Candesartan, an angiotensin II AT₁-receptor blocker and PPAR-γ agonist, reduces lesion volume and improves motor and memory function after traumatic brain injury in mice
- PMID: 22892395
- PMCID: PMC3499714
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2012.152
Candesartan, an angiotensin II AT₁-receptor blocker and PPAR-γ agonist, reduces lesion volume and improves motor and memory function after traumatic brain injury in mice
Abstract
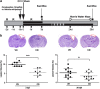
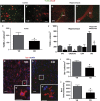
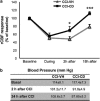
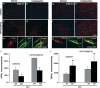
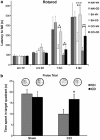
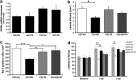
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) results in complex pathological reactions, the initial lesion worsened by secondary inflammation and edema. Angiotensin II (Ang II) is produced in the brain and Ang II receptor type 1 (AT₁R) overstimulation produces vasoconstriction and inflammation. Ang II receptor blockers (ARBs) are neuroprotective in models of stroke but little is known of their effect when administered in TBI models. We therefore performed controlled cortical impact (CCI) injury on mice to investigate whether the ARB candesartan would mitigate any effects of TBI. We administered candesartan or vehicle to mice 5 h before CCI injury. Candesartan treatment reduced the lesion volume after CCI injury by approximately 50%, decreased the number of dying neurons, lessened the number of activated microglial cells, protected cerebral blood flow (CBF), and reduced the expression of the cytokine TGFβ1 while increasing expression of TGFβ3. Candesartan-treated mice also showed better motor skills on the rotarod 3 days after injury, and improved performance in the Morris water maze 4 weeks after injury. These results indicate that candesartan is neuroprotective, reducing neuronal injury, decreasing lesion volume and microglial activation, protecting CBF and improving functional behavior in a mouse model of TBI. Co-treatment with a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ) antagonist significantly reduced some of the beneficial effects of candesartan after CCI, suggesting that PPARγ activation may contribute to part or to all of the neuroprotective effect of candesartan. Overall, our data suggest that ARBs with dual AT₁R-blocking and PPARγ activation properties may have therapeutic value in treating TBI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Mouse Brain After Traumatic Brain Injury Reveals That the Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Candesartan Acts Through Novel Pathways.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 22;15:636259. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.636259. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33828448 Free PMC article.
-
Neurorestoration after traumatic brain injury through angiotensin II receptor blockage.Brain. 2015 Nov;138(Pt 11):3299-315. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv172. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Brain. 2015. PMID: 26115674 Free PMC article.
-
Candesartan prevents resiniferatoxin-induced sensory small-fiber neuropathy in mice by promoting angiotensin II-mediated AT2 receptor stimulation.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Nov;126:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.039. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28882562
-
Angiotensin II AT(1) receptor blockers as treatments for inflammatory brain disorders.Clin Sci (Lond). 2012 Nov;123(10):567-90. doi: 10.1042/CS20120078. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22827472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candesartan.2017 Jan 13. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. 2017 Jan 13. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. PMID: 31643728 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Mouse Brain After Traumatic Brain Injury Reveals That the Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Candesartan Acts Through Novel Pathways.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 22;15:636259. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.636259. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33828448 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and biomarker effects of candesartan in non-hypertensive adults with prodromal Alzheimer's disease.Brain Commun. 2022 Oct 25;4(6):fcac270. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac270. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 36440097 Free PMC article.
-
The extended renin-angiotensin system: a promising _target for traumatic brain injury therapeutics.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Jun;15(6):1025-1026. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.270304. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31823875 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Blockage Limits Brain Damage and Improves Functional Outcome After Brain Injury in Aged Animals Despite Age-Dependent Reduction in AT1 Expression.Front Aging Neurosci. 2019 Apr 26;11:63. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00063. eCollection 2019. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31105549 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-_targeting AAV9P1-mediated neuronal reprogramming in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Mar;19(3):629-635. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.380907. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37721294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An J, Nakajima T, Kuba K, Kimura A. Losartan inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory signaling through a PPARgamma-dependent mechanism in human THP-1 macrophages. Hypertens Res Off J Jap Soc Hypertens. 2010;33:831–835. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Jezova M, Zhou J, Saavedra JM. Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade decreases brain artery inflammation in a stress-prone rat strain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004a;1018:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Zhou J, Macova M, Imboden H, Saavedra JM. Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade reverses pathological hypertrophy and inflammation in brain microvessels of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke. 2004b;35:1726–1731. - PubMed
-
- Ariza M, Matarin MD, Junque C, Mataro M, Clemente I, Moral P, et al. Influence of Angiotensin-converting enzyme polymorphism on neuropsychological subacute performance in moderate and severe traumatic brain injury. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006;18:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Awad AS. Effect of combined treatment with curcumin and candesartan on ischemic brain damage in mice. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;20:541–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

