Inhibitory Effect of Astaxanthin on Oxidative Stress-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction-A Mini-Review
- PMID: 30134611
- PMCID: PMC6165470
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10091137
Inhibitory Effect of Astaxanthin on Oxidative Stress-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction-A Mini-Review
Abstract
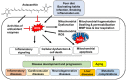
Oxidative stress is a major contributor to the pathogenesis of various human diseases as well as to the aging process. Mitochondria, as the center of cellular metabolism and major regulators of redox balance, play a critical role in disease development and progression. Mitochondrial dysfunction involving structural and metabolic impairment is prominent in oxidative stress-related diseases. Increased oxidative stress can damage mitochondria, and subsequent mitochondrial dysfunction generates excesses of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species that cause cellular damage. Mitochondrial dysfunction also activates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, resulting in cellular death. Astaxanthin, a red-colored xanthophyll carotenoid, exerts an anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effect on various cell lines. In this manner astaxanthin maintains mitochondrial integrity under various pathological conditions. In this review, the inhibitory effects of astaxanthin on oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and related disease development are discussed.
Keywords: astaxanthin; disease prevention; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astaxanthin but not quercetin preserves mitochondrial integrity and function, ameliorates oxidative stress, and reduces heat-induced skeletal muscle injury.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):13292-13302. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28006. Epub 2019 Jan 4. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30609021
-
Astaxanthin-mediated Nrf2 activation ameliorates glucocorticoid-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired bone formation of glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 May 14;19(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04775-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38745231 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of astaxanthin on a combination of D-galactose and jet lag-induced aging model in mice.Endocr J. 2018 May 28;65(5):569-578. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0500. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Endocr J. 2018. PMID: 29526991
-
Astaxanthin: A Potential Mitochondrial-_targeted Antioxidant Treatment in Diseases and with Aging.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 11;2019:3849692. doi: 10.1155/2019/3849692. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31814873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming of human cells in response to oxidative stress: implications in the pathophysiology and therapy of mitochondrial diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5510-26. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140306103401. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606797 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary dimethylglycine sodium salt supplementation improves growth performance, redox status, and skeletal muscle function of intrauterine growth-restricted weaned piglets.J Anim Sci. 2021 Jul 1;99(7):skab186. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab186. J Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34107017 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenger Agent, Astaxanthin, in the Protection of Cisplatin-Treated Patients Against Hearing Loss.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Dec 18;13:4291-4303. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S212313. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31908415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic role of astaxanthin derived from shrimp against certain metabolic disorders.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Nov 30;10(1):12-20. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2623. eCollection 2022 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 35035906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[METTL3 inhibitor STM2457 improves metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease by regulating mitochondrial function in mice].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Oct 20;43(10):1689-1696. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.10.06. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37933644 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Effects of Supplementation with Anti-Inflammatory Compound Extracted from Herbs in Healthy and Obese Cats.Vet Med (Auckl). 2020 Mar 16;11:39-44. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S240516. eCollection 2020. Vet Med (Auckl). 2020. PMID: 32215260 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical