α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits Expression of IL-8 by Suppressing Activation of MAPK, Jak/Stat, and NF-κB in H. pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial AGS Cells
- PMID: 26632410
- PMCID: PMC4696963
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.260
α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits Expression of IL-8 by Suppressing Activation of MAPK, Jak/Stat, and NF-κB in H. pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial AGS Cells
Abstract
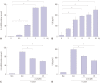
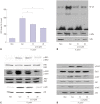
The epithelial cytokine response, associated with reactive oxygen species (ROS), is important in Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-induced inflammation. H. pylori induces the production of ROS, which may be involved in the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (Jak/Stat), and oxidant-sensitive transcription factor, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), and thus, expression of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in gastric epithelial cells. α-lipoic acid, a naturally occurring thiol compound, is a potential antioxidant. It shows beneficial effects in treatment of oxidant-associated diseases including diabetes. The present study is purposed to investigate whether α-lipoic acid inhibits expression of inflammatory cytokine IL-8 by suppressing activation of MAPK, Jak/Stat, and NF-κB in H. pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. Gastric epithelial AGS cells were pretreated with or without α-lipoic acid for 2 h and infected with H. pylori in a Korean isolate (HP99) at a ratio of 300:1. IL-8 mRNA expression was analyzed by RT-PCR analysis. IL-8 levels in the medium were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. NF-κB-DNA binding activity was determined by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Phospho-specific and total forms of MAPK and Jak/Stat were assessed by Western blot analysis. ROS levels were determined using dichlorofluorescein fluorescence. As a result, H. pylori induced increases in ROS levels, mRNA, and protein levels of IL-8, as well as the activation of MAPK [extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1/2 (JNK1/2), p38], Jak/Stat (Jak1/2, Stat3), and NF-κB in AGS cells, which was inhibited by α-lipoic acid. In conclusion, α-lipoic acid may be beneficial for prevention and/or treatment of H. pylori infection-associated gastric inflammation.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; IL-8; Jak/Stat; MAPK; NF-κB; α-lipoic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Jak1/Stat3 is an upstream signaling of NF-κB activation in Helicobacter pylori-induced IL-8 production in gastric epithelial AGS cells.Yonsei Med J. 2015 May;56(3):862-6. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.3.862. Yonsei Med J. 2015. PMID: 25837197 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori in a Korean isolate activates mitogen-activated protein kinases, AP-1, and NF-kappaB and induces chemokine expression in gastric epithelial AGS cells.Lab Invest. 2004 Jan;84(1):49-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.labinvest.3700010. Lab Invest. 2004. PMID: 14631383
-
Beta-carotene inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric epithelial AGS cells.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;60 Suppl 7:131-7. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20388956
-
Chemokine expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa.J Gastroenterol. 1998 Oct;33(5):613-7. doi: 10.1007/s005350050146. J Gastroenterol. 1998. PMID: 9773923 Review.
-
Oxidative stress in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cell injury.Inflammopharmacology. 2005;13(1-3):63-74. doi: 10.1163/156856005774423962. Inflammopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 16259728 Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive Oxygen Species and H. pylori Infection: A Comprehensive Review of Their Roles in Gastric Cancer Development.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Sep 2;12(9):1712. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091712. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Carotene Inhibits Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-10 and Invasion in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells.Molecules. 2021 Mar 12;26(6):1567. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061567. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33809289 Free PMC article.
-
Astaxanthin Inhibits Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Interleukin-8 Expression in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells.Nutrients. 2018 Sep 18;10(9):1320. doi: 10.3390/nu10091320. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30231525 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoic acid rejuvenates aged intestinal stem cells by preventing age-associated endosome reduction.EMBO Rep. 2020 Aug 5;21(8):e49583. doi: 10.15252/embr.201949583. Epub 2020 Jul 9. EMBO Rep. 2020. PMID: 32648369 Free PMC article.
-
Korean Red Ginseng Extract Inhibits IL-8 Expression via Nrf2 Activation in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Epithelial Cells.Nutrients. 2022 Feb 28;14(5):1044. doi: 10.3390/nu14051044. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35268019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peek RM, Jr, Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:28–37. - PubMed
-
- Seo JH, Lim JW, Kim H, Kim KH. Helicobacter pylori in a Korean isolate activates mitogen-activated protein kinases, AP-1, and NF-kappaB and induces chemokine expression in gastric epithelial AGS cells. Lab Invest. 2004;84:49–62. - PubMed
-
- Kim H. Oxidative stress in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cell injury. Inflammopharmacology. 2005;13:63–74. - PubMed
-
- O'Shea JJ, Gadina M, Schreiber RD. Cytokine signaling in 2002: new surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell. 2002;109:S121–S131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

