Accuracy of Heart Rate Watches: Implications for Weight Management
- PMID: 27232714
- PMCID: PMC4883747
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154420
Accuracy of Heart Rate Watches: Implications for Weight Management
Abstract
Background: Wrist-worn monitors claim to provide accurate measures of heart rate and energy expenditure. People wishing to lose weight use these devices to monitor energy balance, however the accuracy of these devices to measure such parameters has not been established.
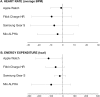
Aim: To determine the accuracy of four wrist-worn devices (Apple Watch, Fitbit Charge HR, Samsung Gear S and Mio Alpha) to measure heart rate and energy expenditure at rest and during exercise.
Methods: Twenty-two healthy volunteers (50% female; aged 24 ± 5.6 years) completed ~1-hr protocols involving supine and seated rest, walking and running on a treadmill and cycling on an ergometer. Data from the devices collected during the protocol were compared with reference methods: electrocardiography (heart rate) and indirect calorimetry (energy expenditure).
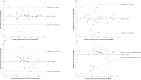
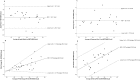
Results: None of the devices performed significantly better overall, however heart rate was consistently more accurate than energy expenditure across all four devices. Correlations between the devices and reference methods were moderate to strong for heart rate (0.67-0.95 [0.35 to 0.98]) and weak to strong for energy expenditure (0.16-0.86 [-0.25 to 0.95]). All devices underestimated both outcomes compared to reference methods. The percentage error for heart rate was small across the devices (range: 1-9%) but greater for energy expenditure (9-43%). Similarly, limits of agreement were considerably narrower for heart rate (ranging from -27.3 to 13.1 bpm) than energy expenditure (ranging from -266.7 to 65.7 kcals) across devices.
Conclusion: These devices accurately measure heart rate. However, estimates of energy expenditure are poor and would have implications for people using these devices for weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wrist-worn devices for the measurement of heart rate and energy expenditure: A validation study for the Apple Watch 6, Polar Vantage V and Fitbit Sense.Eur J Sport Sci. 2023 Feb;23(2):165-177. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2021.2023656. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Eur J Sport Sci. 2023. PMID: 34957939
-
Accuracy of Apple Watch Measurements for Heart Rate and Energy Expenditure in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Mar 19;7(3):e11889. doi: 10.2196/11889. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019. PMID: 30888332 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Consumer Wearable Heart Rate Measurement During an Ecologically Valid 24-Hour Period: Intraindividual Validation Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Mar 11;7(3):e10828. doi: 10.2196/10828. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019. PMID: 30855232 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy and Acceptability of Wrist-Wearable Activity-Tracking Devices: Systematic Review of the Literature.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Jan 21;24(1):e30791. doi: 10.2196/30791. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 35060915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical Activity Measurement Accuracy in Individuals With Chronic Lung Disease: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis of Method Comparison Studies.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015 Nov;96(11):2079-88.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2015.05.015. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015. PMID: 26049088 Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of the Apple Watch for Heart Rate Variability Measurements during Relax and Mental Stress in Healthy Subjects.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Aug 10;18(8):2619. doi: 10.3390/s18082619. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30103376 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy and Precision of Energy Expenditure, Heart Rate, and Steps Measured by Combined-Sensing Fitbits Against Reference Measures: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022 Apr 13;10(4):e35626. doi: 10.2196/35626. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022. PMID: 35416777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validity of the Apple Watch® for monitoring push counts in people using manual wheelchairs.J Spinal Cord Med. 2021 Mar;44(2):212-220. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2019.1576444. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Spinal Cord Med. 2021. PMID: 30811310 Free PMC article.
-
Heart rate and sentiment experimental data with common timeline.Data Brief. 2017 Oct 23;15:851-861. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.10.037. eCollection 2017 Dec. Data Brief. 2017. PMID: 29379849 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Earbud and Wristwatch Heart Rate Monitors during Aerobic and Resistance Training.Int J Exerc Sci. 2019 Mar 1;12(4):374-384. eCollection 2019. Int J Exerc Sci. 2019. PMID: 30899350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haskell WL, Lee I-M, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, et al. Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med Sci Sport Exerc. 2007;39: 1423–1434. - PubMed
-
- Forecast unit sales of health and fitness trackers worldwide from 2014 to 2015 (in millions), by region. Statista. 2015. Available: http://www.statista.com/statistics/413265/health-and-fitness-tracker-wor....
-
- Smart watches and Smart Bands Dominate Fast-Growing Wearables Market. CCS Insight. 2014. Available: http://www.ccsinsight.com/press/company-news/1944-smartwatchesand-smart-....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

