M1 and M2 macrophages: the chicken and the egg of immunity
- PMID: 25138714
- PMCID: PMC4429858
- DOI: 10.1159/000364945
M1 and M2 macrophages: the chicken and the egg of immunity
Abstract
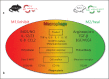
The purpose of this perspective is to describe a critical advance in understanding how immune responses work. Macrophages are required for all animal life: 'Inhibit' type macrophages in all animals (called M1) can rapidly kill pathogens, and are thus the primary host defense, and 'Heal' type macrophages (M2) routinely repair and maintain tissue integrity. Macrophages perform these activities in all animals without T cells, and also in T cell-deficient vertebrates. Although adaptive immunity can amplify macrophage polarization, the long-held notion that macrophages need to be 'activated' or 'alternatively activated' by T cells is incorrect; indeed, immunology has had it backward. M1/M2-type macrophages necessarily direct T cells toward Th1- or Th2-like activities, respectively. That such macrophage-innate activities are the central directing element in immune responses is a dramatic change in understanding how immune systems operate. Most important, this revelation is opening up whole new approaches to immunotherapy. For example, many modern diseases, such as cancer and atherosclerosis, may not display 'foreign' antigens. However, there are clear imbalances in M1/M2-type responses. Correcting such innate imbalances can result in better health. Macrophages are the chicken and the egg of immunity.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Janus face of macrophages in immunity.J Innate Immun. 2014;6(6):713-5. doi: 10.1159/000367718. Epub 2014 Sep 10. J Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 25322689 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Anatomy of a discovery: m1 and m2 macrophages.Front Immunol. 2015 May 5;6:212. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00212. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25999950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M1 and M2 Macrophages: Oracles of Health and Disease.Crit Rev Immunol. 2012;32(6):463-88. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v32.i6.10. Crit Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23428224 Review.
-
Polarization of immune responses in fish: The 'macrophages first' point of view.Mol Immunol. 2016 Jan;69:146-56. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.09.026. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26471699 Review.
-
The Janus face of macrophages in immunity.J Innate Immun. 2014;6(6):713-5. doi: 10.1159/000367718. Epub 2014 Sep 10. J Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 25322689 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2019 May 24;10:1084. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01084. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31178859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eradication of HIV-1 from the macrophage reservoir: an uncertain goal?Viruses. 2015 Mar 31;7(4):1578-98. doi: 10.3390/v7041578. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25835530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic impact of tumor-associated macrophage infiltration in non-small cell lung cancer: A systemic review and meta-analysis.Onco_target. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):34217-28. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.9079. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 27144518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Role of the Ron Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Underlying Central Nervous System Inflammation in Health and Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 19;9:513. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00513. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29616029 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocyte migration into atherosclerotic plaque.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Jan;35(1):40-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303227. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25301842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human mesenchymal stromal cells reduce influenza A H5N1-associated acute lung injury in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 29;113(13):3621-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601911113. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26976597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dzik JM. The ancestry and cumulative evolution of immune reactions. Acta Biochim Pol. 2010;57:443–466. - PubMed
-
- Cooper EL. Evolution of immune systems from self/not self to danger to artificial immune systems (AIS) Phys Life Rev. 2010;7:55–78. - PubMed
-
- Mills CD. M1 and M2 macrophages: oracles of health and disease. Crit Rev Immunol. 2012;32:463–488. - PubMed
-
- Mills CD, Kincaid K, Alt JM, Heilman MJ, Hill AM. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol. 2000;164:6166–6173. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

