Insulin receptor substrate in brain-enriched exosomes in subjects with major depression: on the path of creation of biosignatures of central insulin resistance
- PMID: 32536688
- PMCID: PMC7787430
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-020-0804-7
Insulin receptor substrate in brain-enriched exosomes in subjects with major depression: on the path of creation of biosignatures of central insulin resistance
Abstract
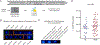
Insulin signaling is critical for neuroplasticity, cerebral metabolism as well as for systemic energy metabolism. In rodent studies, impaired brain insulin signaling with resultant insulin resistance (IR) modulates synaptic plasticity and the corresponding behavioral functions. Despite discoveries of central actions of insulin, in vivo molecular mechanisms of brain IR until recently have proven difficult to study in the human brain. In the current study, we leveraged recent technological advances in molecular biology and herein report an increased number of exosomes enriched for L1CAM, a marker predominantly expressed in the brain, in subjects with major depressive disorder (MDD) as compared with age- and sex-matched healthy controls (HC). We also report increased concentration of the insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) in L1CAM+ exosomes in subjects with MDD as compared with age- and sex-matched HC. We found a relationship between expression of IRS-1 in L1CAM+ exosomes and systemic IR as assessed by homeostatic model assessment of IR in HC, but not in subjects with MDD. The increased IRS-1 levels in L1CAM+ exosomes were greater in subjects with MDD and were associated with suicidality and anhedonia. Finally, our data suggested sex differences in serine-312 phosphorylation of IRS-1 in L1CAM+ exosomes in subjects with MDD. These findings provide a starting point for creating mechanistic framework of brain IR in further development of personalized medicine strategies to effectively treat MDD.
© 2020. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures
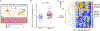
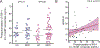
Similar articles
-
Exosomal biomarkers of brain insulin resistance associated with regional atrophy in Alzheimer's disease.Hum Brain Mapp. 2017 Apr;38(4):1933-1940. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23494. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017. PMID: 28105773 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunctionally phosphorylated type 1 insulin receptor substrate in neural-derived blood exosomes of preclinical Alzheimer's disease.FASEB J. 2015 Feb;29(2):589-96. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-262048. Epub 2014 Oct 23. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25342129 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-signaling abnormalities in drug-naïve first-episode schizophrenia: Transduction protein analyses in extracellular vesicles of putative neuronal origin.Eur Psychiatry. 2019 Oct;62:124-129. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2019.08.012. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Eur Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31590015 Free PMC article.
-
Consolidating evidence on the role of insulin resistance in major depressive disorder.Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 1;37(1):23-28. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000905. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 37972981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking atypical depression and insulin resistance-related disorders via low-grade chronic inflammation: Integrating the phenotypic, molecular and neuroanatomical dimensions.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Mar;93:335-352. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.020. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33359233 Review.
Cited by
-
Is Nasal Dysbiosis a Required Component for Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder?Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug 9. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04375-2. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39120823 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle approach to major psychiatric disorders.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2023 Sep;273(6):1279-1293. doi: 10.1007/s00406-022-01497-3. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36302978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between the triglyceride-glucose index and depression in individuals with chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional study from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2020.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 27;103(39):e39834. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039834. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39331934 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of Extracellular Vesicles as "Liquid Biopsy" for Neurological Disorders: Boom or Bust.Pharmacol Rev. 2024 Feb 13;76(2):199-227. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000788. Pharmacol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38351075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human neurosecretome: extracellular vesicles and particles (EVPs) of the brain for intercellular communication, therapy, and liquid-biopsy applications.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 17;10:1156821. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1156821. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37266331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biessels GJ, Reagan LP. Hippocampal insulin resistance and cognitive dysfunction. Nat Rev Neurosci 2015; 16(11): 660–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

