Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor
- PMID: 24172901
- PMCID: PMC5389864
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12711
Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor
Abstract
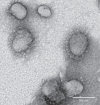
The 2002-3 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) was one of the most significant public health events in recent history. An ongoing outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus suggests that this group of viruses remains a key threat and that their distribution is wider than previously recognized. Although bats have been suggested to be the natural reservoirs of both viruses, attempts to isolate the progenitor virus of SARS-CoV from bats have been unsuccessful. Diverse SARS-like coronaviruses (SL-CoVs) have now been reported from bats in China, Europe and Africa, but none is considered a direct progenitor of SARS-CoV because of their phylogenetic disparity from this virus and the inability of their spike proteins to use the SARS-CoV cellular receptor molecule, the human angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2). Here we report whole-genome sequences of two novel bat coronaviruses from Chinese horseshoe bats (family: Rhinolophidae) in Yunnan, China: RsSHC014 and Rs3367. These viruses are far more closely related to SARS-CoV than any previously identified bat coronaviruses, particularly in the receptor binding domain of the spike protein. Most importantly, we report the first recorded isolation of a live SL-CoV (bat SL-CoV-WIV1) from bat faecal samples in Vero E6 cells, which has typical coronavirus morphology, 99.9% sequence identity to Rs3367 and uses ACE2 from humans, civets and Chinese horseshoe bats for cell entry. Preliminary in vitro testing indicates that WIV1 also has a broad species tropism. Our results provide the strongest evidence to date that Chinese horseshoe bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-CoV, and that intermediate hosts may not be necessary for direct human infection by some bat SL-CoVs. They also highlight the importance of pathogen-discovery programs _targeting high-risk wildlife groups in emerging disease hotspots as a strategy for pandemic preparedness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Bats as animal reservoirs for the SARS coronavirus: hypothesis proved after 10 years of virus hunting.Virol Sin. 2013 Dec;28(6):315-7. doi: 10.1007/s12250-013-3402-x. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Virol Sin. 2013. PMID: 24174406 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Evolutionary Arms Race between Virus and Host Drives Genetic Diversity in Bat Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus Spike Genes.J Virol. 2020 Sep 29;94(20):e00902-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00902-20. Print 2020 Sep 29. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32699095 Free PMC article.
-
Difference in receptor usage between severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus and SARS-like coronavirus of bat origin.J Virol. 2008 Feb;82(4):1899-907. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01085-07. Epub 2007 Dec 12. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18077725 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Coronavirus ORF8 Protein Is Acquired from SARS-Related Coronavirus from Greater Horseshoe Bats through Recombination.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10532-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01048-15. Epub 2015 Aug 12. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26269185 Free PMC article.
-
A review of studies on animal reservoirs of the SARS coronavirus.Virus Res. 2008 Apr;133(1):74-87. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.03.012. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 17451830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular epidemiology, evolution and phylogeny of SARS coronavirus.Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Jul;71:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Infect Genet Evol. 2019. PMID: 30844511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and characterization of spike S2-specific monoclonal antibodies with reactivity to pan-coronaviruses.Virol Sin. 2023 Oct 27;39(1):169-72. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.10.008. Online ahead of print. Virol Sin. 2023. PMID: 39491181 Free PMC article.
-
The complex relationship between viruses and inflammatory bowel disease - review and practical advices for the daily clinical decision-making during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021 Apr 12;14:1756284820988198. doi: 10.1177/1756284820988198. eCollection 2021. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33953797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural selection in the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in bats created a generalist virus and highly capable human pathogen.PLoS Biol. 2021 Mar 12;19(3):e3001115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001115. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2021. PMID: 33711012 Free PMC article.
-
Can ACE2 Receptor Polymorphism Predict Species Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2?Front Public Health. 2021 Feb 10;8:608765. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.608765. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33643982 Free PMC article.
-
In silico molecular docking analysis for repurposing therapeutics against multiple proteins from SARS-CoV-2.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 5;886:173430. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173430. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32758569 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

