Abstract
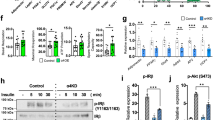
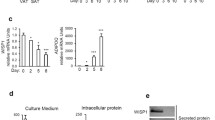
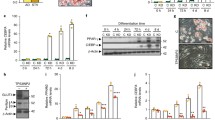
WIP1, as a critical phosphatase, plays many important roles in various physiological and pathological processes through dephosphorylating different substrate proteins. However, the functions of WIP1 in adipogenesis and fat accumulation are not clear. Here, we report that WIP1-deficient mice show impaired body weight growth, dramatically decreased fat mass, and significantly reduced triglyceride and leptin levels in circulation. This dysregulation of adipose development caused by the deletion of WIP1 occurs as early as adipogenesis. In contrast, lentivirus-mediated WIP1 phosphatase overexpression significantly increases the adipogenesis of pre-adipocytes via an enzymatic activity-dependent mechanism. PPARγ is a master gene of adipogenesis, and the phosphorylation of PPARγ at serine 112 strongly inhibits adipogenesis; however, very little is known about the negative regulation of this phosphorylation. Here, we show that WIP1 phosphatase plays a pro-adipogenic role by interacting directly with PPARγ and dephosphorylating p-PPARγ S112 in vitro and in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- aP2:
-
Adipocyte protein 2
- C/EBP:
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PPAR:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- WIP1:
-
Wildtpye p53-induced phosphatase 1
References
Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS, Marks JS (2003) Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. Jama 289(1):76–79
Bray GA, Bellanger T (2006) Epidemiology, trends, and morbidities of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Endocr 29(1):109–117. doi:10.1385/ENDO:29:1:109
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM (2014) What we talk about when we talk about fat. Cell 156(1–2):20–44. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.012
Tang QQ, Lane MD (2012) Adipogenesis: from stem cell to adipocyte. Annu Rev Biochem 81:715–736. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-052110-115718
Willson TM, Lambert MH, Kliewer SA (2001) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and metabolic disease. Annu Rev Biochem 70:341–367. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.341
Lefterova MI, Haakonsson AK, Lazar MA, Mandrup S (2014) PPARgamma and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond. Trends Endocrinol Metabol TEM 25 (6):293–302. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2014.04.001
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Spiegelman BM (1994) Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR gamma 2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell 79(7):1147–1156
Imai T, Takakuwa R, Marchand S, Dentz E, Bornert JM, Messaddeq N, Wendling O, Mark M, Desvergne B, Wahli W, Chambon P, Metzger D (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is required in mature white and brown adipocytes for their survival in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(13):4543–4547. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400356101
Floyd ZE, Stephens JM (2012) Controlling a master switch of adipocyte development and insulin sensitivity: covalent modifications of PPARgamma. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822(7):1090–1095. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.03.014
Choi JH, Banks AS, Estall JL, Kajimura S, Bostrom P, Laznik D, Ruas JL, Chalmers MJ, Kamenecka TM, Bluher M, Griffin PR, Spiegelman BM (2010) Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARgamma by Cdk5. Nature 466(7305):451–456. doi:10.1038/nature09291
Choi JH, Banks AS, Kamenecka TM, Busby SA, Chalmers MJ, Kumar N, Kuruvilla DS, Shin Y, He Y, Bruning JB, Marciano DP, Cameron MD, Laznik D, Jurczak MJ, Schurer SC, Vidovic D, Shulman GI, Spiegelman BM, Griffin PR (2011) Antidiabetic actions of a non-agonist PPARgamma ligand blocking Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation. Nature 477(7365):477–481. doi:10.1038/nature10383
Hu E, Kim JB, Sarraf P, Spiegelman BM (1996) Inhibition of adipogenesis through MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation of PPARgamma. Science 274(5295):2100–2103
Rangwala SM, Rhoades B, Shapiro JS, Rich AS, Kim JK, Shulman GI, Kaestner KH, Lazar MA (2003) Genetic modulation of PPARgamma phosphorylation regulates insulin sensitivity. Dev Cell 5(4):657–663
Hinds TD Jr, Stechschulte LA, Cash HA, Whisler D, Banerjee A, Yong W, Khuder SS, Kaw MK, Shou W, Najjar SM, Sanchez ER (2011) Protein phosphatase 5 mediates lipid metabolism through reciprocal control of glucocorticoid receptor and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma). J Biol Chem 286(50):42911–42922. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.311662
Grankvist N, Honkanen RE, Sjoholm A, Ortsater H (2013) Genetic disruption of protein phosphatase 5 in mice prevents high-fat diet feeding-induced weight gain. FEBS Lett 587 (23):3869–3874. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.10.022
Jacob W, Rosenzweig D, Vazquez-Martin C, Duce SL, Cohen PT (2015) Decreased adipogenesis and adipose tissue in mice with inactivated protein phosphatase 5. Biochem J 466(1):163–176. doi:10.1042/BJ20140428
Zhu YH, Bulavin DV (2012) Wip1-dependent signaling pathways in health and diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 106:307–325. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-396456-4.00001-8
Lowe J, Cha H, Lee MO, Mazur SJ, Appella E, Fornace AJ Jr (2012) Regulation of the Wip1 phosphatase and its effects on the stress response. Frontiers in bioscience 17:1480–1498
Yi W, Hu X, Chen Z, Liu L, Tian Y, Chen H, Cong YS, Yang F, Zhang L, Rudolph KL, Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Ju Z (2015) Phosphatase Wip1 controls antigen-independent B-cell development in a p53-dependent manner. Blood 126(5):620–628. doi:10.1182/blood-2015-02-624114
Zhu Y, Demidov ON, Goh AM, Virshup DM, Lane DP, Bulavin DV (2014) Phosphatase WIP1 regulates adult neurogenesis and WNT signaling during aging. J Clin Invest 124(7):3263–3273. doi:10.1172/JCI73015
Ruark E, Snape K, Humburg P, Loveday C, Bajrami I, Brough R, Rodrigues DN, Renwick A, Seal S, Ramsay E, Duarte Sdel V, Rivas MA, Warren-Perry M, Zachariou A, Campion-Flora A, Hanks S, Murray A, Ansari Pour N, Douglas J, Gregory L, Rimmer A, Walker NM, Yang TP, Adlard JW, Barwell J, Berg J, Brady AF, Brewer C, Brice G, Chapman C, Cook J, Davidson R, Donaldson A, Douglas F, Eccles D, Evans DG, Greenhalgh L, Henderson A, Izatt L, Kumar A, Lalloo F, Miedzybrodzka Z, Morrison PJ, Paterson J, Porteous M, Rogers MT, Shanley S, Walker L, Gore M, Houlston R, Brown MA, Caufield MJ, Deloukas P, McCarthy MI, Todd JA, Breast, Ovarian Cancer Susceptibility C, Wellcome Trust Case Control C, Turnbull C, Reis-Filho JS, Ashworth A, Antoniou AC, Lord CJ, Donnelly P, Rahman N (2013) Mosaic PPM1D mutations are associated with predisposition to breast and ovarian cancer. Nature 493 (7432):406–410. doi:10.1038/nature11725
Filipponi D, Muller J, Emelyanov A, Bulavin DV (2013) Wip1 controls global heterochromatin silencing via ATM/BRCA1-dependent DNA methylation. Cancer cell 24(4):528–541. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2013.08.022
Chew J, Biswas S, Shreeram S, Humaidi M, Wong ET, Dhillion MK, Teo H, Hazra A, Fang CC, Lopez-Collazo E, Bulavin DV, Tergaonkar V (2009) WIP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB signalling. Nat Cell Biol 11(5):659–666. doi:10.1038/ncb1873
Lu X, Ma O, Nguyen TA, Jones SN, Oren M, Donehower LA (2007) The Wip1 Phosphatase acts as a gatekeeper in the p53-Mdm2 autoregulatory loop. Cancer cell 12(4):342–354. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2007.08.033
Zhang L, Liu L, He Z, Li G, Liu J, Song Z, Jin H, Rudolph KL, Yang H, Mao Y, Zhang L, Zhang H, Xiao Z, Ju Z (2015) Inhibition of wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 promotes liver regeneration in mice by direct activation of mammalian _target of rapamycin. Hepatology 61(6):2030–2041. doi:10.1002/hep.27755
Le Guezennec X, Brichkina A, Huang YF, Kostromina E, Han W, Bulavin DV (2012) Wip1-dependent regulation of autophagy, obesity, and atherosclerosis. Cell Metab 16(1):68–80. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.06.003
Choi J, Nannenga B, Demidov ON, BulavIN DV, Cooney A, Brayton C, Zhang Y, Mbawuike IN, Bradley A, Appella E, Donehower LA (2002) Mice deficient for the wild-type p53-induced phosphatase gene (Wip1) exhibit defects in reproductive organs, immune function, and cell cycle control. Mol Cell Biol 22(4):1094–1105
Zhu YH, Zhang CW, Lu L, Demidov ON, Sun L, Yang L, Bulavin DV, Xiao ZC (2009) Wip1 regulates the generation of new neural cells in the adult olfactory bulb through p53-dependent cell cycle control. Stem cells 27(6):1433–1442. doi:10.1002/stem.65
Sun S, Guo Z, Xiao X, Liu B, Liu X, Tang PH, Mao N (2003) Isolation of mouse marrow mesenchymal progenitors by a novel and reliable method. Stem cells 21(5):527–535. doi:10.1634/stemcells.21-5-527
Shreeram S, Demidov ON, Hee WK, Yamaguchi H, Onishi N, Kek C, Timofeev ON, Dudgeon C, Fornace AJ, Anderson CW, Minami Y, Appella E, Bulavin DV (2006) Wip1 phosphatase modulates ATM-dependent signaling pathways. Mol Cell 23(5):757–764. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.07.010
Rosen ED, MacDougald OA (2006) Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7 (12):885–896. doi:10.1038/nrm2066
Barsh GS, Schwartz MW (2002) Genetic approaches to studying energy balance: perception and integration. Nat Rev Genet 3(8):589-600. doi:10.1038/nrg862
Armata HL, Chamberland S, Watts L, Ko HJ, Lee Y, Jung DY, Kim JK, Sluss HK (2015) Deficiency of the tumor promoter gene wip1 induces insulin resistance. Molecular endocrinology 29(1):28–39. doi:10.1210/me.2014-1136
Acknowledgements
We greatly appreciate Dr. Zhi-Cheng Xiao for providing WIP1 KO mice strain, Dr. Kai Gao (Institute of Laboratory Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences) for providing technical assistance in MRI assay, and the couple of Dr. Ming Shi and Dr. Dan Liu for providing technical supports in molecular biology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by Chinese National Basic Research Development Program (No. 2011CB910802) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31401000 and 81430044).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Zhang, L., Xu, L. et al. WIP1 phosphatase is a critical regulator of adipogenesis through dephosphorylating PPARγ serine 112. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 74, 2067–2079 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2450-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2450-4