Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria
- PMID: 24287491
- PMCID: PMC3873673
- DOI: 10.3390/ph6121451
Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria
Abstract
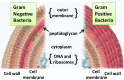
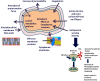
The increasing resistance of microorganisms to conventional chemicals and drugs is a serious and evident worldwide problem that has prompted research into the identification of new biocides with broad activity. Plants and their derivatives, such as essential oils, are often used in folk medicine. In nature, essential oils play an important role in the protection of plants. Essential oils contain a wide variety of secondary metabolites that are capable of inhibiting or slowing the growth of bacteria, yeasts and moulds. Essential oils and their components have activity against a variety of _targets, particularly the membrane and cytoplasm, and in some cases, they completely change the morphology of the cells. This brief review describes the activity of essential oils against pathogenic bacteria.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Growth inhibition of pathogenic bacteria and some yeasts by selected essential oils and survival of L. monocytogenes and C. albicans in apple-carrot juice.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009 Apr;6(3):387-94. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2008.0195. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009. PMID: 19278342
-
Essential Oils: An Impending Substitute of Synthetic Antimicrobial Agents to Overcome Antimicrobial Resistance.Curr Drug _targets. 2019;20(6):605-624. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666181031122917. Curr Drug _targets. 2019. PMID: 30378496 Review.
-
Allergenic components, biocides, and analysis techniques of some essential oils used in food products.J Food Sci. 2021 Jun;86(6):2225-2241. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15753. Epub 2021 Jun 6. J Food Sci. 2021. PMID: 34091909 Review.
-
Evaluation of Plant Origin Essential Oils as Herbal Biocides for the Protection of Caves Belonging to Natural and Cultural Heritage Sites.Microorganisms. 2021 Aug 30;9(9):1836. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9091836. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34576731 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of essential oils of medicinal plants from growth of plant pathogenic fungi.Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2011;76(4):705-14. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22702190
Cited by
-
Leptin, adiponectin, biochemicals, metabolic hormones and performance characteristics of broiler administered with spices essential oil.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2024 Nov 23;56(9):392. doi: 10.1007/s11250-024-04237-y. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2024. PMID: 39579269
-
Insights into antibacterial design: Computational modeling of eugenol derivatives _targeting DNA gyrase.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 19;10(20):e39394. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39394. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39498057 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Thyme (Thymus vulgaris) Essential Oil on Bacterial Growth and Expression of Some Virulence Genes in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis.Vet Med Sci. 2024 Nov;10(6):e70088. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70088. Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39474775 Free PMC article.
-
First Report on Salvia Sahendica Boiss & Buhs roots biocomponents characterization by GC-MS and HPLC and Antibacterial Potency.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 22;14(1):24916. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76679-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39438657 Free PMC article.
-
Randomised-crossover clinical trial on the substantivity of a single application of a gel containing chlorhexidine and o-cymen-5-ol on the oral biofilm and saliva.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 19;24(1):1247. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05042-7. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39427170 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Abad M.J., Ansuategui M., Bermejo P. Active antifungal substances from natural sources. ARCHIVOC. 2007;2007:116–145.
-
- Chorianopoulos N.G., Giaouris E.D., Skandamis P.N., Haroutounian S.A., Nychas G.J.E. Disinfectant test against monoculture and mixed-culture biofilms composed of technological, spoilage and pathogenic bacteria: Bactericidal effect of essential oil and hydrosol of Satureja thymbra and comparison with standard acid-base sanitizers. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008;104:1586–1599. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03694.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources