3D Micro/Nanopatterning of a Vinylferrocene Copolymer
- PMID: 32456151
- PMCID: PMC7287958
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25102438
3D Micro/Nanopatterning of a Vinylferrocene Copolymer
Abstract
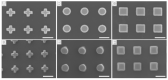
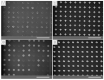
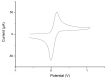
In nanoimprint lithography (NIL), a pattern is created by mechanical deformation of an imprint resist via embossing with a stamp, where the adhesion behavior during the filling of the imprint stamp and its subsequent detachment may impose some practical challenges. Here we explored thermal and reverse NIL patterning of polyvinylferrocene and vinylferrocene-methyl methacrylate copolymers to prepare complex non-spherical objects and patterns. While neat polyvinylferrocene was found to be unsuitable for NIL, freshly-prepared vinylferrocene-methyl methacrylate copolymers, for which identity and purity were established, have been structured into 3D-micro/nano-patterns using NIL. The cross-, square-, and circle-shaped columnar structures form a 3 × 3 mm arrangement with periodicity of 3 µm, 1 µm, 542 nm, and 506 nm. According to our findings, vinylferrocene-methyl methacrylate copolymers can be imprinted without further additives in NIL processes, which opens the way for redox-responsive 3D-nano/micro-objects and patterns via NIL to be explored in the future.
Keywords: copolymer; methyl methacrylate; reverse nanoimprint lithography; vinylferrocene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vinylferrocene homopolymer and copolymers: an electrochemical comparison.Anal Sci. 2008 Mar;24(3):339-43. doi: 10.2116/analsci.24.339. Anal Sci. 2008. PMID: 18332540
-
Patchy nanocapsules of poly(vinylferrocene)-based block copolymers for redox-responsive release.ACS Nano. 2012 Oct 23;6(10):9042-9. doi: 10.1021/nn3031589. Epub 2012 Oct 5. ACS Nano. 2012. PMID: 23020219
-
Nanoimprinted thin films of reactive, azlactone-containing polymers: combining methods for the topographic patterning of cell substrates with opportunities for facile post-fabrication chemical functionalization.Biomacromolecules. 2009 Apr 13;10(4):994-1003. doi: 10.1021/bm900045c. Biomacromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19290643 Free PMC article.
-
UV-nanoimprint lithography: structure, materials and fabrication of flexible molds.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013 May;13(5):3145-72. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2013.7437. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23858828 Review.
-
Interfacial Interactions during Demolding in Nanoimprint Lithography.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Mar 24;12(4):349. doi: 10.3390/mi12040349. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reversible Photo-Induced Reshaping of Imprinted Microstructures Using a Low Molecular Azo Dye.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jan 31;14(3):586. doi: 10.3390/polym14030586. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35160576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manners I. Polymer science with main group elements and transition metals. Macromol. Symp. 2003;196:57–62. doi: 10.1002/masy.200390176. - DOI
-
- Abd-El-Aziz A., Manners I. Neutral and Cationic Macromolecules based on Iron Sandwich Complexes. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2005;15:157–195.
-
- Gao Y., Shreeve J.M. Ferrocene-containing Liquid Crystalline Polymers. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2007;17:19–36. doi: 10.1007/s10904-006-9095-y. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

