2, the IL-33R, by Th2 cells requires GATA3. Resting Th2 cells express little GATA3, which is increased by IL-33 and a STAT5 activator, in turn increasing T1ST2 from its low-level expression on resting Th2 cells. Th2 cells that have upregulated T1ST2 produce IL-13, but not IL-4, in response to IL-33 plus a STAT5 activator in an antigen-independent, NF-kappaB-dependent, cyclosporin A (CsA)-resistant manner. Similarly, Th17 cells produce IL-17A in response to IL-1beta and a STAT3 activator and Th1 cells produce IFNgamma in response to IL-18 and a STAT4 inducer. Thus, each effector Th cell produces cytokines without antigenic stimulation in response to an IL-1 family member and a specific STAT activator, implying an innate mechanism through which memory CD4 T cells are recruited by an induced cytokine environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
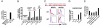
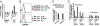
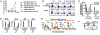

Similar articles
-
Enforced expression of GATA3 allows differentiation of IL-17-producing cells, but constrains Th17-mediated pathology.Eur J Immunol. 2008 Sep;38(9):2573-86. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737840. Eur J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18792410
-
The effects of electroacupuncture on TH1/TH2 cytokine mRNA expression and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in the splenic T cells of traumatized rats.Anesth Analg. 2009 Nov;109(5):1666-73. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181b5a234. Anesth Analg. 2009. PMID: 19843806
-
Early growth response protein-1 (Egr-1) is preferentially expressed in T helper type 2 (Th2) cells and is involved in acute transcription of the Th2 cytokine interleukin-4.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 15;285(3):1643-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.011585. Epub 2009 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19915002 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-27 in T cell immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jan 27;16(2):2851-63. doi: 10.3390/ijms16022851. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25633106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GATA-3 promotes Th2 responses through three different mechanisms: induction of Th2 cytokine production, selective growth of Th2 cells and inhibition of Th1 cell-specific factors.Cell Res. 2006 Jan;16(1):3-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310002. Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16467870 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Immune Regulatory Roles of Interleukin-33 in Pathological Conditions.Cells. 2022 Oct 14;11(20):3237. doi: 10.3390/cells11203237. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 31;109(5):1673-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115884109. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22307629 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33-responsive lineage- CD25+ CD44(hi) lymphoid cells mediate innate type 2 immunity and allergic inflammation in the lungs.J Immunol. 2012 Feb 1;188(3):1503-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102832. Epub 2011 Dec 23. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22198948 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue Cytokine IL-33 Modulates the Cytotoxic CD8 T Lymphocyte Activity During Nutrient Deprivation by Regulation of Lineage-Specific Differentiation Programs.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 24;10:1698. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01698. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31396219 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous extracts from dietary supplements influence the production of inflammatory cytokines in immortalized and primary T lymphocytes.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2009 Dec 14;9:51. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-9-51. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2009. PMID: 20003431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmitz J, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–490. - PubMed
-
- Moritz DR, Rodewald HR, Gheyselinck J, Klemenz R. The IL-1 receptor-related T1 antigen is expressed on immature and mature mast cells and on fetal blood mast cell progenitors. J Immunol. 1998;161:4866–4874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

