Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains
- PMID: 24108358
- PMCID: PMC3826637
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3575
Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains
Abstract
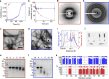
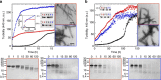
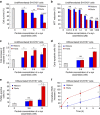
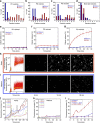
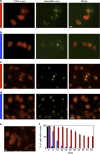
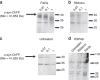
α-Synuclein aggregation is implicated in a variety of diseases including Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, pure autonomic failure and multiple system atrophy. The association of protein aggregates made of a single protein with a variety of clinical phenotypes has been explained for prion diseases by the existence of different strains that propagate through the infection pathway. Here we structurally and functionally characterize two polymorphs of α-synuclein. We present evidence that the two forms indeed fulfil the molecular criteria to be identified as two strains of α-synuclein. Specifically, we show that the two strains have different structures, levels of toxicity, and in vitro and in vivo seeding and propagation properties. Such strain differences may account for differences in disease progression in different individuals/cell types and/or types of synucleinopathies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy.Nature. 2020 Feb;578(7794):273-277. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1984-7. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32025029 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein occurs physiologically as a helically folded tetramer that resists aggregation.Nature. 2011 Aug 14;477(7362):107-10. doi: 10.1038/nature10324. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21841800 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characteristics of alpha-synuclein oligomers stabilized by the flavonoid baicalein.J Mol Biol. 2008 Oct 31;383(1):214-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.039. Epub 2008 Aug 23. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18775438 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein Conformational Strains as Drivers of Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Neurodegenerative Diseases.J Mol Biol. 2023 Jun 15;435(12):168011. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168011. Epub 2023 Feb 13. J Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36792008 Review.
-
Neuropathology and molecular diagnosis of Synucleinopathies.Mol Neurodegener. 2021 Dec 18;16(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00501-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 34922583 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of N-terminal Acetylation of α-Synuclein on Phospholipid Membrane Binding and Fibril Structure.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 30;291(40):21110-21122. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.726612. Epub 2016 Aug 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27531743 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Different Alpha-Synuclein Strains in Synucleinopathies, Similarities with other Neurodegenerative Diseases.J Parkinsons Dis. 2015;5(2):217-27. doi: 10.3233/JPD-150543. J Parkinsons Dis. 2015. PMID: 25757830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Versatile Structures of α-Synuclein.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Jun 20;9:48. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00048. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27378848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
O-GlcNAc forces an α-synuclein amyloid strain with notably diminished seeding and pathology.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 May;20(5):646-655. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01551-2. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38347213 Free PMC article.
-
Novel C. elegans models of Lewy body disease reveal pathological protein interactions and widespread miRNA dysregulation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Aug 30;81(1):377. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05383-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39212733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ross C. A. & Poirier M. A. Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Med. 10 Suppl, S10-7 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Goedert M. Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 492–501 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Lee H. J., Choi C. & Lee S. J. Membrane-bound alpha-synuclein has a high aggregation propensity and the ability to seed the aggregation of the cytosolic form. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 671–678 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Jensen P. H., Nielsen M. S., Jakes R., Dotti C. G. & Goedert M. Binding of alpha-synuclein to brain vesicles is abolished by familial Parkinson’s disease mutation. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 26292–26294 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

