The Cross-Talk Between EGFR and E-Cadherin
- PMID: 35127732
- PMCID: PMC8811214
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.828673
The Cross-Talk Between EGFR and E-Cadherin
Abstract
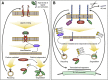
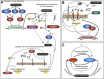
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and adhesion protein E-cadherin are major regulators of proliferation and differentiation in epithelial cells. Consistently, defects in both EGFR and E-cadherin-mediated intercellular adhesion are linked to various malignancies. These defects in either are further exacerbated by the reciprocal interactions between the two transmembrane proteins. On the one hand, EGFR can destabilize E-cadherin adhesion by increasing E-cadherin endocytosis, modifying its interactions with cytoskeleton and decreasing its expression, thus promoting tumorigenesis. On the other hand, E-cadherin regulates EGFR localization and tunes its activity. As a result, loss and mutations of E-cadherin promote cancer cell invasion due to uncontrolled activation of EGFR, which displays enhanced surface motility and changes in endocytosis. In this minireview, we discuss the molecular and cellular mechanisms of the cross-talk between E-cadherin and EGFR, highlighting emerging evidence for the role of endocytosis in this feedback, as well as its relevance to tissue morphogenesis, homeostasis and cancer progression.
Keywords: adhesion; cancer; epithelia; morphogenesis; signalling.
Copyright © 2022 Ramírez Moreno and Bulgakova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced activation of epidermal growth factor receptor caused by tumor-derived E-cadherin mutations.Cancer Res. 2008 Feb 1;68(3):707-14. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1588. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18245470
-
Cross-talk between EGFR and T-cadherin: EGFR activation promotes T-cadherin localization to intercellular contacts.Cell Signal. 2013 May;25(5):1044-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23411345
-
EGF/EGFR axis contributes to the progression of cholangiocarcinoma through the induction of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Hepatol. 2014 Aug;61(2):325-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.03.033. Epub 2014 Apr 3. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24704591
-
No one-way street: cross-talk between e-cadherin and receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling: a mechanism to regulate RTK activity.Cancer Biol Ther. 2005 Jan;4(1):28-31. doi: 10.4161/cbt.4.1.1431. Epub 2005 Jan 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15662113 Review.
-
Interplay between EGFR, E-cadherin, and PTP1B in epidermal homeostasis.Tissue Barriers. 2023 Jul 3;11(3):2104085. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2022.2104085. Epub 2022 Jul 24. Tissue Barriers. 2023. PMID: 35875939 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt signaling couples G2 phase control with differentiation during hematopoiesis in Drosophila.Dev Cell. 2024 Sep 23;59(18):2477-2496.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.05.023. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Dev Cell. 2024. PMID: 38866012
-
A novel noncanonical function for IRF6 in the recycling of E-cadherin.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Jul 1;35(7):ar102. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-11-0430. Epub 2024 May 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38809584 Free PMC article.
-
E-cadherin interacts with EGFR resulting in hyper-activation of ERK in multiple models of breast cancer.Oncogene. 2024 May;43(19):1445-1462. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03007-2. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38509231
-
Emerging roles and mechanisms of ERK pathway mechanosensing.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Nov 10;80(12):355. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05007-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37947896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin-dependent recruitment of AGO2 to the zonula adherens.Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Dec 1;34(13):ar129. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E22-03-0099-T. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37819702 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

