Granulysin delivered by cytotoxic cells damages endoplasmic reticulum and activates caspase-7 in _target cells
- PMID: 21296981
- PMCID: PMC6959523
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003409
Granulysin delivered by cytotoxic cells damages endoplasmic reticulum and activates caspase-7 in _target cells
Abstract
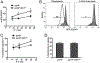
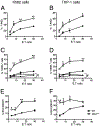
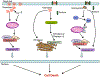
Granulysin is a human cytolytic molecule present in cytotoxic granules with perforin and granzymes. Recombinant 9-kDa granulysin kills a variety of microbes, including bacteria, yeast, fungi, and parasites, and induces apoptosis in tumor cells by causing intracellular calcium overload, mitochondrial damage, and activation of downstream caspases. Reasoning that granulysin delivered by cytotoxic cells may work in concert with other molecules, we crossed granulysin transgenic (GNLY(+/-)) mice onto perforin (perf)- or granzyme B (gzmb)-deficient mice to examine granulysin-mediated killing in a more physiologic whole-cell system. Splenocytes from these animals were activated in vitro with IL-15 to generate cytolytic T cells and NK cells. Cytotoxic cells expressing granulysin require perforin, but not granzyme B, to cause apoptosis of _targets. Whereas granzyme B induces mitochondrial damage and activates caspases-3 and -9 in _targets, cytotoxic cell-delivered granulysin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and activates caspase-7 with no effect on mitochondria or caspases-3 and -9. In addition, recombinant granulysin and cell-delivered granulysin activate distinct apoptotic pathways in _target cells. These findings suggest that cytotoxic cells have evolved multiple nonredundant cell death pathways, enabling host defense to counteract escape mechanisms employed by pathogens or tumor cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Killer lymphocytes use granulysin, perforin and granzymes to kill intracellular parasites.Nat Med. 2016 Feb;22(2):210-6. doi: 10.1038/nm.4023. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 26752517 Free PMC article.
-
A distinct pathway of cell-mediated apoptosis initiated by granulysin.J Immunol. 2001 Jul 1;167(1):350-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.1.350. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11418670
-
Real-time detection of CTL function reveals distinct patterns of caspase activation mediated by Fas versus granzyme B.J Immunol. 2014 Jul 15;193(2):519-28. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301668. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24928990 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme B: a natural born killer.Immunol Rev. 2003 Jun;193:31-8. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2003.00044.x. Immunol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12752668 Review.
-
Granulysin: The attractive side of a natural born killer.Immunol Lett. 2020 Jan;217:126-132. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.11.005. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Immunol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31726187 Review.
Cited by
-
Delayed Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions: Molecular Recognition, Genetic Susceptibility, and Immune Mediators.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 10;11(1):177. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010177. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36672685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from natural killer cells use multiple cytotoxic proteins and killing mechanisms to _target cancer cells.J Extracell Vesicles. 2019 Mar 12;8(1):1588538. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2019.1588538. eCollection 2019. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019. PMID: 30891164 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking the CCL2-CCR2 Axis Using CCL2-Neutralizing Antibody Is an Effective Therapy for Hepatocellular Cancer in a Mouse Model.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Feb;16(2):312-322. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0124. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 27980102 Free PMC article.
-
Granulysin expressed in a humanized mouse model induces apoptotic cell death and suppresses tumorigenicity.Onco_target. 2016 Aug 22;8(48):83495-83508. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.11473. eCollection 2017 Oct 13. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 29137359 Free PMC article.
-
Datura stramonium essential oil composition and it's immunostimulatory potential against colon cancer cells.3 Biotech. 2020 Oct;10(10):451. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02438-4. Epub 2020 Sep 25. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 33062579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lieberman J 2003. The ABCs of granule-mediated cytotoxicity: new weapons in the arsenal. Nat. Rev. Immunol 3: 361–370. - PubMed
-
- Lowin B, Hahne M, Mattmann C, and Tschopp J. 1994. Cytolytic T-cell cytotoxicity is mediated through perforin and Fas lytic pathways. Nature 370: 650–652. - PubMed
-
- Kägi D, Ledermann B, Bürki K, Seiler P, Odermatt B, Olsen KJ, Podack ER, Zinkernagel RM, and Hengartner H. 1994. Cytotoxicity mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is greatly impaired in perforin-deficient mice. Nature 369: 31–37. - PubMed
-
- Kojima H, Shinohara N, Hanaoka S, Someya-Shirota Y, Takagaki Y, Ohno H, Saito T, Katayama T, Yagita H, Okumura K, et al. 1994. Two distinct pathways of specific killing revealed by perforin mutant cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 1: 357–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

