Contaminants in Grain-A Major Risk for Whole Grain Safety?
- PMID: 30200531
- PMCID: PMC6163171
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10091213
Contaminants in Grain-A Major Risk for Whole Grain Safety?
Abstract
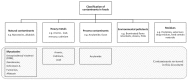
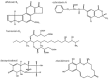
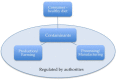
Grains are the main energy and carbohydrate sources for human nutrition globally. Governmental and non-governmental authorities recommend whole grains as a healthy food choice. The role of contaminants in (whole) grains and how to mitigate any potential risk following their consumption has not been reported. With this narrative review, we shed light on the potential human health risk from contaminants in whole grains and elaborate strategies to mitigate such risk. We found that grains represent a significant source of food-borne contaminants, the main ones being; mycotoxins including (A) aflatoxin B1; (B) ochratoxin A; (C) fumonisin B1; (D) deoxynivalenol; (E) zearalenone; toxic metals like arsenic, cadmium and lead; as well as process contaminants such as acrylamide. Whole grains usually contain more contaminants than refined products. However, whole grains also provide more nutrients that may reduce the impact of these contaminants. Strict regulatory thresholds aim to minimize the risk of contaminants to public health. The consumer can further impact on the mitigation of any risk by eating a healthy diet filled with nutrient-dense foods such as whole grains and probiotics. The risk posed by contaminants from whole grains do not outweigh the known nutritional benefits of whole grain consumption.
Keywords: contaminants; diet; human health; metal; mycotoxin; risk mitigation; whole grain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of Mycotoxins during Fermentation of Whole Grain Sorghum to Whole Grain Ting (a Southern African Food).Toxins (Basel). 2019 Mar 25;11(3):180. doi: 10.3390/toxins11030180. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30934589 Free PMC article.
-
Mycotoxin Determination and Occurrence in Pseudo-Cereals Intended for Food and Feed: A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jun 4;15(6):379. doi: 10.3390/toxins15060379. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37368680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous Determination of Multi-Mycotoxins in Cereal Grains Collected from South Korea by LC/MS/MS.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Mar 16;9(3):106. doi: 10.3390/toxins9030106. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28300780 Free PMC article.
-
[Propagation of toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins in various grains].Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 1993 Jan-Feb;29(1):70-9. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 1993. PMID: 8475024 Russian.
-
Effect of processing on mycotoxin content in grains.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015;55(12):1672-83. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.701254. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015. PMID: 24915313 Review.
Cited by
-
Exposure to mycotoxins from the consumption of corn-based breakfast cereals in the United Arab Emirates.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 28;14(1):25761. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74529-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39468151 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatory Effects of Acrylamide and Deoxynivalenol on In Vitro Cell Viability and Cytochrome P450 Enzymes of Human HepaRG Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;16(9):389. doi: 10.3390/toxins16090389. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330847 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined ICP-MS, ESEM-EDX, and HAADF-STEM-EDX Approach for the Assessment of Metal Sub-Micro- and Nanoparticles in Wheat Grain.Molecules. 2024 Jul 2;29(13):3148. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133148. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999099 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Analog Rice Made from Cassava and Banana with the Addition of Katuk Leaf (Sauropus androgynous L. Merr.) and Soy Lecithin for Lactating Women.Foods. 2024 May 7;13(10):1438. doi: 10.3390/foods13101438. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38790738 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating effects of whole grain consumption on type 2 diabetes, colorectal cancer and cardiovascular disease: a burden of proof study.Nutr J. 2024 May 14;23(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12937-024-00957-x. Nutr J. 2024. PMID: 38741117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FAO Staple Foods: What Do People Eat? [(accessed on 13 July 2018)]; Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/u8480e/u8480e07.htm.
-
- FAO World Food Situation. [(accessed on 13 August 2018)]; Available online: http://www.fao.org/worldfoodsituation/csdb/en/
-
- EC . Laying Down Community Procedures for Contaminants in Food. Offcial Journal of the European Communities; Brussels, Belgium: 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical