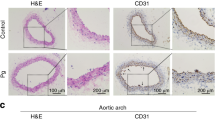
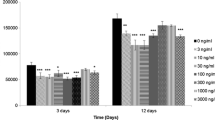
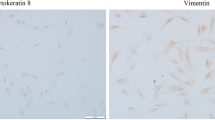
Abstract
Porphyromonas gingivalis is a major periodontal pathogen. The lipopolysaccharide (LPS) secreted fromP. gingivalis is implicated in the initiation and progression of periodontitis. Aberrant angiogenesis is often associated with lesion formation in chronic periodontitis. In this study, we report thatP. gingivalis LPS activates angiogenic cascade, migration, invasion and tube formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Furthermore,P. gingivalis LPS potently stimulatedin vivo neovascularization in chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) and the mouse Matrigel plug assay.P. gingivalis LPS had no effect on the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) or its receptor, Flk-1, implying thatP. gingivalis LPS-induced angiogenesis may result from its direct action on endothelial cells.P. gingivalis LPS evoked activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK1/2 in HUVECs, which is closely linked to angiogenesis. Taken together, these results strongly suggestP. gingivalis LPS plays an important role in the pathological angiogenesis for periodontal diseases, such as periodontitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amar, S. and Han, X., The impact of periodontal infection on systemic diseases.Med. Sci. Monit, 9, RA291–9 (2003).
Beck, J., Garcia, R., Heiss, G, Vokonas, P. S., and Offenbacher, S., Periodontal disease and cardiovascular disease.J. Periodontol., 67, 1123–1137 (1996).
Booth, V., Young, S., Cruchley, A., Taichman, N. S., and Paleolog, E., Vascular endothelial growth factor in human periodontal disease.J. Periodontal. Res., 33, 491–499 (1998).
Bussolino, R, Mantovani, A., and Persico, G, Molecular mechanisms of blood vessel formation.Trends Biochem. Sci., 22, 251–256 (1997).
Carmeliet, P. and Jain, R. K., Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases.Nature, 407, 249–257 (2000).
Chiu, B., Multiple infections in carotid atherosclerotic plaques.Am. Heart J., 138, S534–6 (1999).
Egelberg, J., The blood vessels of the dento-gingival junction.J. Periodontal. Res., 1, 163–179 (1966).
Faure, E., Equils, O., Sieling, P. A., Thomas, L., Zhang, F. X., Kirschning, C. J., Polentarutti, N., Muzio, M., and Arditi, M., Bacterial lipopolysaccharide activates NF-kappaB through toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) in cultured human dermal endothelial cells. Differential expression of TLR-4 and TLR-2 in endothelial cells.J. Biol. Chem., 275, 11058–11063 (2000).
Folkman, J., How is blood vessel growth regulated in normal and neoplastic tissue? G.H.A. Clowes Memorial Award Lecture.Cancer Res., 46, 467–473 (1986).
Harmey, J. H., Bucana, C. D., Lu, W., Byrne, A. M., McDonnell, S., Lynch, C., Bouchier-Hayes, D., and Dong, Z., Lipopoly-saccharide-induced metastatic growth is associated with increased angiogenesis, vascular permeability and tumor cell invasion.Int. J. Cancer, 101, 415–422 (2002).
Johnson, R. B., Serio, F. G, and Dai, X., Vascular endothelial growth factors and progression of periodontal diseases.J. Periodontol., 70, 848–852 (1999).
Kim, M. S., Kwon, H. J., Lee, Y. M., Baek, J. H., Jang, J. E., Lee, S. W., Moon, E. J., Kim, H. S., Lee, S. K. and Chung, H. Y., Kim, C. W., and Kim, K. W., Histone deacetylases induce angiogenesis by negative regulation of tumor suppressor genes.Nat. Med., 7, 437–443 (2001).
Kim, Y. M., Kim, Y. M., Lee, Y. M., Kim, H. S., Kim, J. D., Choi, Y., Kim, K. W., Lee, S. Y, and Kwon, Y. G., TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE) induces angiogenesis through the activation of Src and phospholipase C (PLC) in human endothelial cells.J. Biol. Chem., 277, 6799–6805 (2002).
Kuzuya, M., Satake, S., Ramos, M. A., Kanda, S., Koike, T., Yoshino, K., Ikeda, S., and Iguchi, A., Induction of apoptotic cell death in vascular endothelial cells cultured in three- dimensional collagen lattice.Exp. Cell Res., 248, 498–508 (1999).
Lee, M. S., Moon, E. J., Lee, S. W., Kim, M. S., Kim, K. W., and Kim, Y. J., Angiogenic activity of pyruvic acid inin vivo and in vitro angiogenesis models.Cancer Res., 61, 3290–3293 (2001).
Leibovich, S. J., Chen, J. R, Pinhal-Enfield, G., Belem, P. C., Elson, G., Rosania, A., Ramanathan, M., Montesinos, C., Jacobson, M., Schwarzschild, M. A., Fink, J. S., and Cronstein, B., Synergistic up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in murine macrophages by adenosine A(2A) receptor agonists and endotoxin.Am. J. Pathol., 160, 2231–2244 (2002).
Li, A., Dubey, S., Varney, M. L., Dave, B. J., and Singh, R. K., IL- 8 directly enhanced endothelial cell survival, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinases production and regulated angiogenesis.J. Immunol., 170, 3369–3376 (2003).
Mattsby-Baltzer, I., Jakobsson, A., Sorbo, J., and Norrby, K., Endotoxin is angiogenic.Int. J. Exp. Pathol., 75, 191–196 (1994).
Medzhitov, R., Preston-Hurlburt, P., Kopp, E., Stadlen, A., Chen, C., Ghosh, S., and Janeway, C. A., Jr., MyD88 is an adaptor protein in the hToll/IL-1 receptor family signaling pathways.Mol. Cell, 2, 253–258 (1998).
Muzio, M., Natoli, G, Saccani, S., Levrero, M., and Mantovani, A., The human toll signaling pathway: divergence of nuclear factor kappaB and JNK/SAPK activation upstream of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6).J. Exp. Med., 187, 2097–2101 (1998).
Offenbacher, S., Periodontal diseases: pathogenesis.Ann. Periodontol., 1, 821–878 (1996).
Pidgeon, G. P., Harmey, J. H., Kay, E., Da Costa, M., Redmond, H. P., and Bouchier-Hayes, D. J., The role of endotoxin/ lipopolysaccharide in surgically induced tumour growth in a murine model of metastatic disease.Br. J. Cancer, 81, 1311- 1317 (1999).
Pollet, I., Opina, C. J., Zimmerman, C., Leong, K. G, Wong, F., and Karsan, A., Bacterial lipopolysaccharide directly induces angiogenesis through TRAF6-mediated activation of NF- kappaB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase.Blood, 102, 1740–1742 (2003).
Polverini, P. J., The pathophysiology of angiogenesis.Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med., 6, 230–247 (1995).
Slots, J. and Genco, R. J., Black-pigmented bacteroides species, capnocytophaga species, and actinobacillus actinomycetem-comitans in human periodontal disease: virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction.J. Dent. Res., 63, 412–421 (1984).
Slots, J. and Ting, M., Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and porphyromonas gingivalis in human periodontal disease: occurrence and treatment.Periodontol., 2000 20, 82–121 (1999).
Suthin, K., Matsushita, K., Machigashira, M., Tatsuyama, S., Imamura, T, Torii, M., and Izumi, Y, Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor by periodontal pathogens in gingival fibroblasts.J. Periodontal. Res., 38, 90–96 (2003).
Tobias, P. S., Gegner, J., Tapping, R., Orr, S., Mathison, J., Lee, J. D., Kravchenko, V, Han, J., and Ulevitch, R. J., Lipopoly-saccharide dependent cellular activation.J. Periodontal. Res., 32, 99–103 (1997).
van der Wal, A. C. and Becker, A. E., Atherosclerotic plaque rupture-pathologic basis of plaque stability and instability.Cardiovasc. Res., 41, 334–344 (1999).
Wang, P. L. and Ohura, K., Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopoly- saccharide signaling in gingival fibroblasts-CD14 and toll-like receptors.Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med., 13, 132–142 (2002).
Yu, Y. and Sato, J. D., MAP kinases, phosphatidylinositol 3- Kinase, and p70 S6 kinase mediate the mitogenic response of human endothelial cells to vascular endothelial growth factor.J. Cell. Physiol., 178, 235–246 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koo, T.H., Jun, H.O., Bae, SK. et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis, Periodontal pathogen, lipopolysaccharide induces angiogenesisvia extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation in human vascular endothelial cells. Arch Pharm Res 30, 34–42 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977776
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977776