Highly Selective, Aptamer-Based, Ultrasensitive Nanogold Colorimetric Smartphone Readout for Detection of Cd(II)
- PMID: 31362377
- PMCID: PMC6695641
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24152745
Highly Selective, Aptamer-Based, Ultrasensitive Nanogold Colorimetric Smartphone Readout for Detection of Cd(II)
Abstract
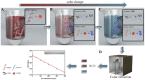
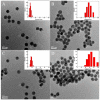
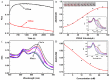
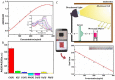
A highly selective and sensitive method for Cd(II) detection was developed based on aptamer and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) combined with a colorimetric smartphone readout. The experimental conditions such as reaction time of polydiene dimethyl ammonium chloride (PDDA) and AuNPs, PDDA dose, time of aptamer and PDDA incubation, and aptamer concentration were optimized. Under the optimized conditions, the color and red(R) value of the solution was concentration-dependent on Cd(II). The proposed method exhibited a linear range of 1-400 ng/mL (r2 = 0.9794) with a limit of detection (LOD) of 1 ng/mL. This method had been successfully applied to test and quantify Cd(II) in water and rice samples, and the results were in full agreement with those from the atomic absorption spectrometer. Therefore, low-cost colorimetry demonstrated its potential for practical application in visual or quantitative detection with a smartphone. This approach can be readily applied to other analytes.
Keywords: Cd(II); aptamer; colorimetry; nanogold; smartphone readout.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In-situ detection of cadmium with aptamer functionalized gold nanoparticles based on smartphone-based colorimetric system.Talanta. 2020 Feb 1;208:120231. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120231. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Talanta. 2020. PMID: 31816705
-
A label-free hairpin aptamer probe for colorimetric detection of adenosine triphosphate based on the anti-aggregation of gold nanoparticles.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2019 Jun 15;217:122-127. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.03.081. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2019. PMID: 30928837
-
Ultrasensitive aptamer biosensor for malathion detection based on cationic polymer and gold nanoparticles.Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Nov 15;85:445-449. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.05.042. Epub 2016 May 13. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016. PMID: 27208476
-
Recent Aptamer-Based Biosensors for Cd2+ Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;13(6):612. doi: 10.3390/bios13060612. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in nanomaterials for colorimetric cancer detection.J Mater Chem B. 2021 Jan 28;9(4):921-938. doi: 10.1039/d0tb02163f. Epub 2020 Dec 24. J Mater Chem B. 2021. PMID: 33367450 Review.
Cited by
-
Label-Free and Sensitive Determination of Cadmium Ions Using a Ti-Modified Co3O4-Based Electrochemical Aptasensor.Biosensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 30;10(12):195. doi: 10.3390/bios10120195. Biosensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33266040 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in aptamer applications for analytical biochemistry.Anal Biochem. 2022 May 1;644:113894. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2020.113894. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Anal Biochem. 2022. PMID: 32763306 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone-Based Image Analysis for Rapid Evaluation of Kiwifruit Quality during Cold Storage.Foods. 2022 Jul 15;11(14):2113. doi: 10.3390/foods11142113. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35885355 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Aptamer Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 2;21(3):979. doi: 10.3390/s21030979. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33540523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Facile Aptasensor for Instantaneous Determination of Cadmium Ions Based on Fluorescence Amplification Effect of MOPS on FAM-Labeled Aptamer.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;11(5):133. doi: 10.3390/bios11050133. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afkhami A., Ghaedi H., Madrakian T., Rezaeivala M. Highly sensitive simultanous electrochemical determination of trace amounts of Pb(II) and Cd(II) using a carbon paste electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and a newly synthesized Schiff base. Electrochim. Acta. 2013;89:377–386. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.11.050. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

