Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2
- PMID: 35273146
- PMCID: PMC8913741
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28865-w
Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2.Nat Commun. 2022 Mar 24;13(1):1694. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29480-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35332153 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
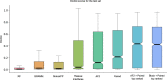
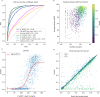
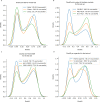
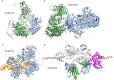
Predicting the structure of interacting protein chains is a fundamental step towards understanding protein function. Unfortunately, no computational method can produce accurate structures of protein complexes. AlphaFold2, has shown unprecedented levels of accuracy in modelling single chain protein structures. Here, we apply AlphaFold2 for the prediction of heterodimeric protein complexes. We find that the AlphaFold2 protocol together with optimised multiple sequence alignments, generate models with acceptable quality (DockQ ≥ 0.23) for 63% of the dimers. From the predicted interfaces we create a simple function to predict the DockQ score which distinguishes acceptable from incorrect models as well as interacting from non-interacting proteins with state-of-art accuracy. We find that, using the predicted DockQ scores, we can identify 51% of all interacting pairs at 1% FPR.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
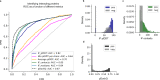
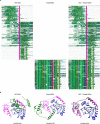
Similar articles
-
DockQ: A Quality Measure for Protein-Protein Docking Models.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 25;11(8):e0161879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161879. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27560519 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting residue-specific qualities of individual protein models using residual neural networks and graph neural networks.Proteins. 2022 Dec;90(12):2091-2102. doi: 10.1002/prot.26400. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Proteins. 2022. PMID: 35842895 Free PMC article.
-
DockQ v2: improved automatic quality measure for protein multimers, nucleic acids, and small molecules.Bioinformatics. 2024 Oct 1;40(10):btae586. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae586. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39348158 Free PMC article.
-
AI-Based Protein Structure Prediction in Drug Discovery: Impacts and Challenges.J Chem Inf Model. 2022 Jul 11;62(13):3142-3156. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c00026. Epub 2022 Jun 21. J Chem Inf Model. 2022. PMID: 35727311 Review.
-
Integrating Large-Scale Protein Structure Prediction into Human Genetics Research.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2024 Aug;25(1):123-140. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-120622-020615. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38621234 Review.
Cited by
-
Zfp260 choreographs the early stage osteo-lineage commitment of skeletal stem cells.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 24;15(1):10186. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54640-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39582024 Free PMC article.
-
AlphaFold2, SPINE-X, and Seder on Four Hard CASP _targets.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2867:141-152. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4196-5_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39576579
-
Beyond AlphaFold2: The Impact of AI for the Further Improvement of Protein Structure Prediction.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2867:121-139. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4196-5_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39576578 Review.
-
A potent and selective anti-glutathione peroxidase 4 nanobody as a ferroptosis inducer.Chem Sci. 2024 Oct 29;15(46):19420-19431. doi: 10.1039/d4sc05448b. eCollection 2024 Nov 27. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39568902 Free PMC article.
-
ProBID-Net: a deep learning model for protein-protein binding interface design.Chem Sci. 2024 Oct 30. doi: 10.1039/d4sc02233e. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39568891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liddington, R. C. Structural Basis of Protein–Protein Interactions. Protein-Protein Interactions261, 3–14 10.1385/1-59259-762-9:003 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Keskin O, Gursoy A, Ma B, Nussinov R. Principles of protein-protein interactions: what are the preferred ways for proteins to interact? Chem. Rev. 2008;108:1225–1244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

