Nanoparticles for cell labeling
- PMID: 20938522
- PMCID: PMC6454877
- DOI: 10.1039/c0nr00493f
Nanoparticles for cell labeling
Abstract
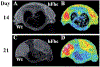
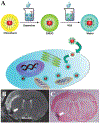
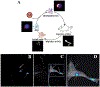
Cell based therapeutics are emerging as powerful regimens. To better understand the migration and proliferation mechanisms of implanted cells, a means to track cells in living subjects is essential, and to achieve that, a number of cell labeling techniques have been developed. Nanoparticles, with their superior physical properties, have become the materials of choice in many investigations along this line. Owing to inherent magnetic, optical or acoustic attributes, these nanoparticles can be detected by corresponding imaging modalities in living subjects at a high spatial and temporal resolution. These features allow implanted cells to be separated from host cells; and have advantages over traditional histological methods, as they permit non-invasive, real-time tracking in vivo. This review attempts to give a summary of progress in using nanotechnology to monitor cell trafficking. We will focus on direct cell labeling techniques, in which cells ingest nanoparticles that bear traceable signals, such as iron oxide or quantum dots. Ferritin and MagA reporter genes that can package endogenous iron or iron supplement into iron oxide nanoparticles will also be discussed.
Figures
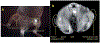
Similar articles
-
Poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide)-coated maghemite nanoparticles for labeling and tracking mesenchymal stem cells.2009 Dec 23 [updated 2010 Feb 16]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2009 Dec 23 [updated 2010 Feb 16]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641410 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Comparison of reporter gene and iron particle labeling for tracking fate of human embryonic stem cells and differentiated endothelial cells in living subjects.Stem Cells. 2008 Apr;26(4):864-73. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0843. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Stem Cells. 2008. PMID: 18218820 Free PMC article.
-
Functional investigations on embryonic stem cells labeled with clinically translatable iron oxide nanoparticles.Nanoscale. 2014 Aug 7;6(15):9025-33. doi: 10.1039/c4nr01004c. Nanoscale. 2014. PMID: 24969040
-
Labeling stem cells with ferumoxytol, an FDA-approved iron oxide nanoparticle.J Vis Exp. 2011 Nov 4;(57):e3482. doi: 10.3791/3482. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 22083287 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal, rhodamine B isothiocyanate-incorporated, silica-coated magnetic nanoparticle–labeled human cord blood–derived mesenchymal stem cells for cell tracking.2009 Dec 11 [updated 2010 Jan 28]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2009 Dec 11 [updated 2010 Jan 28]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641578 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Essential parameters to consider for the characterization of optical imaging probes.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012 Jul;7(7):1101-7. doi: 10.2217/nnm.12.79. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22846094 Free PMC article.
-
Matched-pair, 86Y/90Y-labeled, bivalent RGD/bombesin antagonist, [RGD-Glu-[DO3A]-6-Ahx-RM2], as a potential theranostic agent for prostate cancer.Nucl Med Biol. 2018 Jul-Aug;62-63:71-77. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Nucl Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29929115 Free PMC article.
-
Stem/Stromal Cells for Treatment of Kidney Injuries With Focus on Preclinical Models.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Jun 15;5:179. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00179. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29963554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Core-shell magnetoelectric nanorobot - A remotely controlled probe for _targeted cell manipulation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 29;8(1):1755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20191-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29379076 Free PMC article.
-
_targeted nanoprobes reveal early time point kinetics in vivo by time-resolved MRI.Theranostics. 2011 Apr 26;1:274-6. doi: 10.7150/thno/v01p0274. Theranostics. 2011. PMID: 21562633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carpenter MK, Frey-Vasconcells J and Rao MS, Nat. Biotechnol, 2009, 27, 606–613. - PubMed
-
- Marin-Garcia J and Goldenthal MJ, Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther, 2006, 1, 1–11. - PubMed
-
- Hart LS and El-Deiry WS, J. Clin. Oncol, 2008, 26, 2901–2910. - PubMed
-
- Na HB, Song IC and Hyeon T, Adv. Mater, 2009, 21, 2133–2148.
-
- Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER and Mattoussi H, Nat. Mater, 2005, 4, 435–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

