Abstract
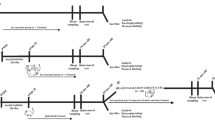
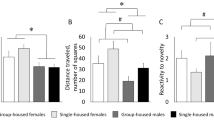
The present study was designed to investigate the modulation of the stress responses by the environmental conditions and its putative neurobiological mechanisms. For that an integrative study on the effects of environmental enrichment and isolation housing on (1) the corticosterone, dopamine and acetylcholine responses to acute restraint stress in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of the awake rat; (2) the mRNA levels of glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) in the PFC, and (3) the behavioral responses to stress, related to the PFC (habituation to a novel environment, spatial-working memory and inhibitory avoidance response) was performed. Male Wistar rats were maintained from 3 to 6 months of age in two different conditions: enriched (EC) or impoverished (IC). Animals were stereotaxically implanted with bilateral guide cannulae in the PFC to perform microdialysis experiments to evaluate the concentrations of corticosterone, dopamine and acetylcholine. EC animals showed lower increases of corticosterone and dopamine but not of acetylcholine than IC animals in the PFC in response to acute restraint stress (20 min). In the PFC, GR mRNA levels showed a trend towards an enhancement in EC animals. EC reduced the days to learn the spatial working memory task (radial-water maze). Spatial working memory, however, was not different between groups in either basal or stress conditions. Inhibitory avoidance response was reduced in EC rats. The changes produced by EC in the neurochemical, neuroendocrine and behavioral parameters evaluated suggest that EC rats could show a better coping during an acute stress challenge.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EC:
-
Environmental enrichment conditions
- GRs:
-
Glucocorticoid receptors
- IC:
-
Impoverished conditions
- NS:
-
Non significant
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
References
Abercrombie ED, Keefe KA, DiFrischia DS, Zigmond MJ (1989) Differential effect of stress on in vivo dopamine release in striatum, nucleus accumbens, and medial frontal cortex. J Neurochem 52:1655–1658
Ago Y, Arikawa S, Yata M, Yano K, Abe M, Takuma K, Matsuda T (2009) Role of prefrontal dopaminergic neurotransmission in glucocorticoid receptor-mediated modulation of methamphetamine-induced hyperactivity. Synapse 63:7–14
Amat J, Baratta MV, Paul E, Bland ST, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2005) Medial prefrontal cortex determines how stressor controllability affects behavior and dorsal raphe nucleus. Nat Neurosci 8:365–371
Antoni FA (1986) Hypothalamic control of adrenocorticotropin secretion: advances since the discovery of 41-residue corticotropin-releasing factor. Endocr Rev 7:351–378
Arnsten AFT, Goldman-Rakic PS (1998) Noise stress impairs prefrontal cortical cognitive function in monkeys: evidence for a hyperdopaminergic mechanism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55:362–368
Barsegyan A, Mackenzie SM, Kurose BD, McGaugh JL, Roozendaal B (2010) Glucocorticoids in the prefrontal cortex enhance memory consolidation and impair working memory by a common neural mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:16655–16660
Berridge CW, Mitton E, Clark W, Roth RH (1999) Engagement in a non-escape (displacement) behavior elicits a selective and lateralized suppression of frontal cortical dopaminergic utilization in stress. Synapse 32:187–197
Bimonte HA, Nelson ME, Granholm A-CE (2003) Age-related deficits as working memory load increases: relationships with growth factors. Neurobiol Aging 24:37–48
Birrell JM, Brown VJ (2000) Medial frontal cortex mediates perceptual attentional set shifting in the rat. J Neurosci 20:4320–4324
Bland ST, Hargrave D, Pepin JL, Amat J, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2003) Stressor controllability modulates stress-induced dopamine and serotonin efflux and morphine-induced serotonin efflux in the medial prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1589–1596
Bruce SM (2000) The neurobiology of stress: from serendipity to clinical relevance. Brain Res 886:172–189
Butts KA, Weinberg J, Young AH, Phillips AG (2011) Glucocorticoid receptors in the prefrontal cortex regulate stress-evoked dopamine efflux and aspects of executive function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:18459–18464
Carlson JN, Fitzgerald LW, Keller RW Jr, Glick SD (1993) Lateralized changes in prefrontal cortical dopamine activity induced by controllable and uncontrollable stress in the rat. Brain Res 630:178–187
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Coco ML, Weiss JM (2005) Neural substrates of coping behavior in the rat: possible importance of mesocorticolimbic dopamine system. Behav Neurosci 119:429–445
Croft AP, O’Callaghan MJ, Shaw SG, Connolly G, Jacquot C, Little HJ (2008) Effects of minor laboratory procedures, adrenalectomy, social defeat or acute alcohol on regional brain concentrations of corticosterone. Brain Res 1238:12–22
Cullinan WE, Herman JP, Battaglia DF, Akil H, Watson SJ (1995) Pattern and time course of immediate early gene expression in rat brain following acute stress. Neuroscience 64:477–505
Davis M, Hithcock JM, Bowers MB, Berridge CW, Melia KR, Roth RH (1994) Stress-induced activation of prefrontal cortex dopamine turnover: blockade by lesions of the amygdala. Brain Res 664:207–210
Day JC, Kornecook TJ, Quirion R (2001) Application of in vivo microdialysis to the study of cholinergic systems. Methods 23:21–39
Del Arco A, Mora F (2002) NMDA and AMPA/kainate glutamatergic agonists increase the extracellular concentrations of GABA in the prefrontal cortex of the freely moving rat: modulation by endogenous dopamine. Brain Res Bull 57:623–630
Del Arco A, Segovia G, Garrido P, de Blas M, Mora F (2007) Stress, prefrontal cortex and environmental enrichment: studies on dopamine and acetylcholine release and working memory performance in rats. Behav Brain Res 176:267–273
Diamond DM, Fleshner M, Ingersoll N, Rose GM (1996) Psychological stress impairs spatial working memory: relevance to electrophysiological studies of hippocampal function. Behav Neurosci 110:661–672
Diamond DM, Park CR, Heman KL, Rose GM (1999) Exposing rats to a predator impairs spatial working memory in the radial arm water maze. Hippocampus 9:542–552
Diorio D, Viau V, Meaney MJ (1993) The role of the medial prefrontal cortex (cingulate gyrus) in the regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. J Neurosci 13:3839–3847
Droste SK, Collins A, Lightman SL, Linthorst ACE, Reul JMHM (2009) Distinct, time-dependent effects of voluntary exercise on circadian and ultradian rhythms and stress responses of free corticosterone in the rat hippocampus. Endocrinology 150:4170–4179
Elliott BM, Grunberg NE (2005) Effects of social and physical enrichment on open field activity differ in male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. Behav Brain Res 165:187–196
Feenstra MG, Botterblom MH, van Uum JF (1995) Novelty-induced increase in dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex in vivo: inhibition by diazepam. Neurosci Lett 189:81–84
Fernández-Teruel A, Escorihuela RM, Castellano B, González B, Tobeña A (1997) Neonatal handling and environmental enrichment effects on emotionality, novelty/reward seeking, and age-related cognitive and hippocampal impairments: focus on the Roman rat lines. Behav Genet 27:513–526
Floresco SB, Seamans JK, Phillips AG (1997) Selective roles for hippocampal, prefrontal cortical, and ventral striatal circuits in radial-arm maze tasks with or without a delay. J Neurosci 17:1880–1890
Fox C, Merali Z, Harrison C (2006) Therapeutic and protective effect of environmental enrichment against psychogenic and neurogenic stress. Behav Brain Res 175:1–8
Galani R, Berthel M-C, Lazarus C, Majchrzak M, Barbelivien A, Kelche C, Cassel J-C (2007) The behavioral effects of enriched housing are not altered by serotonin depletion but enrichment alters hippocampal neurochemistry. Neurobiol Learn Mem 88:1–10
Garrido P, de Blas M, Del Arco A, Segovia G, Mora F (2012a) Aging increases basal but not stress-induced levels of corticosterone in the brain of the awake rat. Neurobiol Aging 33:375–382
Garrido P, De Blas M, Giné E, Santos Á, Mora F (2012b) Aging impairs the control of prefrontal cortex on the release of corticosterone in response to stress and on memory consolidation. Neurobiol Aging 33(827):e821–e829
Gisquet-Verrier P, Delatour B (2006) The role of the rat prelimbic/infralimbic cortex in working memory: not involved in the short-term maintenance but in monitoring and processing functions. Neuroscience 141:585–596
Goldman-Rakic PS (1995) Cellular basis of working memory. Neuron 14:477–485
Goldstein LE, Rasmusson AM, Bunney BS, Roth RH (1996) Role of the amygdala in the coordination of behavioral, neuroendocrine, and prefrontal cortical monoamine responses to psychological stress in the rat. J Neurosci 16:4787–4798
Hains AB, Arnsten AFT (2008) Molecular mechanisms of stress-induced prefrontal cortical impairment: implications for mental illness. Learn Mem 15:551–564
Hennessy MB, Foy T (1987) Nonedible material elicits chewing and reduces the plasma corticosterone response during novelty exposure in mice. Behav Neurosci 101:237–245
Herman JP, Ostrander MM, Mueller NK, Figueiredo H (2005) Limbic system mechanisms of stress regulation: hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:1201–1213
Hernandez LF, Segovia G, Mora F (2003) Effects of activation of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors on the extracellular concentrations of dopamine, acetylcholine, and GABA in striatum of the awake rat: a microdialysis study. Neurochem Res 28:1819–1827
Hoffmann LC, Schütte SRM, Koch M, Schwabe K (2009) Effect of “enriched environment” during development on adult rat behavior and response to the dopamine receptor agonist apomorphine. Neuroscience 158:1589–1598
Horger BA, Roth RH (1996) The role of mesoprefrontal dopamine neurons in stress. Crit Rev Neurobiol 10:395–418
Imperato A, Puglisi-Allegra S, Casolini P, Zocchi A, Angelucci L (1989) Stress-induced enhancement of dopamine and acetylcholine release in limbic structures: role of corticosterone. Eur J Pharmacol 165:337–338
Jacobson L, Sapolsky R (1991) The role of the hippocampus in feedback regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Endocr Rev 12:118–134
Jankord R, Herman JP (2008) Limbic regulation of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical function during acute and chronic stress. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1148:64–73
Jones KR, Myers B, Herman JP (2011) Stimulation of the prelimbic cortex differentially modulates neuroendocrine responses to psychogenic and systemic stressors. Physiol Behav 104:266–271
Kitchener P, Di Blasi F, Borrelli E, Piazza PV (2004) Differences between brain structures in nuclear translocation and DNA binding of the glucocorticoid receptor during stress and the circadian cycle. Eur J Neurosci 19:1837–1846
Larsson F, Winblad B, Mohammed AH (2002) Psychological stress and environmental adaptation in enriched vs. impoverished housed rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:193–207
Lee EHY, Hsu WL, Ma YL, Lee PJ, Chao CC (2003) Enrichment enhances the expression of sgk, a glucocorticoid-induced gene, and facilitates spatial learning through glutamate AMPA receptor mediation. Eur J Neurosci 18:2842–2852
Leger M, Bouet V, Freret T, Darmaillacq A-S, Dacher M, Dauphin F, Boulouard M, Schumann-Bard P (2012) Environmental enrichment improves recent but not remote memory in association with a modified brain metabolic activation profile in adult mice. Behav Brain Res 228:22–29
Leggio MG, Mandolesi L, Federico F, Spirito F, Ricci B, Gelfo F, Petrosini L (2005) Environmental enrichment promotes improved spatial abilities and enhanced dendritic growth in the rat. Behav Brain Res 163:78–90
Lehmann ML, Herkenham M (2011) Environmental enrichment confers stress resiliency to social defeat through an infralimbic cortex-dependent neuroanatomical pathway. J Neurosci 31:6159–6173
Lengvári I, Liposits ZS (1977) Diurnal changes in endogenous corticosterone content of some brain regions of rats. Brain Res 124:571–575
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lupien SJ, Maheu F, Tu M, Fiocco A, Schramek TE (2007) The effects of stress and stress hormones on human cognition: implications for the field of brain and cognition. Brain Cogn 65:209–237
Maier SF, Amat J, Baratta MV, Paul E, Watkins LR (2006) Behavioral control, the medial prefrontal cortex, and resilience. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 8:397–406
Mark GP, Rada PV, Shors TJ (1996) Inescapable stress enhances extracellular acetylcholine in the rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex but not the nucleus accumbens or amygdala. Neuroscience 74:767–774
McEwen BS, De Kloet ER, Rostene W (1986) Adrenal steroid receptors and actions in the nervous system. Physiol Rev 66:1121–1188
Meaney MJ, Aitken DH (1985) [3H]Dexamethasone binding in rat frontal cortex. Brain Res 328:176–180
Mizoguchi K, Ishige A, Takeda S, Aburada M, Tabira T (2004) Endogenous glucocorticoids are essential for maintaining prefrontal cortical cognitive function. J Neurosci 24:5492–5499
Mlynarik M, Johansson BB, Jezova D (2004) Enriched environment influences adrenocortical response to immune challenge and glutamate receptor gene expression in rat hippocampus. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1018:273–280
Moncek F, Duncko R, Johansson BB, Jezova D (2004) Effect of environmental enrichment on stress related systems in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 16:423–431
Mora F, Segovia G, del Arco A (2007) Aging, plasticity and environmental enrichment: structural changes and neurotransmitter dynamics in several areas of the brain. Brain Res Rev 55:78–88
Mora F, Segovia G, del Arco A, de Blas M, Garrido P (2012) Stress, neurotransmitters, corticosterone and body–brain integration. Brain Res 1476:71–85
Murphy BL, Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS, Roth RH (1996) Increased dopamine turnover in the prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance in rats and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1325–1329
Oitzl MS, Fluttert M, Ron de Kloet E (1994) The effect of corticosterone on reactivity to spatial novelty is mediated by central mineralocorticosteroid receptors. Eur J Neurosci 6:1072–1079
Olsson T, Mohammed AH, Donaldson LF, Henriksson BG, Seckl JR (1994) Glucocorticoid receptor and NGFI-A gene expression are induced in the hippocampus after environmental enrichment in adult rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 23:349–353
Park CR, Campbell AM, Woodson JC, Smith TP, Fleshner M, Diamond DM (2006) Permisive influence of the stress in the expression of a U-shaped relationship between serum corticosterone levels and spatial memory errors in rats. Dose Response 4:55–74
Park CR, Zoladz PR, Conrad CD, Fleshner M, Diamond DM (2008) Acute predator stress impairs the consolidation and retrieval of hippocampus-dependent memory in male and female rats. Learn Mem 15:271–280
Paul AD (2004) An overview of the tasks used to test working memory in rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:699–709
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Peña Y, Prunell M, Rotllant D, Armario A, Escorihuela RM (2009) Enduring effects of environmental enrichment from weaning to adulthood on pituitary-adrenal function, pre-pulse inhibition and learning in male and female rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 34:1390–1404
Radley JJ, Arias CM, Sawchenko PE (2006) Regional differentiation of the medial prefrontal cortex in regulating adaptive responses to acute emotional stress. J Neurosci 26:12967–12976
Ragozzino ME (2002) The effects of dopamine D(1) receptor blockade in the prelimbic–infralimbic areas on behavioral flexibility. Learn Mem 9:18–28
Reul JMHM, Kloet ERD (1985) Two receptor systems for corticosterone in rat brain: microdistribution and differential occupation. Endocrinology 117:2505–2511
Rich EL, Shapiro ML (2007) Prelimbic/infralimbic inactivation impairs memory for multiple task switches, but not flexible selection of familiar tasks. J Neurosci 27:4747–4755
Richard CT (1999) The influences of rearing environment and neonatal choline dietary supplementation on spatial learning and memory in adult rats. Behav Brain Res 105:173–188
Robbins TW (2005) Controlling stress: how the brain protects itself from depression. Nat Neurosci 8:261–262
Robbins TW, Roberts AC (2007) Differential regulation of fronto-executive function by the monoamines and acetylcholine. Cereb Cortex 17:i151–i160
Roozendaal B, McEwen BS, Chattarji S (2009a) Stress, memory and the amygdala. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:423–433
Roozendaal B, McReynolds JR, Van der Zee EA, Lee S, McGaugh JL, McIntyre CK (2009b) Glucocorticoid effects on memory consolidation depend on functional interactions between the medial prefrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci 29:14299–14308
Rossato JI, Bevilaqua LR, Izquierdo I, Medina JH, Cammarota M (2009) Dopamine controls persistence of long-term memory storage. Science 325:1017–1020
Sandi C, Pinelo-Nava T (2007) Stress and memory: behavioral effects and neurobiological mechanisms. Neural Plast 2007:78970
Sandi C, Venero C, Guaza C (1996) Novelty-related rapid locomotor effects of corticosterone in rats. Eur J Neurosci 8:794–800
Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU (2000) How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr Rev 21:55–89
Sarter M, Bruno JP (1997) Cognitive functions of cortical acetylcholine: toward a unifying hypothesis. Brain Res Rev 23:28–46
Schloesser RJ, Lehmann M, Martinowich K, Manji HK, Herkenham M (2010) Environmental enrichment requires adult neurogenesis to facilitate the recovery from psychosocial stress. Mol Psychiatry 15:1152–1163
Schrijver NC, Bahr NI, Weiss IC, Wurbel H (2002) Dissociable effects of isolation rearing and environmental enrichment on exploration, spatial learning and HPA activity in adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:209–224
Seamans JK, Floresco SB, Phillips AG (1998) D1 receptor modulation of hippocampus “prefrontal cortical circuits integrating spatial memory with executive functions in the rat”. J Neurosci 18:1613–1621
Seamans JK, Phillips AF (1994) Selective memory impairments produced by transient lidocaine-induced lesions of the nucleus accumbens in rats. Behav Neurosci 108:456–468
Segovia G, Del Arco A, de Blas M, Garrido P, Mora F (2008a) Effects of an enriched environment on the release of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex produced by stress and on working memory during aging in the awake rat. Behav Brain Res 187:304–311
Segovia G, Del Arco A, Garrido P, de Blas M, Mora F (2008b) Environmental enrichment reduces the response to stress of the cholinergic system in the prefrontal cortex during aging. Neurochem Int 52:1198–1203
Segovia G, del Arco A, Mora F (2009) Environmental enrichment, prefrontal cortex, stress, and aging of the brain. J Neural Transm 116:1007–1016
Shukitt-Hale B, McEwen JJ, Szprengiel A, Joseph JA (2004) Effect of age on the radial arm water maze—a test of spatial learning and memory. Neurobiol Aging 25:223–229
Stalnaker TA, España RA, Berridge CW (2009) Coping behavior causes asymmetric changes in neuronal activation in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Synapse 63:82–85
Sullivan RM (2004) Hemispheric asymmetry in stress processing in rat prefrontal cortex and the role of mesocortical dopamine. Stress 7:131–143
Sztainberg Y, Kuperman Y, Tsoory M, Lebow M, Chen A (2010) The anxiolytic effect of environmental enrichment is mediated via amygdalar CRF receptor type 1. Mol Psychiatry 15:905–917
Szyf M, McGowan P, Meaney MJ (2008) The social environment and the epigenome. Environ Mol Mutagen 49:46–60
Thierry AM, Tassin JP, Blanc G, Glowinski J (1976) Selective activation of the mesocortical DA system by stress. Nature 263:242–244
Thoeringer CK, Sillaber I, Roedel A, Erhardt A, Mueller MB, Ohl F, Holsboer F, Keck ME (2007) The temporal dynamics of intrahippocampal corticosterone in response to stress-related stimuli with different emotional and physical load: an in vivo microdialysis study in C57BL/6 and DBA/2 inbred mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32:746–757
Weinberg MS, Johnson DC, Bhatt AP, Spencer RL (2010) Medial prefrontal cortex activity can disrupt the expression of stress response habituation. Neuroscience 168:744–756
Williams GV, Castner SA (2006) Under the curve: critical issues for elucidating D1 receptor function in working memory. Neuroscience 139:263–276
Zimmermann A, Stauffacher M, Langhans W, Wurbel H (2001) Enrichment-dependent differences in novelty exploration in rats can be explained by habituation. Behav Brain Res 121:11–20
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by SAF-2006-01554 and SAF-2009-09053. Pedro Garrido and Marta de Blas are recipients for fellowships from the Ministerio de Educación and Universidad Complutense de Madrid, respectively. The authors deeply acknowledge the excellent technical support of Ángela Amores.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
P. Garrido and M. De Blas contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrido, P., De Blas, M., Ronzoni, G. et al. Differential effects of environmental enrichment and isolation housing on the hormonal and neurochemical responses to stress in the prefrontal cortex of the adult rat: relationship to working and emotional memories. J Neural Transm 120, 829–843 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0935-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0935-3