PAR-TERRA directs homologous sex chromosome pairing
- PMID: 28692038
- PMCID: PMC5553554
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3432
PAR-TERRA directs homologous sex chromosome pairing
Abstract
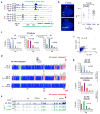
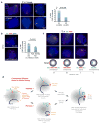
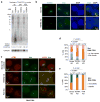
In mammals, homologous chromosomes rarely pair outside meiosis. One exception is the X chromosome, which transiently pairs during X-chromosome inactivation (XCI). How two chromosomes find each other in 3D space is not known. Here, we reveal a required interaction between the X-inactivation center (Xic) and the telomere in mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells. The subtelomeric, pseudoautosomal regions (PARs) of the two sex chromosomes (X and Y) also undergo pairing in both female and male cells. PARs transcribe a class of telomeric RNA, dubbed PAR-TERRA, which accounts for a vast majority of all TERRA transcripts. PAR-TERRA binds throughout the genome, including to the PAR and Xic. During X-chromosome pairing, PAR-TERRA anchors the Xic to the PAR, creating a 'tetrad' of pairwise homologous interactions (Xic-Xic, PAR-PAR, and Xic-PAR). Xic pairing occurs within the tetrad. Depleting PAR-TERRA abrogates pairing and blocks initiation of XCI, whereas autosomal PAR-TERRA induces ectopic pairing. We propose a 'constrained diffusion model' in which PAR-TERRA creates an interaction hub to guide Xic homology searching during XCI.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sensing X chromosome pairs before X inactivation via a novel X-pairing region of the Xic.Science. 2007 Dec 7;318(5856):1632-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1149420. Science. 2007. PMID: 18063799
-
PAR-TERRA is the main contributor to telomeric repeat-containing RNA transcripts in normal and cancer mouse cells.RNA. 2021 Jan;27(1):106-121. doi: 10.1261/rna.076281.120. Epub 2020 Oct 30. RNA. 2021. PMID: 33127860 Free PMC article.
-
Ensuring meiotic DNA break formation in the mouse pseudoautosomal region.Nature. 2020 Jun;582(7812):426-431. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2327-4. Epub 2020 May 27. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32461690 Free PMC article.
-
The tricky path to recombining X and Y chromosomes in meiosis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Sep;1267:18-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06593.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22954211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
X inactivation Xplained.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007 Oct;17(5):387-93. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2007.08.001. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007. PMID: 17869504 Review.
Cited by
-
TbTRF suppresses the TERRA level and regulates the cell cycle-dependent TERRA foci number with a TERRA binding activity in its C-terminal Myb domain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 4;49(10):5637-5653. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab401. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34048580 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Regulation of Mouse Hippocampal Gene Expression Sex Differences by Chromosomal Content and Gonadal Sex.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Aug;59(8):4669-4702. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02860-0. Epub 2022 May 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35589920 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the consequences of deleting the X inactivation center.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 22;118(25):e2102683118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2102683118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34161282 Free PMC article.
-
The makings of TERRA R-loops at chromosome ends.Cell Cycle. 2021 Sep;20(18):1745-1759. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1962638. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34432566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomere Transcription in MLL-Rearranged Leukemia Cell Lines: Increased Levels of TERRA Associate with Lymphoid Lineage and Are Independent of Telomere Length and Ploidy.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 16;11(3):925. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030925. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azzalin CM, Reichenbach P, Khoriauli L, Giulotto E, Lingner J. Telomeric Repeat Containing RNA and RNA Surveillance Factors at Mammalian Chromosome Ends. Science. 2007;318:798–801. - PubMed
-
- Schoeftner S, Blasco MA. Developmentally regulated transcription of mammalian telomeres by DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II. Nature Cell Biology. 2007;10:228–236. - PubMed
-
- Azzalin CM, Lingner J. Telomere functions grounding on TERRA firma. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25:29–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

