Direct chemical evidence for sphingolipid domains in the plasma membranes of fibroblasts
- PMID: 23359681
- PMCID: PMC3581929
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1216585110
Direct chemical evidence for sphingolipid domains in the plasma membranes of fibroblasts
Abstract
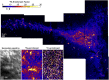
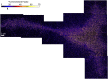
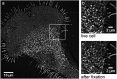
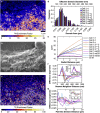
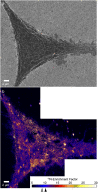
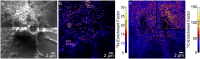
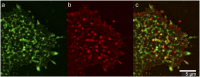
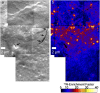
Sphingolipids play important roles in plasma membrane structure and cell signaling. However, their lateral distribution in the plasma membrane is poorly understood. Here we quantitatively analyzed the sphingolipid organization on the entire dorsal surface of intact cells by mapping the distribution of (15)N-enriched ions from metabolically labeled (15)N-sphingolipids in the plasma membrane, using high-resolution imaging mass spectrometry. Many types of control experiments (internal, positive, negative, and fixation temperature), along with parallel experiments involving the imaging of fluorescent sphingolipids--both in living cells and during fixation of living cells--exclude potential artifacts. Micrometer-scale sphingolipid patches consisting of numerous (15)N-sphingolipid microdomains with mean diameters of ∼200 nm are always present in the plasma membrane. Depletion of 30% of the cellular cholesterol did not eliminate the sphingolipid domains, but did reduce their abundance and long-range organization in the plasma membrane. In contrast, disruption of the cytoskeleton eliminated the sphingolipid domains. These results indicate that these sphingolipid assemblages are not lipid rafts and are instead a distinctly different type of sphingolipid-enriched plasma membrane domain that depends upon cortical actin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sphingolipid domains in the plasma membranes of fibroblasts are not enriched with cholesterol.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 7;288(23):16855-16861. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.473207. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23609440 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol is enriched in the sphingolipid patches on the substrate near nonpolarized MDCK cells, but not in the sphingolipid domains in their plasma membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 Oct;1860(10):2004-2011. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.04.008. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 29684331
-
Sphingolipid Organization in the Plasma Membrane and the Mechanisms That Influence It.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Jan 10;4:154. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00154. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28119913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yeast Sphingolipid-Enriched Domains and Membrane Compartments in the Absence of Mannosyldiinositolphosphorylceramide.Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 6;10(6):871. doi: 10.3390/biom10060871. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32517183 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Bodipy-labeled sphingolipid and cholesterol analogs to examine membrane microdomains in cells.Histochem Cell Biol. 2008 Nov;130(5):819-32. doi: 10.1007/s00418-008-0509-5. Epub 2008 Sep 27. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18820942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Secondary-ion mass spectrometry of genetically encoded _targets.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015 May 4;54(19):5784-8. doi: 10.1002/anie.201411692. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015. PMID: 25783034 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry Imaging Reveals Changes in the Lipid Structure of the Plasma Membranes of Hippocampal Neurons following Drugs Affecting Neuronal Activity.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 May 5;12(9):1542-1551. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00031. Epub 2021 Apr 26. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33896172 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MCC/Eisosome in Fungal Lipid Homeostasis.Biomolecules. 2019 Jul 25;9(8):305. doi: 10.3390/biom9080305. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31349700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma membrane effects of sphingolipid-synthesis inhibition by myriocin in CHO cells: a biophysical and lipidomic study.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 19;12(1):955. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04648-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35046440 Free PMC article.
-
Eliciting the impacts of cellular noise on metabolic trade-offs by quantitative mass imaging.Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 19;10(1):848. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08717-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30783105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fujita A, Cheng J, Fujimoto T. Segregation of GM1 and GM3 clusters in the cell membrane depends on the intact actin cytoskeleton. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1791(5):388–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

