RCAN-11R peptide provides immunosuppression for fully mismatched islet allografts in mice
- PMID: 28596584
- PMCID: PMC5465209
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02934-3
RCAN-11R peptide provides immunosuppression for fully mismatched islet allografts in mice
Abstract
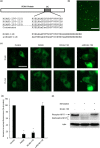
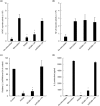
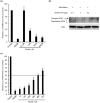
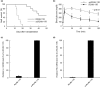
Calcineurin inhibitors have been used for transplant therapy. However, the inhibition of calcineurin outside the immune system has a number of side effects. We previously developed a cell-permeable inhibitor of NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T cells) using the polyarginine peptide delivery system. This peptide (11R-VIVIT) selectively interferes with calcineurin-NFAT interaction without affecting the activity of calcineurin phosphatase and provides immunosuppression for fully mismatched islet allografts in mice. However, our recent study showed that 11R-VIVIT affected cell viability in vitro when it was used at higher concentration because of the VIVIT sequence. The aim of this study is to develop a safer NFAT inhibitor (RCAN-11R) that does not affect cell viability, and which is less toxic than calcineurin inhibitors. The minimal sequence of the protein family of regulators of calcineurin (RCAN) that is responsible for the inhibition of calcineurin-NFAT signaling was recently characterized. The peptide could selectively interfere with the calcineurin-NFAT interaction without affecting the activity of calcineurin phosphatase, similar to 11R-VIVIT. RCAN-11R did not affect cell viability when it was used at a higher concentration than the toxic concentration of 11R-VIVIT. RCAN-11R could therefore be useful as a therapeutic agent that is less toxic than current drugs or 11R-VIVIT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delivery of the VIVIT Peptide to Human Glioma Cells to Interfere with Calcineurin-NFAT Signaling.Molecules. 2021 Aug 7;26(16):4785. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164785. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443374 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting the calcineurin-NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T cells) signaling pathway with a regulator of calcineurin-derived peptide without affecting general calcineurin phosphatase activity.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 3;284(14):9394-401. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805889200. Epub 2009 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19189965 Free PMC article.
-
A new cell-permeable peptide allows successful allogeneic islet transplantation in mice.Nat Med. 2004 Mar;10(3):305-9. doi: 10.1038/nm994. Epub 2004 Feb 8. Nat Med. 2004. PMID: 14770176
-
Therapeutic potential of VIVIT, a selective peptide inhibitor of nuclear factor of activated T cells, in cardiovascular disorders.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2007 Summer;25(2):175-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2007.00011.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2007. PMID: 17614939 Review.
-
[Calcineurin inhibitors and calcineurin-NFAT system].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2010;33(5):249-61. doi: 10.2177/jsci.33.249. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2010. PMID: 21048386 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Delivery of the VIVIT Peptide to Human Glioma Cells to Interfere with Calcineurin-NFAT Signaling.Molecules. 2021 Aug 7;26(16):4785. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164785. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443374 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast as a Model to Find New Drugs and Drug _targets for VPS13-Dependent Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 4;23(9):5106. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095106. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of FOXO4/NFAT2 signaling pathway in dysfunction of human coronary endothelial cells and inflammatory infiltration of vasculitis in Kawasaki disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1090056. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1090056. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36700213 Free PMC article.
-
Partial Inhibition of Calcineurin Activity by Rcn2 as a Potential Remedy for Vps13 Deficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 26;22(3):1193. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031193. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33530471 Free PMC article.
-
Modified cell-permeable JNK inhibitors efficiently prevents islet apoptosis and improves the outcome of islet transplantation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 23;8(1):11082. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29481-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30038242 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

