Biological and molecular characterization of Aromia bungii (Faldermann, 1835) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), an emerging pest of stone fruits in Europe
- PMID: 32346054
- PMCID: PMC7188857
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-63959-9
Biological and molecular characterization of Aromia bungii (Faldermann, 1835) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), an emerging pest of stone fruits in Europe
Abstract
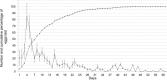
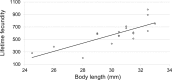
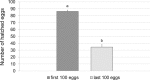
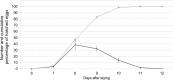
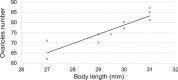
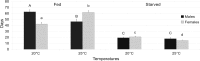
The red-necked longhorn beetle (RLB) Aromia bungii (Fald.) is an emerging pest of stone fruit trees, native to East Asia, accidentally introduced in Europe (Germany and Italy) and Japan. Threatening seriously the stone fruit crops in Europe, RLB was added to both the EPPO A1 and priority pest lists of quarantine species. Molecular analyses highlighted that all specimens recovered in southern Italy share the same haplotype, different from the German one, supporting that the invasive process in Europe started from at least two independent introductions. To fill the existing gap of biological knowledge about A. bungii, several laboratory tests were carried out on specimens collected in the outbreak area of Naples (Italy). Results suggest a high biotic potential of the RLB Italian population. Females showed a short pre-oviposition period while the period of oviposition lasted about three weeks, with a rate of 24.2 eggs/day. Each female laid an average of 587.5 eggs and spawned the largest amount of eggs during the first week after emergence. Fed males live up to 62 days at 20 °C while fed females about 63 days at 25 °C. These results are crucial to draw up a multi-facet IPM approach against A. bungii in the outbreak areas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Differences among Established Populations of Aromia bungii (Faldermann, 1835) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in Japan: Suggestion of Multiple Introductions.Insects. 2022 Feb 21;13(2):217. doi: 10.3390/insects13020217. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35206790 Free PMC article.
-
Electroantennographic Responses of Aromia bungii (Faldermann, 1835) (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae) to a Range of Volatile Compounds.Insects. 2019 Aug 27;10(9):274. doi: 10.3390/insects10090274. Insects. 2019. PMID: 31461927 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a male-produced sex-aggregation pheromone for a highly invasive cerambycid beetle, Aromia bungii.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 4;7(1):7330. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07520-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28779104 Free PMC article.
-
Host marking pheromone (HMP) in the Mexican fruit fly Anastrepha ludens.Chimia (Aarau). 2010;64(1-2):37-42. doi: 10.2533/chimia.2010.37. Chimia (Aarau). 2010. PMID: 21137682 Review.
-
Managing invasive populations of Asian longhorned beetle and citrus longhorned beetle: a worldwide perspective.Annu Rev Entomol. 2010;55:521-46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-112408-085427. Annu Rev Entomol. 2010. PMID: 19743916 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous detections of Olenecamptusbilobus (Fabricius, 1801) (Cerambycidae, Dorcaschematini) in Europe.Biodivers Data J. 2023 Dec 1;11:e114432. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.11.e114432. eCollection 2023. Biodivers Data J. 2023. PMID: 38078289 Free PMC article.
-
The spread of Carpophilus truncatus is on the razor's edge between an outbreak and a pest invasion.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 7;12(1):18841. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23520-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36344625 Free PMC article.
-
The Bugs in the Bags: The Risk Associated with the Introduction of Small Quantities of Fruit and Plants by Airline Passengers.Insects. 2022 Jul 10;13(7):617. doi: 10.3390/insects13070617. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35886793 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal Prevalence of the Invasive Longhorn Beetle Aromia bungii in Osaka Prefecture, Japan.Insects. 2022 Feb 23;13(3):222. doi: 10.3390/insects13030222. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35323520 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Differences among Established Populations of Aromia bungii (Faldermann, 1835) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in Japan: Suggestion of Multiple Introductions.Insects. 2022 Feb 21;13(2):217. doi: 10.3390/insects13020217. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35206790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lupi D, et al. Insects and globalization: Sustainable control of exotic species in Italian agro-forestry ecosystems. Landsc. Manag. Funct. Biodivers. IOBC-WPRS Bull. 2014;100:87–90.
-
- Bosco L, Moraglio ST, Tavella L. Halyomorpha halys, a serious threat for hazelnut in newly invaded areas. J. Pest. Sci. 2018;91:661–670. doi: 10.1007/s10340-017-0937-x. - DOI
-
- Garonna AP, et al. The spread of the non-native pine tortoise scale Toumeyella parvicornis (Hemiptera: Coccidae) in Europe: a major threat to Pinus pinea in Southern Italy. iForest. 2018;11:628–634. doi: 10.3832/ifor2864-011. - DOI
-
- Gressitt JL. Destructive long-horned beetle borers at Canton, China. Spec. Publ. Lingnan. N. H. Surv. Mus. 1942;1:1–60.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

