Abstract
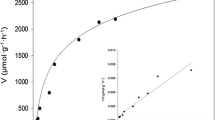
Most yeast hexose transporters studied so far at the molecular level mediate facilitated diffusion of glucose and fructose. Here, we report that a novel Kluyveromyces lactis gene, FRT1, encodes a proton-coupled fructose-uptake transporter. Frt1, when expressed in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae hxt null mutant strain that is unable to take up monosaccharides, restored growth on fructose. Determination of substrate specificities and kinetic parameters revealed Frt1 as a fructose transporter with a K m of 0.16±0.02 mM. Uptake of fructose was accompanied by an initial alkalization of the medium, indicating a proton-coupled uptake mechanism. Deletion of the FRT1 gene in a K. lactis strain already deleted for its RAG1 and HGT1 hexose transporter genes completely prevented uptake of and growth with fructose but not with glucose. Kinetic parameters of Frt1 in K. lactis, as assessed in a rag1 hgt1 mutant strain, were comparable with those obtained after heterologous expression in S. cerevisiae. Transcription of the FRT1 gene, which was undetectable when cells were grown in ethanol, was induced by various sugars. Our results indicate that, unlike S. cerevisiae, K. lactis exhibits proton symport systems for the uptake of hexoses, in addition to their facilitated diffusion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker L, Kühn C, Weise A, Schulz A, Gebhardt C, Hirner B, Hellmann H (2000) SUT2, a putative sucrose sensor in sieve elements. Plant Cell 12:1153–1164
Betina S, Goffrini P, Ferrero I, Wésolowski-Louvel M (2001) RAG4 gene encodes a glucose sensor in Kluyveromyces lactis. Genetics 158:541–548
Billard P, Menart S, Blaisonneau J, Bolotin-Fukuhara M, Fukuhara H, Wésolowski-Louvel M (1996) Glucose uptake in Kluyveromyces lactis: role of the HGT1 gene in glucose transport. J Bacteriol 178:5860–5866
Birnboim HC, Doly J (1979) A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 7:1513–1523
Boles E, Hollenberg CP (1997) The molecular genetics of hexose transport in yeasts. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:85–111
Boles E, Zimmermann FK (1993) Saccharomyces cerevisiae phosphoglucose isomerase and fructose bisphosphate aldolase can be replaced functionally by the corresponding enzymes of Escherichia coli and Drosophila melanogaster. Curr Genet 23:187–191
Breunig KD, Kuger P (1987) Functional homology between the yeast regulatory proteins GAL4 and LAC9: LAC9-mediated transcriptional activation in Kluyveromyces lactis involves protein binding to a regulatory sequence homologous to the GAL4 protein-binding site. Mol Cell Biol 7:4400–4406
Breunig KD, Bolotin-Fukuhara M, Bianchi MM, Bourgarel D, Falcone C, Ferrero II, Frontali L, Goffrini P, Krijger JJ, Mazzoni C, Milkowski C, Steensma HY, Wésolowski-Louvel M, Zeeman AM (2000) Regulation of primary carbon metabolism in Kluyveromyces lactis. Enzyme Microb Technol 26:771–780
Chen XJ, Wésolowski-Louvel M, Fukuhara H (1992) Glucose transport in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. II. Transcriptional regulation of the glucose transporter gene RAG1. Mol Gen Genet 233:97–105
De Deken RH (1966) The Crabtree effect: a regulatory system in yeast. J Gen Microbiol 44:149–156
Fan J, Chaturvedi V, Shen SH (2002) Identification and phylogenetic analysis of a glucose transporter gene family from the human pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. J Mol Evol 55:336–346
Gietz RD, Sugino A (1988) New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene 74:527–534
Gietz D, St Jean A, Woods RA, Schiestl RH (1992) Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res 20:1425
Goffrini P, Algeri AA, Donnini C, Wésolowski-Louvel M, Ferrero I (1989) RAG1 and RAG2: nuclear genes involved in the dependence/independence on mitochondrial respiratory function for growth on sugars. Yeast 5:99–106
Goncalves P, Rodrigues de Sousa H, Spencer-Martins I (2000) FSY1, a novel gene encoding a specific fructose/H(+) symporter in the type strain of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. J Bacteriol 182:5628–5630
Güldener U, Heck S, Fiedler T, Beinhauer J, Hegemann JH (1996) A new efficient gene disruption cassette for repeated use in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 24:2519–2524
Hamacher T, Becker J, Gárdonyi M, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Boles E (2002) Characterization of the xylose-transporting properties of yeast hexose transporters and their influence on xylose utilization. Microbiology 148:2783–2788
Heiland S, Radovanovic N, Höfer M, Winderickx J, Lichtenberg H (2000) Multiple hexose transporters of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Bacteriol 182:2153–2162
Hofmann K, Bucher P, Falquet L, Bairoch A (1999) The PROSITE database, its status in 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27:215–219
Maier A, Völker B, Boles E, Fuhrmann GF (2002) Characterisation of glucose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with plasma membrane vesicles (countertransport) and intact cells (initial uptake) with single Hxt1, Hxt2, Hxt3, Hxt4, Hxt6, Hxt7 or Gal2 transporters. FEMS Yeast Res 2:539–550
Marger MD, Saier MH (1993) A major superfamily of transmembrane facilitators that catalyse uniport, symport and antiport. Trends Biochem Sci 18:13–20
Milkowski C, Krampe S, Weirich J, Hasse V, Boles E, Breunig KD (2001) Feedback regulation of glucose transporter gene transcription in Kluyveromyces lactis by glucose uptake. J Bacteriol 183:5223–5229
Mulder W, Scholten IH, Boer RW de, Grivell LA (1994) Sequence of the HAP3 transcription factor of Kluyveromyces lactis predicts the presence of a novel 4-cysteine zinc-finger motif. Mol Gen Genet 245:96–106
Reifenberger E, Boles E, Ciriacy M (1997) Kinetic characterization of individual hexose transporters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their relation to the triggering mechanisms of glucose repression. Eur J Biochem 245:324–333
Riesmeier JW, Willmitzer L, Frommer WB (1992). Isolation and characterization of a sucrose carrier cDNA from spinach by functional expression in yeast. EMBO J 11:4705–4713
Riley MI, Sreekrishna K, Bhairi S, Dickson RC (1987) Isolation and characterization of mutants of Kluyveromyces lactis defective in lactose transport. Mol Gen Genet 208:145–151
Rothstein RJ (1983) One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol 101:202–211
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Souciet J, Aigle M, Artiguenave F, Blandin G, Bolotin-Fukuhara M, Bon E, Brottier P, Casaregola S, Montigny J de, Dujon B, Durrens P, Gaillardin C, Lepingle A, Llorente B, Malpertuy A, Neuveglise C, Ozier-Kalogeropoulos O, Potier S, Saurin W, Tekaia F, Toffano-Nioche C, Wesolowski-Louvel M, Wincker P, Weissenbach J (2000) Genomic exploration of the hemiascomycetous yeasts: 1. A set of yeast species for molecular evolution studies. FEBS Lett 487:3–12
Urk H van, Postma E, Scheffers WA, Dijken JP van (1989) Glucose transport in Crabtree-positive and Crabtree-negative yeasts. J Gen Microbiol 135:2399–2406
Varma A, Singh BB, Karnani N, Lichtenberg-Frate H, Höfer M, Magee BB, Prasad R (2000) Molecular cloning and functional characterisation of a glucose transporter, CaHGT1, of Candida albicans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 182:15–21
Weierstall T, Hollenberg CP, Boles E (1999) Cloning and characterization of three genes (SUT1–3) encoding glucose transporters of the yeast Pichia stipitis. Mol Microbiol 31:871–883
Weirich J, Goffrini P, Kuger P, Ferrero I, Breunig KD (1997) Influence of mutations in hexose-transporter genes on glucose repression in Kluyveromyces lactis. Eur J Biochem 249:248–257
Wésolowski-Louvel M, Goffrini P, Ferrero I, Fukuhara H (1992) Glucose transport in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. I. Properties of an inducible low-affinity glucose transporter gene. Mol Gen Genet 233:89–96
Wieczorke R, Krampe S, Weierstall T, Freidel K, Hollenberg CP, Boles E (1999) Concurrent knock-out of at least 20 transporter genes is required to block uptake of hexoses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 464:123–128
Wood V, Gwilliam R, Rajandream MA, Lyne M, Lyne R, Stewart A, et al (2002) The genome sequence of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nature 415:871–880
Zimmermann FK (1975) Procedures used in the induction of mitotic recombination and mutation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat Res 31:71–86
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank C.P. Hollenberg for his kind support. We wish to thank K. Breunig, M. Wésolowski-Louvel and W. Frommer for the provision of yeast strains and plasmids. This work was supported by a grant from the European Commission (QLK3-CT-2001-00533, EFFEXPORT project) to E.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diezemann, A., Boles, E. Functional characterization of the Frt1 sugar transporter and of fructose uptake in Kluyveromyces lactis . Curr Genet 43, 281–288 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-003-0392-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-003-0392-5