A mechanism for the evolution of phosphorylation sites
- PMID: 22078888
- PMCID: PMC3220604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.052
A mechanism for the evolution of phosphorylation sites
Abstract
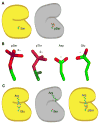
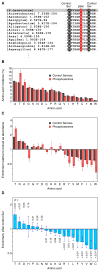
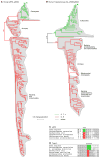
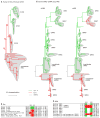
Protein phosphorylation provides a mechanism for the rapid, reversible control of protein function. Phosphorylation adds negative charge to amino acid side chains, and negatively charged amino acids (Asp/Glu) can sometimes mimic the phosphorylated state of a protein. Using a comparative genomics approach, we show that nature also employs this trick in reverse by evolving serine, threonine, and tyrosine phosphorylation sites from Asp/Glu residues. Structures of three proteins where phosphosites evolved from acidic residues (DNA topoisomerase II, enolase, and C-Raf) show that the relevant acidic residues are present in salt bridges with conserved basic residues, and that phosphorylation has the potential to conditionally restore the salt bridges. The evolution of phosphorylation sites from glutamate and aspartate provides a rationale for why phosphorylation sometimes activates proteins, and helps explain the origins of this important and complex process.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular evolution before the origin of species.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2002 May-Jul;79(1-3):77-133. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6107(02)00012-3. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12225777 Review.
-
Evolution and phyletic distribution of two-component signal transduction systems.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Apr;13(2):219-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.12.011. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20133179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loops and repeats in proteins as footprints of molecular evolution.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012 Dec;77(13):1487-99. doi: 10.1134/S000629791213007X. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012. PMID: 23379524 Review.
-
Classification and Lineage Tracing of SH2 Domains Throughout Eukaryotes.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1555:59-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6762-9_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28092027
-
Complex salt bridges in proteins: statistical analysis of structure and function.J Mol Biol. 1995 Dec 8;254(4):761-70. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0653. J Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7500348
Cited by
-
Phosphoproteomics-directed manipulation reveals SEC22B as a hepatocellular signaling node governing metabolic actions of glucagon.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 27;15(1):8390. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52703-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39333498 Free PMC article.
-
PTMoreR-enabled cross-species PTM mapping and comparative phosphoproteomics across mammals.Cell Rep Methods. 2024 Sep 16;4(9):100859. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100859. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Cell Rep Methods. 2024. PMID: 39255793 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional effects of phosphopriming and scaffolding in the kinase GSK-3β.Sci Signal. 2024 Sep 3;17(852):eado0881. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.ado0881. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Sci Signal. 2024. PMID: 39226374
-
Cellular Site-Specific Incorporation of Noncanonical Amino Acids in Synthetic Biology.Chem Rev. 2024 Sep 25;124(18):10577-10617. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00938. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39207844 Review.
-
CLK2 Condensates Reorganize Nuclear Speckles and Induce Intron Retention.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(38):e2309588. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309588. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39119950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abascal F, Zardoya R, Posada D. ProtTest: selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2104–2105. - PubMed
-
- Alonso A, Sasin J, Bottini N, Friedberg I, Osterman A, Godzik A, Hunter T, Dixon J, Mustelin T. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell. 2004;117:699–711. - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Ballif BA, Villen J, Beausoleil SA, Schwartz D, Gygi SP. Phosphoproteomic analysis of the developing mouse brain. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004;3:1093–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

