Inhibition of beta-cell sodium-calcium exchange enhances glucose-dependent elevations in cytoplasmic calcium and insulin secretion
- PMID: 20413506
- PMCID: PMC2889768
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0630
Inhibition of beta-cell sodium-calcium exchange enhances glucose-dependent elevations in cytoplasmic calcium and insulin secretion
Abstract
Objective: The sodium-calcium exchanger isoform 1 (NCX1) regulates cytoplasmic calcium (Ca(2+)(c)) required for insulin secretion in beta-cells. NCX1 is alternatively spliced, resulting in the expression of splice variants in different tissues such as NCX1.3 and -1.7 in beta-cells. As pharmacological inhibitors of NCX1 splice variants are in development, the pharmacological profile of beta-cell NCX1.3 and -1.7 and the cellular effects of NCX1 inhibition were investigated.
Research design and methods: The patch-clamp technique was used to examine the pharmacological profile of the NCX1 inhibitor KB-R7943 on recombinant NCX1.3 and -1.7 activity. Ca(2+) imaging and membrane capacitance were used to assess the effects of KB-R7943 on Ca(2+)(c) and insulin secretion in mouse and human beta-cells and islets.
Results: NCX1.3 and -1.7 calcium extrusion (forward-mode) activity was approximately 16-fold more sensitive to KB-R7943 inhibition compared with cardiac NCX1.1 (IC(50s) = 2.9 and 2.4 vs. 43.0 micromol/l, respectively). In single mouse/human beta-cells, 1 micromol/l KB-R7943 increased insulin granule exocytosis but was without effect on alpha-cell glucagon granule exocytosis. KB-R7943 also augmented sulfonylurea and glucose-stimulated Ca(2+)(c) levels and insulin secretion in mouse and human islets, although KB-R7943 was without effect under nonstimulated conditions.
Conclusions: Islet NCX1 splice variants display a markedly greater sensitivity to pharmacological inhibition than the cardiac NCX1.1 splice variant. NCX1 inhibition resulted in glucose-dependent increases in Ca(2+)(c) and insulin secretion in mouse and human islets. Thus, we identify beta-cell NCX1 splice variants as _targets for the development of novel glucose-sensitive insulinotropic drugs for type 2 diabetes.
Figures
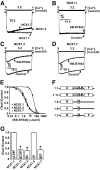
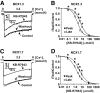
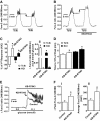
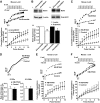
Similar articles
-
Reactive oxygen species directly modify sodium-calcium exchanger activity in a splice variant-dependent manner.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009 Nov;47(5):595-602. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.05.011. Epub 2009 May 28. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19481548
-
Splice variant-dependent regulation of beta-cell sodium-calcium exchange by acyl-coenzyme As.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Oct;22(10):2293-306. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0053. Epub 2008 Jul 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18635667 Free PMC article.
-
Heterozygous inactivation of the Na/Ca exchanger increases glucose-induced insulin release, β-cell proliferation, and mass.Diabetes. 2011 Aug;60(8):2076-85. doi: 10.2337/db10-0924. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21659499 Free PMC article.
-
Na(+)/Ca (2+) exchange and the plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase in β-cell function and diabetes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:385-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_33. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224897 Review.
-
The Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and the Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase in β-cell function and diabetes.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Jan 10;663:72-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.009. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 28780165 Review.
Cited by
-
A multi-layered network model identifies Akt1 as a common modulator of neurodegeneration.Mol Syst Biol. 2023 Dec 6;19(12):e11801. doi: 10.15252/msb.202311801. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Mol Syst Biol. 2023. PMID: 37984409 Free PMC article.
-
The context-dependent role of the Na+/Ca2+-exchanger (NCX) in pancreatic stellate cell migration.Pflugers Arch. 2023 Oct;475(10):1225-1240. doi: 10.1007/s00424-023-02847-3. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 37566113 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Voltage-Gated Na+ Currents Exerted by KB-R7943 (2-[2-[4-(4-nitrobenzyloxy)phenyl]ethyl]isothiourea), an Inhibitor of Na+-Ca2+ Exchanging Process.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 16;24(2):1805. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021805. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675319 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Ion-Transporting Proteins on the Digestive System Under Hypoxia.Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 14;13:870243. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.870243. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36187789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the Intracellular Sodium Homeostasis in Chemotaxis of Activated Murine Neutrophils.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 8;11:2124. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02124. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Festa A, Williams K, Hanley AJ, Haffner SM: β-cell dysfunction in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and early type 2 diabetes: comparison of surrogate markers with first-phase insulin secretion from an intravenous glucose tolerance test. Diabetes 2008;57:1638–1644 - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study 16: overview of 6 years' therapy of type II diabetes: a progressive disease. Diabetes 1995;44:1249–1258 - PubMed
-
- Del Prato S, Aragona M, Coppelli A: Sulfonylureas and hypoglycaemia. Diabetes Nutr Metab 2002;15:444–450; discussion 450–441 - PubMed
-
- Rorsman P, Renstrom E: Insulin granule dynamics in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2003;46:1029–1045 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

