MicroRNA-24 inhibits the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells in patients with atherosclerosis by _targeting importin-α3 and regulating inflammatory responses
- PMID: 29250154
- PMCID: PMC5729696
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5355
MicroRNA-24 inhibits the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells in patients with atherosclerosis by _targeting importin-α3 and regulating inflammatory responses
Abstract
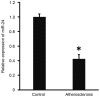
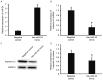
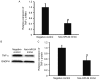
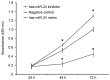
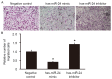
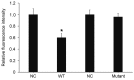
The aim of the present study was to measure the level of microRNA (miRNA or miR)-24 in the serum of patients with atherosclerosis and to investigate the effect of miR-24 on the expression of importin-α3 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, as well as the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells. A total of 30 patients with atherosclerosis admitted to hospital between January and June 2016 were enrolled in the present study; 30 healthy subjects with a similar age range were enrolled as controls. Peripheral blood (10 ml) was collected from all participants. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were transfected with miR-24 mimic using Lipofectamine 2000. _targetScan was used to elucidate whether importin-α3 (KPNA4) was a _target gene of miR-24. Expression levels of miR-24 and mRNAs were measured using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and protein expression was determined using western blotting. Cell Counting Kit 8 assay was used to assess the proliferation of HUVECs, and a Transwell assay was performed to detect the migration of HUVECs. Expression of miR-24 in peripheral blood from patients with atherosclerosis was significantly lower when compared with healthy subjects (P<0.05). Overexpression of miR-24 was demonstrated to significantly inhibit the transcription and translation of the importin-α3 gene (P<0.05) and negatively regulate the expression of endothelial inflammatory factor TNF-α (P<0.05). Furthermore, overexpression of miR-24 significantly inhibited the proliferation and migration of HUVECs (P<0.05), and miR-24 knockdown significantly promoted these processes (P<0.05). The results of the present study suggest that miR-24 exerts its effect in atherosclerosis by blocking the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway, regulating inflammation in endothelial cells, and inhibiting the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; importin-α3; microRNA.
Figures
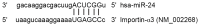
Similar articles
-
Reduced expression of microRNA-199a-3p is associated with vascular endothelial cell injury induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Oct;16(4):3639-3645. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6655. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30233719 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect and related mechanism of microRNA-181 attenuates oxidized low density lipoprotein induced vascular endothelial cell injury].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2017 Mar 24;45(3):230-234. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2017.03.011. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28316180 Chinese.
-
Up-regulation of microRNA-503 by high glucose reduces the migration and proliferation but promotes the apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by inhibiting the expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jun;22(11):3515-3523. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201806_15178. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29917206
-
Overexpression of microRNA-506-3p aggravates the injury of vascular endothelial cells in patients with hypertension by downregulating Beclin1 expression.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Mar;15(3):2844-2850. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5733. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29456688 Free PMC article.
-
[Potential role of microRNA-181b on atherosclerosis].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2015 Jun;43(6):516-20. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26420120 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal dynamics of circulating miRNAs in a swine model of familial hypercholesterolemia during early atherosclerosis.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 7;13(1):19355. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46762-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37935844 Free PMC article.
-
miR-24 _targets SARS-CoV-2 co-factor Neuropilin-1 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells: Insights for COVID-19 neurological manifestations.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2021 Feb 2:rs.3.rs-192099. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-192099/v1. Res Sq. 2021. Update in: Noncoding RNA. 2021 Feb 02;7(1):9. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7010009 PMID: 33564755 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Post-transcriptional control of haemostatic genes: mechanisms and emerging therapeutic concepts in thrombo-inflammatory disorders.Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Jul 6;119(8):1624-1640. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad046. Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 36943786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Validation of a MicroRNA Panel to Differentiate Between Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Controls.J Rheumatol. 2020 Feb;47(2):188-196. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.181029. Epub 2019 May 15. J Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31092710 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circUBR4 regulates ox-LDL-induced proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells through miR-185-5p/FRS2 axis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;476(11):3899-3910. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04207-0. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34159479
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
