Polymers and Plastics Modified Electrodes for Biosensors: A Review
- PMID: 32456314
- PMCID: PMC7287907
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25102446
Polymers and Plastics Modified Electrodes for Biosensors: A Review
Abstract
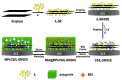
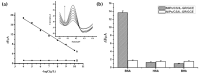
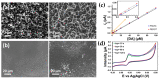
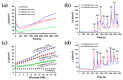
Polymer materials offer several advantages as supports of biosensing platforms in terms of flexibility, weight, conformability, portability, cost, disposability and scope for integration. The present study reviews the field of electrochemical biosensors fabricated on modified plastics and polymers, focusing the attention, in the first part, on modified conducting polymers to improve sensitivity, selectivity, biocompatibility and mechanical properties, whereas the second part is dedicated to modified "environmentally friendly" polymers to improve the electrical properties. These ecofriendly polymers are divided into three main classes: bioplastics made from natural sources, biodegradable plastics made from traditional petrochemicals and eco/recycled plastics, which are made from recycled plastic materials rather than from raw petrochemicals. Finally, flexible and wearable lab-on-a-chip (LOC) biosensing devices, based on plastic supports, are also discussed. This review is timely due to the significant advances achieved over the last few years in the area of electrochemical biosensors based on modified polymers and aims to direct the readers to emerging trends in this field.
Keywords: conducting polymers; flexible electrochemical biosensors; modified bioplastics; modified biopolymers; recyclable plastics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Flexible plastic, paper and textile lab-on-a chip platforms for electrochemical biosensing.Lab Chip. 2018 Jun 26;18(13):1812-1830. doi: 10.1039/c8lc00025e. Lab Chip. 2018. PMID: 29855637 Review.
-
The degradation of single-use plastics and commercially viable bioplastics in the environment: A review.Environ Res. 2023 Aug 15;231(Pt 1):115988. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115988. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37105296 Review.
-
Conducting polymer based electrochemical biosensors.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2016 Mar 28;18(12):8264-77. doi: 10.1039/c5cp06830d. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2016. PMID: 26948182
-
Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on redox polymer/carbon nanotube modified electrodes: a review.Anal Chim Acta. 2015 Jun 30;881:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.02.059. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Anal Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 26041516 Review.
-
Electrochemical sensors and biosensors using laser-derived graphene: A comprehensive review.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Nov 15;168:112565. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112565. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 32927277 Review.
Cited by
-
Biopolymers Used for Receptor Immobilization for Nickel-Detection Biosensors in Food.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Jul 30;14(8):1529. doi: 10.3390/mi14081529. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37630065 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of an Electrochemical Sensor and Nanocomposites: Toward the Electrocatalytic Detection of Neurotransmitters and Their Importance within the Physiological System.ACS Nanosci Au. 2022 Oct 28;3(1):1-27. doi: 10.1021/acsnanoscienceau.2c00039. eCollection 2023 Feb 15. ACS Nanosci Au. 2022. PMID: 37101467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electropolymerized 4-Aminobenzoic Acid Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Simultaneous Determination of Food Azo Dyes.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 11;14(24):5429. doi: 10.3390/polym14245429. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559795 Free PMC article.
-
Differential pulse voltammetry and chronoamperometry as analytical tools for epinephrine detection using a tyrosinase-based electrochemical biosensor.RSC Adv. 2022 Sep 6;12(39):25342-25353. doi: 10.1039/d2ra04045j. eCollection 2022 Sep 5. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36199318 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Medical Wearable Biosensors: Design, Fabrication and Materials Strategies in Healthcare Monitoring.Molecules. 2021 Dec 28;27(1):165. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010165. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011400 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang Y., Yang X., Tan Y., Yuan Q. Recent progress in flexible and wearable bio-electronics based on nanomaterials. Nano Res. 2017;10:1560–1583. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1476-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

