Impact of breast cancer and combination chemotherapy on oxidative stress, hepatic and cardiac markers
- PMID: 23091543
- PMCID: PMC3468784
- DOI: 10.4048/jbc.2012.15.3.306
Impact of breast cancer and combination chemotherapy on oxidative stress, hepatic and cardiac markers
Abstract
Purpose: Carcinoma of the breast is the most prevalent cancer among Egyptian women and constitutes 29% of National Cancer Institute cases. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of breast cancer on oxidative stress, cardiac markers and liver function tests, moreover the role of 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (FAC) in the treatment of breast cancer and its mechanism through changing the measured markers.
Methods: Forty female breast cancer patients who were admitted to the Department of Oncology of the Beni-Suef University Hospital were enrolled in the study. This study included three arms: a control group of healthy age-matched females (n=20), breast cancer patients who weren't receiving treatment (n=20), and patients undergoing treatment with anticancer combination drugs FAC (n=20). Blood samples collected from the control subjects and patients were analysed to determine levels of catalase, reduced glutathione (GSH), uric acid, nitric oxide (NO), malondialdehyde, creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), liver enzymes (alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase), and creatinine.
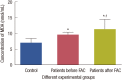
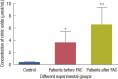
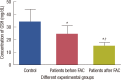
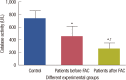
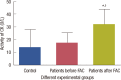
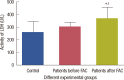
Results: The levels of catalase and GSH were significantly reduced (p<0.05) in breast carcinoma and FAC treated breast cancer patients. The lipid peroxidation and NO levels were significantly enhanced in both untreated and FAC treated breast cancer patients. The CK and LDH were significantly enhanced (p<0.05) in the FAC group.
Conclusion: The results from the present study show that oxidative stress is implicated in breast carcinoma and chemotherapy aggravates this oxidative stress which causes damage to many cellular _targets and has the main side effect of cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; Cardiac function; Chemotherapy; Liver function; Oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress in breast cancer after chemotherapy.Bioinformation. 2022 Dec 31;18(12):1141-1145. doi: 10.6026/973206300181141. eCollection 2022. Bioinformation. 2022. PMID: 37701507 Free PMC article.
-
[Risk of cardiotoxicity of combination treatment radiotherapy and chemotherapy of locally advanced breast carcinoma stage III].Klin Onkol. 2009;22(1):17-21. Klin Onkol. 2009. PMID: 19534435 Czech.
-
Oxidative stress parameters in women with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy and treated with nutraceutical doses of oral glutamine.Acta Cir Bras. 2011;26 Suppl 1:82-7. doi: 10.1590/s0102-86502011000700017. Acta Cir Bras. 2011. PMID: 21971664 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect on Antioxidant Levels in Patients of Breast Carcinoma during Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Mastectomy.Malays J Med Sci. 2010 Apr;17(2):24-8. Malays J Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 22135534 Free PMC article.
-
Doxorubicin in combination with fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide (i.v. FAC regimen, day 1, 21) versus methotrexate in combination with fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide (i.v. CMF regimen, day 1, 21) as adjuvant chemotherapy for operable breast cancer: a study by the GEICAM group.Ann Oncol. 2003 Jun;14(6):833-42. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdg260. Ann Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12796019 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant activity of ginger extract as a daily supplement in cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: a pilot study.Cancer Manag Res. 2017 Jan 31;9:11-18. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S124016. eCollection 2017. Cancer Manag Res. 2017. PMID: 28203106 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-proliferative potentials of Aconitum heterophyllum Root Extract in Human Breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cell lines-Genetic and Antioxidant enzyme approach.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2023 Jul-Sep;15(3):188-195. doi: 10.18502/ajmb.v15i3.12929. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37538242 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Properties of Asiatic Acid against 5-Fluorouracil Chemotherapy in the Hippocampus in an Adult Rat Model.Nutrients. 2018 Aug 9;10(8):1053. doi: 10.3390/nu10081053. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30096914 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Oxidative Stress Markers and Genotoxic Profile Induced by Chemotherapy in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Pilot Study.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:212964. doi: 10.1155/2015/212964. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26576218 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Croton hypoleucus Extract in an Induced-Necrosis Model in Rats.Molecules. 2019 Jul 11;24(14):2533. doi: 10.3390/molecules24142533. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31373296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polyak K. On the birth of breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1552:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Gönenç A, Erten D, Aslan S, Akinci M, Simşek B, Torun M. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in blood and tissue of malignant breast tumor and benign breast disease. Cell Biol Int. 2006;30:376–380. - PubMed
-
- Yeh CC, Hou MF, Tsai SM, Lin SK, Hsiao JK, Huang JC, et al. Superoxide anion radical, lipid peroxides and antioxidant status in the blood of patients with breast cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;361:104–111. - PubMed
-
- Kang DH. Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and breast cancer. AACN Clin Issues. 2002;13:540–549. - PubMed
-
- Birnboim HC. DNA strand breakage in human leukocytes exposed to a tumor promoter, phorbol myristate acetate. Science. 1982;215:1247–1249. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

