Crop Yield and Essential Oil Composition of Two Thymus vulgaris Chemotypes along Three Years of Organic Cultivation in a Hilly Area of Central Italy
- PMID: 34443694
- PMCID: PMC8398316
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26165109
Crop Yield and Essential Oil Composition of Two Thymus vulgaris Chemotypes along Three Years of Organic Cultivation in a Hilly Area of Central Italy
Abstract
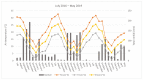
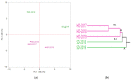
Thymus vulgaris L. is one of the most commonly used medicinal and aromatic plants (MAPs), owing to a range of therapeutic properties of its essential oil. Plant growth, biomass yield, essential oil content and composition are influenced by chemotype, environmental conditions, cultivation techniques and vegetative development. Since in MAPs cultivation special attention is paid on high quality of raw material, the adoption of sustainable agriculture methods is of pivotal importance. Therefore, we evaluated the agronomic and qualitative performances of two Thymus vulgaris L. chemotypes, organically cultivated under the Mediterranean climate of hilly lands of central Italy for three consecutive years (2017-2019). Along the trial, total above-ground dry biomass significantly increased from the 1st to 3rd year after planting and large variations in the main biological, biometric and productive traits were observed between the two chemotypes. The 'thymol' chemotype EO obviously showed thymol as the major constituent (51.26-49.87%) followed by γ-terpinene and p-cymene. The 'linalool' chemotype EO showed high percentages of oxygenated monoterpenes (about 90%) with linalool (75%), linalyl acetate (8.15%) and b-caryophyllene (3.2%) as main constituents. This study highlighted that T. vulgaris can be successfully organically grown in the hilly lands of Tuscany, with interesting biomass and essential oil yields, even though the plants were in the initial years of crop establishment (start in 2017). The introduction of this species into organic cultivation systems could contribute to obtain high-quality raw material, as well as to enhance crop rotation diversification, which is of pivotal importance in the management of organic farms.
Keywords: chemotypes; crop age; harvest time; linalool; organic cultivation; thymol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Essential oil polymorphism of wild growing Hungarian thyme (Thymus pannonicus) populations in the Carpathian Basin.Nat Prod Commun. 2010 Oct;5(10):1681-6. Nat Prod Commun. 2010. PMID: 21121273
-
Qualitative and quantitative variation in monoterpene co-occurrence and composition in the essential oil of Thymus vulgaris chemotypes.J Chem Ecol. 2003 Apr;29(4):859-80. doi: 10.1023/a:1022927615442. J Chem Ecol. 2003. PMID: 12775148
-
Composition of headspace volatiles and essential oils of three Thymus species.Nat Prod Commun. 2014 Nov;9(11):1609-12. Nat Prod Commun. 2014. PMID: 25532293
-
Thymol, thyme, and other plant sources: Health and potential uses.Phytother Res. 2018 Sep;32(9):1688-1706. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6109. Epub 2018 May 22. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 29785774 Review.
-
The Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Essential Oil from Korean Native Thyme Bak-Ri-Hyang (Thymus quinquecostatus Celak.).Molecules. 2022 Jul 1;27(13):4251. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134251. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Anti-Enzymatic Activities, and In Vitro Insecticidal Potential of Origanum compactum (Benth.) Essential Oils.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;13(17):2424. doi: 10.3390/plants13172424. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273908 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "Natural Plant Substances-Structural and Application Aspects: A Theme Issue in Honor of Professor Wieslaw Oleszek".Molecules. 2022 May 26;27(11):3430. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113430. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684367 Free PMC article.
-
Agronomic Evaluation and Chemical Characterization of Lavandula latifolia Medik. under the Semiarid Conditions of the Spanish Southeast.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 15;12(10):1986. doi: 10.3390/plants12101986. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653903 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing Plant's Arsenal: Essential Oils as Promising Tools for Sustainable Management of Potato Late Blight Disease Caused by Phytophthora infestans-A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2023 Oct 27;28(21):7302. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217302. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Thymus vulgaris, Origanum vulgare, Satureja montana and Their Mixture against Clinical Isolates Responsible for Canine Otitis Externa.Vet Sci. 2023 Jan 1;10(1):30. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10010030. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36669031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tohidi B., Rahimmalek M., Trindade H. Review on essential oil, extracts composition, molecular and phytochemical properties of Thymus species in Iran. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019;134:89–99. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.02.038. - DOI
-
- Torras J., Grau M.D., López J.F., Heras F.X.C.D.L. Analysis of essential oils from chemotypes of Thymus vulgaris in Catalonia. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007;87:2327–2333. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2995. - DOI
-
- Granger R., Passet J. Thymus vulgaris spontane de France: Races chimiques et chemotaxonomie. Phytochemistry. 1973;12:1683–1691. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(73)80388-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

