Quantum dot-conjugated anti-GRP78 scFv inhibits cancer growth in mice
- PMID: 22249409
- PMCID: PMC6268310
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17010796
Quantum dot-conjugated anti-GRP78 scFv inhibits cancer growth in mice
Abstract
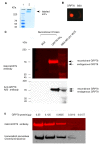
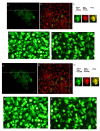
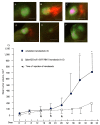
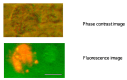
Semiconductor quantum dots (Qdots) have recently been shown to offer significant advantages over conventional fluorescent probes to image and study biological processes. The stability and low toxicity of QDs are well suited for biological applications. Despite this, the potential of Qdots remains limited owing to the inefficiency of existing delivery methods. By conjugating Qdots with small antibody fragments _targeting membrane-bound proteins, such as GRP78, we demonstrate here that the Quantum dot- Anti-GRP78 scFv (Qdot-GRP78) retains its immunospecificity and its distribution can be monitored by visualization of multi-color fluorescence imaging both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover we demonstrate here for the first time that Qdot-GRP78 scFv bioconjugates can be efficiently internalized by cancer cells, thus upregulate phophosphate-AKT-ser473 and possess biological anti-tumour activity as shown by inhibition of breast cancer growth in a xenograft model. This suggests that nanocarrier-conjugated scFvs can be used as a therapeutic antibody for cancer treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of established micrometastases by _targeted drug delivery via cell surface-associated GRP78.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 15;19(8):2107-16. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2991. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23470966 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibodies against the cell surface-associated chaperone GRP78 stimulate tumor growth via tissue factor.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 22;292(51):21180-21192. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.799908. Epub 2017 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29066620 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme B-based cytolytic fusion protein _targeting EpCAM specifically kills triple negative breast cancer cells in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in a subcutaneous mouse tumor model.Cancer Lett. 2016 Mar 28;372(2):201-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.027. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26806809
-
_targeting GRP78 and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer.Future Med Chem. 2013 Jun;5(9):1047-57. doi: 10.4155/fmc.13.77. Future Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23734687 Review.
-
GRP78 _targeting: Hitting two birds with a stone.Life Sci. 2020 Nov 1;260:118317. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118317. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32841659 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Scratching the Surface-An Overview of the Roles of Cell Surface GRP78 in Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 May 10;10(5):1098. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051098. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSP70s in Breast Cancer: Promoters of Tumorigenesis and Potential _targets/Tools for Therapy.Cells. 2021 Dec 7;10(12):3446. doi: 10.3390/cells10123446. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantum dot-based nanoprobes for in vivo _targeted imaging.Curr Mol Med. 2013 Dec;13(10):1549-67. doi: 10.2174/1566524013666131111121733. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24206136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody fragments as nanoparticle _targeting ligands: a step in the right direction.Chem Sci. 2017 Jan 1;8(1):63-77. doi: 10.1039/c6sc02403c. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Chem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28451149 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock proteins: Biological functions, pathological roles, and therapeutic opportunities.MedComm (2020). 2022 Aug 2;3(3):e161. doi: 10.1002/mco2.161. eCollection 2022 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35928554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rogach A.L. Semiconductor Nanocrystal Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Assembly, Spectroscopy, and Applications. Springer; Wien; New York, NY, USA: 2008. p. 372.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

