Dose-dependent cytotoxic effects of boldine in HepG-2 cells-telomerase inhibition and apoptosis induction
- PMID: 25719742
- PMCID: PMC6272231
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20033730
Dose-dependent cytotoxic effects of boldine in HepG-2 cells-telomerase inhibition and apoptosis induction
Abstract
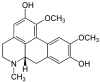
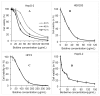
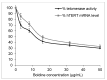
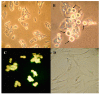
Plant metabolites are valuable sources of novel therapeutic compounds. In an anti-telomerase screening study of plant secondary metabolites, the aporphine alkaloid boldine (1,10-dimethoxy-2,9-dihydroxyaporphine) exhibited a dose and time dependent cytotoxicity against hepatocarcinoma HepG-2 cells. Here we focus on the modes and mechanisms of the growth-limiting effects of this compound. Telomerase activity and expression level of some related genes were estimated by real-time PCR. Modes of cell death also were examined by microscopic inspection, staining methods and by evaluating the expression level of some critically relevant genes. The growth inhibition was correlated with down-regulation of the catalytic subunit of telomerase (hTERT) gene (p < 0.01) and the corresponding reduction of telomerase activity in sub-cytotoxic concentrations of boldine (p < 0.002). However, various modes of cell death were stimulated, depending on the concentration of boldine. Very low concentrations of boldine over a few passages resulted in an accumulation of senescent cells so that HepG-2 cells lost their immortality. Moreover, boldine induced apoptosis concomitantly with increasing the expression of bax/bcl2 (p < 0.02) and p21 (p < 0.01) genes. Boldine might thus be an interesting candidate as a potential natural compound that suppresses telomerase activity in non-toxic concentrations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Boldine, a natural aporphine alkaloid, inhibits telomerase at non-toxic concentrations.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Apr 25;231:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.02.020. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 25746354
-
Antiproliferative effect of the isoquinoline alkaloid papaverine in hepatocarcinoma HepG-2 cells--inhibition of telomerase and induction of senescence.Molecules. 2014 Aug 8;19(8):11846-59. doi: 10.3390/molecules190811846. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25111025 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative effects of crocin in HepG2 cells by telomerase inhibition and hTERT down-regulation.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(5):2305-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.5.2305. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 22901211
-
Boldine and related aporphines: from antioxidant to antiproliferative properties.Nat Prod Commun. 2013 Dec;8(12):1797-800. Nat Prod Commun. 2013. PMID: 24555301 Review.
-
Oxoisoaporphines and Aporphines: Versatile Molecules with Anticancer Effects.Molecules. 2019 Dec 27;25(1):108. doi: 10.3390/molecules25010108. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31892146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro characterization and rational analog design of a novel inhibitor of telomerase assembly in MDA MB 231 breast cancer cell line.Oncol Rep. 2022 Nov;48(5):188. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8403. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36102322 Free PMC article.
-
Modes of Action of Herbal Medicines and Plant Secondary Metabolites.Medicines (Basel). 2015 Sep 8;2(3):251-286. doi: 10.3390/medicines2030251. Medicines (Basel). 2015. PMID: 28930211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical Review in Designing Plant-Based Anticancer Nanoparticles against Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 29;15(6):1611. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061611. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomerase Inhibitors from Natural Products and Their Anticancer Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 21;19(1):13. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010013. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29267203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Gastric Cancer Therapeutic Efficacy through Synergistic Cotreatment of Linderae Radix and Hyperthermia in AGS Cells.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 5;11(10):2710. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102710. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893084 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

