p-Coumaric Acid Attenuates UVB-Induced Release of Stratifin from Keratinocytes and Indirectly Regulates Matrix Metalloproteinase 1 Release from Fibroblasts
- PMID: 25954129
- PMCID: PMC4422964
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.3.241
p-Coumaric Acid Attenuates UVB-Induced Release of Stratifin from Keratinocytes and Indirectly Regulates Matrix Metalloproteinase 1 Release from Fibroblasts
Abstract
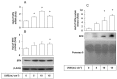
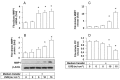
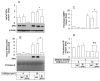
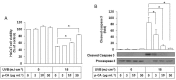
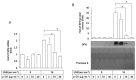
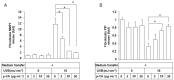
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation-induced loss of dermal extracellular matrix is associated with skin photoaging. Recent studies demonstrated that keratinocyte-releasable stratifin (SFN) plays a critical role in skin collagen metabolism by inducing matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) expression in _target fibroblasts. In the present study, we examined whether SFN released from UVB-irradiated epidermal keratinocytes increases MMP1 release from dermal fibroblasts, and whether these events are affected by p-coumaric acid (p-CA), a natural phenolic compound with UVB-shielding and antioxidant properties. HaCaT cells were exposed to UVB in the absence and presence of p-CA, and the conditioned medium was used to stimulate fibroblasts in medium transfer experiments. The cells and media were analyzed to determine the expressions/releases of SFN and MMP1. UVB exposure increased SFN release from keratinocytes into the medium. The conditioned medium of UVB-irradiated keratinocytes increased MMP1 release from fibroblasts. The depletion of SFN using a siRNA rendered the conditioned medium of UVB-irradiated keratinocytes ineffective at stimulating fibroblasts to release MMP1. p-CA mitigated UVB-induced SFN expression in keratinocytes, and attenuated the MMP1 release by fibroblasts in medium transfer experiments. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that the use of UV absorbers such as p-CA would reduce UV-induced SFN-centered signaling events involved in skin photoaging.
Keywords: Matrix metalloproteinase-1; Skin photoaging; Stratifin; UV.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-1 receptor antagonist attenuates MAP kinase/AP-1 activation and MMP1 expression in UVA-irradiated human fibroblasts induced by culture medium from UVB-irradiated human skin keratinocytes.Int J Mol Med. 2005 Dec;16(6):1117-24. Int J Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16273295
-
Increase of stratifin triggered by ultraviolet irradiation is possibly related to premature aging of human skin.Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23 Suppl 1:32-6. doi: 10.1111/exd.12390. Exp Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25234834
-
Triolein reduces MMP-1 upregulation in dermal fibroblasts generated by ROS production in UVB-irradiated keratinocytes.J Dermatol Sci. 2017 Feb;85(2):124-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.11.010. Epub 2016 Nov 27. J Dermatol Sci. 2017. PMID: 27932255
-
UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes and interleukin-1alpha indirectly increase MAP kinase/AP-1 activation and MMP-1 production in UVA-irradiated dermal fibroblasts.Chin Med J (Engl). 2006 May 20;119(10):827-31. Chin Med J (Engl). 2006. PMID: 16732985
-
[Human skin reconstructed in vitro as a model to study the keratinocyte, the fibroblast and their interactions: photodamage and repair processes].J Soc Biol. 2005;199(4):313-20. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2005032. J Soc Biol. 2005. PMID: 16738525 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Potential Effects of Phenolic Compounds That Can Be Found in Olive Oil on Wound Healing.Foods. 2021 Jul 15;10(7):1642. doi: 10.3390/foods10071642. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34359512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elaeagnus umbellata Fruit Extract Protects Skin from Ultraviolet-Mediated Photoaging in Hairless Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 3;13(2):195. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020195. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397793 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxycinnamic Acids and Their Derivatives: Cosmeceutical Significance, Challenges and Future Perspectives, a Review.Molecules. 2017 Feb 13;22(2):281. doi: 10.3390/molecules22020281. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28208818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoprotective effects of Sargassum thunbergii on ultraviolet B-induced mouse L929 fibroblasts and zebrafish.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 May 21;22(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03609-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35597942 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of p-Coumaric Acid and Ethyl p-Coumarate as the Main Phenolic Components of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Roots.Molecules. 2022 Apr 27;27(9):2781. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092781. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rabe JH, Mamelak AJ, McElgunn PJ, Morison WL, Sauder DN. Photoaging: mechanisms and repair. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Fisher GJ, Kang S, Varani J, Bata-Csorgo Z, Wan Y, Datta S, Voorhees JJ. Mechanisms of photoaging and chronological skin aging. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1462–1470. - PubMed
-
- Kähäri VM, Saarialho-Kere U. Matrix metalloproteinases in skin. Exp Dermatol. 1997;6:199–213. - PubMed
-
- Brennan M, Bhatti H, Nerusu KC, Bhagavathula N, Kang S, Fisher GJ, Varani J, Voorhees JJ. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is the major collagenolytic enzyme responsible for collagen damage in UV-irradiated human skin. Photochem Photobiol. 2003;78:43–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

