Structural requirements of ligands for the oxysterol liver X receptors LXRalpha and LXRbeta
- PMID: 9874807
- PMCID: PMC15128
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.1.266
Structural requirements of ligands for the oxysterol liver X receptors LXRalpha and LXRbeta
Abstract
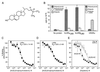
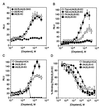
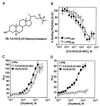
LXRalpha and -beta are nuclear receptors that regulate the metabolism of several important lipids, including cholesterol and bile acids. Previously, we have proposed that LXRs regulate these pathways through their interaction with specific, naturally occurring oxysterols, including 22(R)-hydroxycholesterol, 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol, and 24(S),25-epoxycholesterol. Using a ligand binding assay that incorporates scintillation proximity technology to circumvent many of the problems associated with assaying extremely hydrophobic ligands, we now demonstrate that these oxysterols bind directly to LXRs at concentrations that occur in vivo. To characterize further the structural determinants required for potent LXR ligands, we synthesized and tested a series of related compounds for binding to LXRs and activation of transcription. These studies revealed that position-specific monooxidation of the sterol side chain is requisite for LXR high-affinity binding and activation. Enhanced binding and activation can also be achieved through the use of 24-oxo ligands that act as hydrogen bond acceptors in the side chain. In addition, introduction of an oxygen on the sterol B-ring results in a ligand with LXRalpha-subtype selectivity. These results support the hypothesis that naturally occurring oxysterols are physiological ligands for LXRs and show that a rational, structure-based approach can be used to design potent LXR ligands for pharmacologic use.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sterol intermediates from cholesterol biosynthetic pathway as liver X receptor ligands.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 22;281(38):27816-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603781200. Epub 2006 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16857673
-
Pharmacophore analysis of the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXRalpha.J Med Chem. 2001 Mar 15;44(6):886-97. doi: 10.1021/jm0004749. J Med Chem. 2001. PMID: 11300870
-
The phospholipid transfer protein gene is a liver X receptor _target expressed by macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Mar;23(6):2182-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.2182-2191.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12612088 Free PMC article.
-
The pharmacology of LXR.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005 Aug;5(8):729-40. doi: 10.2174/1389557054553767. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16101409 Review.
-
LXR is crucial in lipid metabolism.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005 Jul;73(1):59-63. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2005.04.009. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005. PMID: 15913974 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxysterols as non-genomic regulators of cholesterol homeostasis.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Mar;23(3):99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.12.002. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22244444 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Receptors and Lipid Sensing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1390:83-105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-11836-4_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36107314
-
The Liver under the Spotlight: Bile Acids and Oxysterols as Pivotal Actors Controlling Metabolism.Cells. 2021 Feb 16;10(2):400. doi: 10.3390/cells10020400. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33669184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential regulation of gene expression by LXRs in response to macrophage cholesterol loading.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Jul;27(7):1036-47. doi: 10.1210/me.2013-1051. Epub 2013 May 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23686114 Free PMC article.
-
Oxysterols in Autoimmunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 12;20(18):4522. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184522. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31547302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

