Calcium-dependent oligomerization of CAR proteins at cell membrane modulates ABA signaling
- PMID: 26719420
- PMCID: PMC4725540
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1512779113
Calcium-dependent oligomerization of CAR proteins at cell membrane modulates ABA signaling
Abstract
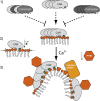
Regulation of ion transport in plants is essential for cell function. Abiotic stress unbalances cell ion homeostasis, and plants tend to readjust it, regulating membrane transporters and channels. The plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) and the second messenger Ca(2+) are central in such processes, as they are involved in the regulation of protein kinases and phosphatases that control ion transport activity in response to environmental stimuli. The identification and characterization of the molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of ABA and Ca(2+) signaling pathways on membrane function are central and could provide opportunities for crop improvement. The C2-domain ABA-related (CAR) family of small proteins is involved in the Ca(2+)-dependent recruitment of the pyrabactin resistance 1/PYR1-like (PYR/PYL) ABA receptors to the membrane. However, to fully understand CAR function, it is necessary to define a molecular mechanism that integrates Ca(2+) sensing, membrane interaction, and the recognition of the PYR/PYL interacting partners. We present structural and biochemical data showing that CARs are peripheral membrane proteins that functionally cluster on the membrane and generate strong positive membrane curvature in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. These features represent a mechanism for the generation, stabilization, and/or specific recognition of membrane discontinuities. Such structures may act as signaling platforms involved in the recruitment of PYR/PYL receptors and other signaling components involved in cell responses to stress.
Keywords: abiotic stress; ion transport; membrane biology; signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C2-domain abscisic acid-related proteins mediate the interaction of PYR/PYL/RCAR abscisic acid receptors with the plasma membrane and regulate abscisic acid sensitivity in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2014 Dec;26(12):4802-20. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.129973. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25465408 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanism of abscisic acid binding and signaling by dimeric PYR1.Science. 2009 Dec 4;326(5958):1373-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1181829. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Science. 2009. PMID: 19933100 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and physiological characterization of the Arabidopsis thaliana Oxidation-related Zinc Finger 2, a plasma membrane protein involved in ABA and salt stress response through the ABI2-mediated signaling pathway.Plant Cell Physiol. 2012 Jan;53(1):193-203. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr162. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22121246
-
A brand new START: abscisic acid perception and transduction in the guard cell.Sci Signal. 2011 Nov 29;4(201):re4. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002164. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 22126965 Review.
-
PYR/PYL/RCAR Receptors Play a Vital Role in the Abscisic-Acid-Dependent Responses of Plants to External or Internal Stimuli.Cells. 2022 Apr 15;11(8):1352. doi: 10.3390/cells11081352. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456031 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The structure and flexibility analysis of the Arabidopsis synaptotagmin 1 reveal the basis of its regulation at membrane contact sites.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Aug 18;4(10):e202101152. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101152. Print 2021 Oct. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34408000 Free PMC article.
-
A C2-Domain Abscisic Acid-Related Gene, IbCAR1, Positively Enhances Salt Tolerance in Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 26;23(17):9680. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179680. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077077 Free PMC article.
-
PfCERLI1 is a conserved rhoptry associated protein essential for Plasmodium falciparum merozoite invasion of erythrocytes.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 16;11(1):1411. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15127-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32179747 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of an ABI-like protein and a Ca2+-ATPase in drought tolerance as revealed by transcript profiling of a sweetpotato somatic hybrid and its parents Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. and I. triloba L.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 21;13(2):e0193193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193193. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29466419 Free PMC article.
-
The tomato IQD gene SUN24 regulates seed germination through ABA signaling pathway.Planta. 2018 Oct;248(4):919-931. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2950-6. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Planta. 2018. PMID: 29968062
References
-
- Serrano R, Rodriguez-Navarro A. Ion homeostasis during salt stress in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13(4):399–404. - PubMed
-
- Bassil E, Blumwald E. The ins and outs of intracellular ion homeostasis: NHX-type cation/H(+) transporters. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2014;22:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Batistič O, Kudla J. Analysis of calcium signaling pathways in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820(8):1283–1293. - PubMed
-
- Cutler SR, Rodriguez PL, Finkelstein RR, Abrams SR. Abscisic acid: Emergence of a core signaling network. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61:651–679. - PubMed
-
- McAinsh MR, Brownlee C, Hetherington AM. Abscisic acid-induced elevation of guard cell cytosolic Ca2+ precedes stomatal closure. Nature. 1990;343(6254):186–188.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

