mTOR Signaling in Cancer and mTOR Inhibitors in Solid Tumor _targeting Therapy
- PMID: 30754640
- PMCID: PMC6387042
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20030755
mTOR Signaling in Cancer and mTOR Inhibitors in Solid Tumor _targeting Therapy
Abstract
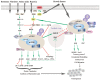
The mammalian or mechanistic _target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway plays a crucial role in regulation of cell survival, metabolism, growth and protein synthesis in response to upstream signals in both normal physiological and pathological conditions, especially in cancer. Aberrant mTOR signaling resulting from genetic alterations from different levels of the signal cascade is commonly observed in various types of cancers. Upon hyperactivation, mTOR signaling promotes cell proliferation and metabolism that contribute to tumor initiation and progression. In addition, mTOR also negatively regulates autophagy via different ways. We discuss mTOR signaling and its key upstream and downstream factors, the specific genetic changes in the mTOR pathway and the inhibitors of mTOR applied as therapeutic strategies in eight solid tumors. Although monotherapy and combination therapy with mTOR inhibitors have been extensively applied in preclinical and clinical trials in various cancer types, innovative therapies with better efficacy and less drug resistance are still in great need, and new biomarkers and deep sequencing technologies will facilitate these mTOR _targeting drugs benefit the cancer patients in personalized therapy.
Keywords: PI3K; cancer; inhibitor; mTOR; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside.Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 Dec;59:125-132. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.07.009. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019. PMID: 31323288 Review.
-
Molecular _targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 May;142(2):164-75. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24333502 Review.
-
_targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian _target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway: an emerging treatment strategy for squamous cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Sep;40(8):980-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.06.006. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 25037117 Review.
-
[mTOR inhibitor].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2011 Jan;38(1):7-11. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2011. PMID: 21368454 Japanese.
-
_targeting PI3K Signaling in Combination Cancer Therapy.Trends Cancer. 2017 Jun;3(6):454-469. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 May 14. Trends Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28718419 Review.
Cited by
-
ATP6V1C1, associated with the tumor microenvironment and mTORC1 signaling pathway, is a potential diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 18;15(1):673. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01578-w. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39557733 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact of mitochondrial-_targeting anthelmintic agents with GLUT1 inhibitor BAY-876 on breast cancer cell metabolism.BMC Cancer. 2024 Nov 16;24(1):1415. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13186-6. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39550554 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted anticancer potential of luteolin: involvement of NF-κB, AMPK/mTOR, PI3K/Akt, MAPK, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Nov 14. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01596-8. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39543054 Review.
-
Exploring a specific type of tissue-resident natural killer cell involved in the anti-tumor and immunotherapy response in human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using scRNA-seq.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 31;13(10):5550-5562. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1535. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39524999 Free PMC article.
-
IL-32γ Induced Autophagy Through Suppression of MET and mTOR Pathways in Liver Tumor Growth Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 30;25(21):11678. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111678. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519229 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

