Nutrient-sensing mechanisms and pathways
- PMID: 25592535
- PMCID: PMC4313349
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14190
Nutrient-sensing mechanisms and pathways
Abstract
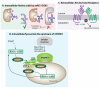
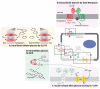
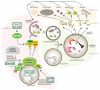
The ability to sense and respond to fluctuations in environmental nutrient levels is a requisite for life. Nutrient scarcity is a selective pressure that has shaped the evolution of most cellular processes. Different pathways that detect intracellular and extracellular levels of sugars, amino acids, lipids and surrogate metabolites are integrated and coordinated at the organismal level through hormonal signals. During food abundance, nutrient-sensing pathways engage anabolism and storage, whereas scarcity triggers homeostatic mechanisms, such as the mobilization of internal stores through autophagy. Nutrient-sensing pathways are commonly deregulated in human metabolic diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amino Acid Sensing in Metabolic Homeostasis and Health.Endocr Rev. 2021 Jan 28;42(1):56-76. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnaa026. Endocr Rev. 2021. PMID: 33053153 Review.
-
Nutrient sensors and their crosstalk.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Jun;55(6):1076-1089. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01006-z. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37258576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothalamic carnitine metabolism integrates nutrient and hormonal feedback to regulate energy homeostasis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 1:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26261054 Review.
-
Coupling nutrient sensing to metabolic homoeostasis: the role of the mammalian _target of rapamycin complex 1 pathway.Proc Nutr Soc. 2012 Nov;71(4):502-10. doi: 10.1017/S0029665112000754. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Proc Nutr Soc. 2012. PMID: 22877732 Review.
-
Regulation of Carbohydrate Energy Metabolism in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2017 Dec;207(4):1231-1253. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.199885. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 29203701 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium channels link cellular respiration to proliferation through a non-conducting mechanism.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Apr 7;12(4):372. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03627-6. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33828089 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic analyses reveal that anti-aging metabolites are depleted by palmitate but increased by oleate in vivo.Cell Cycle. 2015 Aug 3;14(15):2399-407. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1064206. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26098646 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT-2 as a potential _target in pancreatic cancer: the preliminary clue from The Cancer Genome Atlas data.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Oct;13(5):2539-2552. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-900. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36388652 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent modulation of fasting and long-term dietary restriction on acetylcholinesterase in non-neuronal tissues of mice.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;419(1-2):135-45. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2757-3. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27379505
-
Protocol for a randomised controlled trial on the feasibility and effects of 10-hour time-restricted eating on cardiometabolic disease risk among career firefighters doing 24-hour shift work: the Healthy Heroes Study.BMJ Open. 2021 Jun 16;11(6):e045537. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-045537. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34135038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reeds PJ. Dispensable and indispensable amino acids for humans. J. Nutr. 2000;130:1835S–40S. - PubMed
-
- Richieri GV, Kleinfeld AM. Unbound free fatty acid levels in human serum. The Journal of Lipid Research. 1995;36:229–240. - PubMed
-
- Itoh Y, et al. Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through GPR40. Nature. 2003;422:173–176. - PubMed
-
- Hirasawa A, et al. Free fatty acids regulate gut incretin glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion through GPR120. Nat Med. 2005;11:90–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

