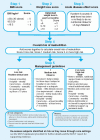
Malnutrition: causes and consequences
- PMID: 21413492
- PMCID: PMC4951875
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.10-6-624
Malnutrition: causes and consequences
Figures
Comment in
-
Acute decompensated heart failure secondary to thiamine deficiency: often a missed diagnosis.Clin Med (Lond). 2011 Apr;11(2):203; author reply 203-4. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.11-2-203a. Clin Med (Lond). 2011. PMID: 21528508 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Malnutrition: etiology, consequences, and assessment of a patient at risk.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;20(3):419-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2006.01.006. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16782522 Review.
-
[Malnutrition in patients on chronic hemodialysis: prevalence, pathogenesis, and treatment].G Ital Nefrol. 2009 Mar-Apr;26(2):201-14. G Ital Nefrol. 2009. PMID: 19382076 Review. Italian.
-
Nutritional risk and malnutrition rates at diagnosis of cancer in patients treated in outpatient settings: Early intervention protocol.Nutrition. 2019 Jan;57:148-153. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.05.021. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Nutrition. 2019. PMID: 30157469
-
Global Leadership Conversation: Addressing Malnutrition.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016 May;40(4):455-7. doi: 10.1177/0148607116640274. Epub 2016 Mar 18. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26993988 No abstract available.
-
Prevalence of malnutrition and current use of nutrition support in cancer patient study.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014 Feb;38(2):163-5. doi: 10.1177/0148607113506940. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24748623 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Gut Microbial Profile Is Associated With Residential Settings and Not Nutritional Status in Adults in Karnataka, India.Front Nutr. 2021 Feb 23;8:595756. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.595756. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33708787 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Potential of Sprouted Cereals, Pseudocereals, and Pulses in Combating Malnutrition.Foods. 2023 Oct 24;12(21):3901. doi: 10.3390/foods12213901. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37959020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Occurrence of Malnutrition among Seniors in Poland Depending on the Place of Residence: An Analysis of Socioeconomic and Health Risk Factors.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 6;16(19):3394. doi: 10.3390/nu16193394. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408361 Free PMC article.
-
Malnutrition among the older adult: an additional challenge for the rehabilitation team-insights of a small population of Switzerland.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 9;12:1436566. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1436566. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39045162 Free PMC article.
-
Khat consumption and undernutrition among adult population in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 23;19(4):e0299538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299538. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38652725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elia M, editor. Guidelines for detection and management of malnutrition. Malnutrition Advisory Group, Standing Committee of BAPEN. Maidenhead: BAPEN, 2000.
-
- Stratton R, Green CJ, Elia M. Disease-related malnutrition: an evidence-based approach to treatment. Oxon: Cabi Publishing, 2003.
-
- Russell CA, Elia M. Nutrition Screening Survey in the UK in 2008. Redditch, Worcestershire: BAPEN, 2009.
-
- Finch S, Doyle W, Lowe C, et al. National diet and nutrition survey. London: The Stationery Office, 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical