Antibody in middle ear fluid of children originates predominantly from sera and nasopharyngeal secretions
- PMID: 22855395
- PMCID: PMC3485881
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.05443-11
Antibody in middle ear fluid of children originates predominantly from sera and nasopharyngeal secretions
Abstract
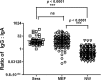
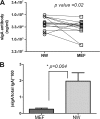
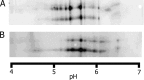
The human middle ear is devoid of any immunocompetent cells in normal mucosa. We sought to determine the source of antibody present in the middle ear of children. Total IgG, IgA, and secretory IgA antibodies were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay from the nasopharyngeal, middle ear, and serum samples of children with acute otitis media. The two-dimensional gel electrophoresis pattern of the entire array of IgA antibodies in the nasal wash (NW) and middle ear fluid (MEF) was compared from the MEF and NW samples using isoelectric focusing and Western blotting. The total IgG and IgA antibodies in the MEF and NW samples of 137 children were compared. The ratio of IgG to IgA in the MEF was significantly different (P < 0.008) compared to NW because IgA levels were higher and IgG levels lower in NW. The IgG/IgA ratio of MEF resembled serum consistent with transudation to the MEF. Small amounts of secretory IgA were detected in MEF but the electrophoresis patterns of the entire array of IgA antibodies in the MEF and NW were virtually identical in each child evaluated; thus, IgA in MEF derived predominantly from serum and the nasopharynx by reflux via the Eustachian tube. The IgG/IgA antibody levels in the MEF and the same composition of IgA antibody in the MEF and NW identifies the predominant source of antibody in the MEF as a transudate of serum combined with nasal secretions refluxed from the nasopharynx in children.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Local antibody response to P6 of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae in otitis-prone and normal children.Acta Otolaryngol. 1993 Jul;113(4):524-9. doi: 10.3109/00016489309135857. Acta Otolaryngol. 1993. PMID: 8379309
-
Immunoglobulins of the middle ear fluid in acute otitis media: relationship to serum immunoglobulin concentrations and bacterial cultures.Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):589-93. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.589-593.1973. Infect Immun. 1973. PMID: 4148623 Free PMC article.
-
The significance of secretory IgA in middle ear fluid.Ann Allergy. 1979 Apr;42(4):236-40. Ann Allergy. 1979. PMID: 571255
-
Comparative analysis of the humoral immune response to Moraxella catarrhalis and Streptococcus pneumoniae surface antigens in children suffering from recurrent acute otitis media and chronic otitis media with effusion.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Jun;19(6):914-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05630-11. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22539468 Free PMC article.
-
Immunologic aspects of otitis media.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2002 Jul;2(4):309-15. doi: 10.1007/s11882-002-0056-4. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2002. PMID: 12044266 Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding the role of bacterial vaccines into life-course vaccination strategies and prevention of antimicrobial-resistant infections.NPJ Vaccines. 2020 Sep 11;5:84. doi: 10.1038/s41541-020-00232-0. eCollection 2020. NPJ Vaccines. 2020. PMID: 32963814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Profile of Heme Acquisition Genes in Disease-Causing and Colonizing Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus haemolyticus.J Clin Microbiol. 2015 Jul;53(7):2132-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00345-15. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Clin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25903577 Free PMC article.
-
Probing Immune-Mediated Clearance of Acute Middle Ear Infection in Mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 24;11:815627. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.815627. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35141173 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent mucosal and systemic responses in children in response to acute otitis media.Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Oct;178(1):94-101. doi: 10.1111/cei.12389. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24889648 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Relationships between Intestinal Regional Lymph Nodes and Immune Responses in Viral Infections in Children.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 28;23(1):318. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010318. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adrian PV, et al. 2004. Development of antibodies against pneumococcal proteins alpha-enolase, immunoglobulin A1 protease, streptococcal lipoprotein rotamase A, and putative proteinase maturation protein A in relation to pneumococcal carriage and otitis media. Vaccine 22:2737–2742 - PubMed
-
- Eskola J, et al. 2001. Efficacy of a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against acute otitis media. N. Engl. J. Med. 344:403–409 - PubMed
-
- He Z, et al. 2007. Detection of gastric pepsin in middle ear fluid of children with otitis media. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 137:59–64 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

