Abstract
Pemphigus is a group of rare, potentially devastating autoimmune diseases of the skin and mucous membranes with high morbidity and potentially lethal outcome. The major clinical variant, pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is caused by a loss of intercellular adhesion of epidermal keratinocytes which is induced by IgG autoantibodies against components of desmosomes. Specifically, IgG against the desmosomal adhesion proteins, desmoglein 3 (Dsg3) and desmoglein 1 (Dsg1), preferentially _target their ectodomains which are presumably critical for the transinteraction and signalling function of these adhesion molecules. There is a close immunogenetic association of PV with the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II alleles, HLA-DRB1*04:02 and HLA-DQB1*05:03. These have been shown to be critical for the presentation of immunodominant peptides to autoreactive CD4+ T helper cells. The importance of autoaggressive T-B cell interaction in the induction of pathogenic IgG autoantibodies which directly cause epidermal loss of adhesion has been demonstrated both clinically (by the use of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab) and experimentally (in PV mouse models). The strong association of clinically active pemphigus with autoantibodies of the IgG4 and IgE subclasses strongly suggests that T helper 2 cells are critical regulators of the immune pathogenesis of pemphigus. Novel therapeutic approaches _target autoreactive T and B cells to specifically interfere with the T cell-dependent activation of B cells leading to the generation of autoantibody-producing plasma cells. Our improved understanding of the autoantibody-driven effector phase of pemphigus has led to the introduction of novel therapies that _target pathogenic autoantibodies such as immunoadsorption and drugs that block pathogenic autoantibody-induced cell signalling events.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kneisel A, Hertl M (2011) Autoimmune bullous skin diseases. Part 2: diagnosis and therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 9(11):927–947. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1610-0387.2011.07809.x
Di Zenzo G, Borradori L, Muller EJ (2016) The pathogenesis of pemphigus: controversy vs complexity. Exp Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.13176
Di Zenzo G, Amber KT, Sayar BS, Muller EJ, Borradori L (2016) Immune response in pemphigus and beyond: progresses and emerging concepts. Semin Immunopathol 38(1):57–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-015-0541-1
Mahoney MG, Wang Z, Rothenberger K, Koch PJ, Amagai M, Stanley JR (1999) Explanations for the clinical and microscopic localization of lesions in pemphigus foliaceus and vulgaris. J Clin Invest 103(4):461–468. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI5252
Sinha AA, Brautbar C, Szafer F, Friedmann A, Tzfoni E, Todd JA, Steinman L, McDevitt HO (1988) A newly characterized HLA DQ beta allele associated with pemphigus vulgaris. Science 239(4843):1026–1029
Ahmed AR, Yunis EJ, Khatri K, Wagner R, Notani G, Awdeh Z, Alper CA (1990) Major histocompatibility complex haplotype studies in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with pemphigus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87(19):7658–7662
Ahmed AR, Wagner R, Khatri K, Notani G, Awdeh Z, Alper CA, Yunis EJ (1991) Major histocompatibility complex haplotypes and class II genes in non-Jewish patients with pemphigus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(11):5056–5060
Tron F, Gilbert D, Joly P, Mouquet H, Drouot L, Ayed MB, Sellami M, Masmoudi H, Makni S (2006) Immunogenetics of pemphigus: an update. Autoimmunity 39(7):531–539
Shams S, Amirzargar AA, Yousefi M, Rezaei N, Solgi G, Khosravi F, Ansaripour B, Moradi B, Nikbin B (2009) HLA class II (DRB, DQA1 and DQB1) allele and haplotype frequencies in the patients with pemphigus vulgaris. J Clin Immunol 29(2):175–179
Yan L, Wang JM, Zeng K (2012) Association between HLA-DRB1 polymorphisms and pemphigus vulgaris: a meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol 167(4):768–777
Kneisel A, Hertl M (2011) Autoimmune bullous skin diseases. Part 1: clinical manifestations. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 9(10):844–856; quiz 857. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1610-0387.2011.07793.x
Martin LK, Werth V, Villanueva E, Segall J, Murrell DF (2009) Interventions for pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD006263
Otten JV, Hashimoto T, Hertl M, Payne AS, Sitaru C (2014) Molecular diagnosis in autoimmune skin blistering conditions. Curr Mol Med 14(1):69–95
Hertl M, Jedlickova H, Karpati S, Marinovic B, Uzun S, Yayli S, Mimouni D, Borradori L, Feliciani C, Ioannides D, Joly P, Kowalewski C, Zambruno G, Zillikens D, Jonkman MF (2015) Pemphigus. S2 guideline for diagnosis and treatment--guided by the European dermatology forum (EDF) in cooperation with the European academy of dermatology and venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 29(3):405–414. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.12772
Ahmed AR, Kaveri S, Spigelman Z (2015) Long-term remissions in recalcitrant pemphigus vulgaris. N Engl J Med 373(27):2693–2694. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1508234
Ahmed AR, Spigelman Z, Cavacini LA, Posner MR (2006) Treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with rituximab and intravenous immune globulin. N Engl J Med 355(17):1772–1779. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa062930
Joly P, Mouquet H, Roujeau JC, D'Incan M, Gilbert D, Jacquot S, Gougeon ML, Bedane C, Muller R, Dreno B, Doutre MS, Delaporte E, Pauwels C, Franck N, Caux F, Picard C, Tancrede-Bohin E, Bernard P, Tron F, Hertl M, Musette P (2007) A single cycle of rituximab for the treatment of severe pemphigus. N Engl J Med 357(6):545–552. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa067752
Slomov E, Loewenthal R, Korostishevsky M, Goldberg I, Brenner S, Gazit E (2005) Pemphigus vulgaris is associated with the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) system. Hum Immunol 66(12):1213–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2005.11.004
Kanwar AJ, Kaur S (1991) Pemphigus in children. Int J Dermatol 30(5):343–346
Qian Y, Jeong JS, Maldonado M, Valenzuela JG, Gomes R, Teixeira C, Evangelista F, Qaqish B, Aoki V, Hans G Jr, Rivitti EA, Eaton D, Diaz LA (2012) Cutting edge: Brazilian pemphigus foliaceus anti-desmoglein 1 autoantibodies cross-react with sand fly salivary LJM11 antigen. J Immunol 189(4):1535–1539. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1200842
Ohzono A, Sogame R, Li X, Teye K, Tsuchisaka A, Numata S, Koga H, Kawakami T, Tsuruta D, Ishii N, Hashimoto T (2015) Clinical and immunological findings in 104 cases of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Br J Dermatol 173(6):1447–1452. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.14162
Amagai M, Nishikawa T, Nousari HC, Anhalt GJ, Hashimoto T (1998) Antibodies against desmoglein 3 (pemphigus vulgaris antigen) are present in sera from patients with paraneoplastic pemphigus and cause acantholysis in vivo in neonatal mice. J Clin Invest 102(4):775–782. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci3647
Brandt O, Rafei D, Podstawa E, Niedermeier A, Jonkman MF, Terra JB, Hein R, Hertl M, Pas HH, Muller R (2012) Differential IgG recognition of desmoglein 3 by paraneoplastic pemphigus and pemphigus vulgaris sera. J Invest Dermatol 132(6):1738–1741. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2012.1
Hashimoto T, Amagai M, Watanabe K, Chorzelski TP, Bhogal BS, Black MM, Stevens HP, Boorsma DM, Korman NJ, Gamou S et al (1995) Characterization of paraneoplastic pemphigus autoantigens by immunoblot analysis. J Invest Dermatol 104(5):829–834
Kazerounian S, Mahoney MG, Uitto J, Aho S (2000) Envoplakin and periplakin, the paraneoplastic pemphigus antigens, are also recognized by pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies. J Invest Dermatol 115(3):505–507. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00088-2.x
Maier L, Udvardi A, Hertl M, Eming R, Schmidt E, Zillikens D, Volc-Platzer B (2017) Paraneoplastic pemphigus with anti-BP180 autoantibodies and Castleman disease. Br J Dermatol 176(3):824–826. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.14877
Schepens I, Jaunin F, Begre N, Laderach U, Marcus K, Hashimoto T, Favre B, Borradori L (2010) The protease inhibitor alpha-2-macroglobulin-like-1 is the p170 antigen recognized by paraneoplastic pemphigus autoantibodies in human. PLoS One 5(8):e12250. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012250
Hashimoto T, Kiyokawa C, Mori O, Miyasato M, Chidgey MA, Garrod DR, Kobayashi Y, Komori K, Ishii K, Amagai M, Nishikawa T (1997) Human desmocollin 1 (Dsc1) is an autoantigen for the subcorneal pustular dermatosis type of IgA pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol 109(2):127–131
Karpati S, Amagai M, Liu WL, Dmochowski M, Hashimoto T, Horvath A (2000) Identification of desmoglein 1 as autoantigen in a patient with intraepidermal neutrophilic IgA dermatosis type of IgA pemphigus. Exp Dermatol 9(3):224–228
Yasuda H, Kobayashi H, Hashimoto T, Itoh K, Yamane M, Nakamura J (2000) Subcorneal pustular dermatosis type of IgA pemphigus: demonstration of autoantibodies to desmocollin-1 and clinical review. Br J Dermatol 143(1):144–148
Ahmed AR, Carrozzo M, Caux F, Cirillo N, Dmochowski M, Alonso AE, Gniadecki R, Hertl M, López-Zabalza MJ, Lotti R, Pincelli C, Pittelkow M, Schmidt E, Sinha AA, Sprecher E, Grando SA (2016) Monopathogenic vs multipathogenic explanations of pemphigus pathophysiology. Exp Dermatol 25(11):839–846. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.13106
Nguyen VT, Ndoye A, Shultz LD, Pittelkow MR, Grando SA (2000) Antibodies against keratinocyte antigens other than desmogleins 1 and 3 can induce pemphigus vulgaris-like lesions. J Clin Invest 106(12):1467–1479. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci10305
Vu TN, Lee TX, Ndoye A, Shultz LD, Pittelkow MR, Dahl MV, Lynch PJ, Grando SA (1998) The pathophysiological significance of nondesmoglein _targets of pemphigus autoimmunity. Development of antibodies against keratinocyte cholinergic receptors in patients with pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol 134(8):971–980
Mao X, Nagler AR, Farber SA, Choi EJ, Jackson LH, Leiferman KM, Ishii N, Hashimoto T, Amagai M, Zone JJ, Payne AS (2010) Autoimmunity to desmocollin 3 in pemphigus vulgaris. Am J Pathol 177(6):2724–2730. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2010.100483
Rafei D, Muller R, Ishii N, Llamazares M, Hashimoto T, Hertl M, Eming R (2011) IgG autoantibodies against desmocollin 3 in pemphigus sera induce loss of keratinocyte adhesion. Am J Pathol 178(2):718–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.10.016
Abasq C, Mouquet H, Gilbert D, Tron F, Grassi V, Musette P, Joly P (2009) ELISA testing of anti-desmoglein 1 and 3 antibodies in the management of pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 145(5):529–535. https://doi.org/10.1001/archdermatol.2009.9
Amagai M, Komai A, Hashimoto T, Shirakata Y, Hashimoto K, Yamada T, Kitajima Y, Ohya K, Iwanami H, Nishikawa T (1999) Usefulness of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant desmogleins 1 and 3 for serodiagnosis of pemphigus. Br J Dermatol 140(2):351–357
Cheng SW, Kobayashi M, Kinoshita-Kuroda K, Tanikawa A, Amagai M, Nishikawa T (2002) Monitoring disease activity in pemphigus with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant desmogleins 1 and 3. Br J Dermatol 147(2):261–265
Daneshpazhooh M, Chams-Davatchi C, Khamesipour A, Mansoori P, Taheri A, Firooz A, Mortazavi H, Esmaili N, Dowlati Y (2007) Desmoglein 1 and 3 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in Iranian patients with pemphigus vulgaris: correlation with phenotype, severity, and disease activity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 21(10):1319–1324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02254.x
Schmidt E, Dahnrich C, Rosemann A, Probst C, Komorowski L, Saschenbrecker S, Schlumberger W, Stocker W, Hashimoto T, Brocker EB, Recke A, Rose C, Zillikens D (2010) Novel ELISA systems for antibodies to desmoglein 1 and 3: correlation of disease activity with serum autoantibody levels in individual pemphigus patients. Exp Dermatol 19(5):458–463. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2010.01069.x
Ruach M, Ohel G, Rahav D, Samueloff A (1995) Pemphigus vulgaris and pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Surv 50(10):755–760
Walker DC, Kolar KA, Hebert AA, Jordon RE (1995) Neonatal pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol 131(11):1308–1311
Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Green KJ, Shimizu N, Nishikawa T (1995) Antigen-specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol 104(6):895–901
Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Shimizu N, Nishikawa T (1994) Absorption of pathogenic autoantibodies by the extracellular domain of pemphigus vulgaris antigen (Dsg3) produced by baculovirus. J Clin Invest 94(1):59–67. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI117349
Amagai M, Karpati S, Prussick R, Klaus-Kovtun V, Stanley JR (1992) Autoantibodies against the amino-terminal cadherin-like binding domain of pemphigus vulgaris antigen are pathogenic. J Clin Invest 90(3):919–926. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI115968
Amagai M, Tsunoda K, Suzuki H, Nishifuji K, Koyasu S, Nishikawa T (2000) Use of autoantigen-knockout mice in developing an active autoimmune disease model for pemphigus. J Clin Invest 105(5):625–631. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI8748
Anhalt GJ, Labib RS, Voorhees JJ, Beals TF, Diaz LA (1982) Induction of pemphigus in neonatal mice by passive transfer of IgG from patients with the disease. N Engl J Med 306(20):1189–1196. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM198205203062001
Roscoe JT, Diaz L, Sampaio SA, Castro RM, Labib RS, Takahashi Y, Patel H, Anhalt GJ (1985) Brazilian pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies are pathogenic to BALB/c mice by passive transfer. J Invest Dermatol 85(6):538–541
Schulze K, Galichet A, Sayar BS, Scothern A, Howald D, Zymann H, Siffert M, Zenhausern D, Bolli R, Koch PJ, Garrod D, Suter MM, Muller EJ (2012) An adult passive transfer mouse model to study desmoglein 3 signaling in pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 132(2):346–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.299
Caldelari R, de Bruin A, Baumann D, Suter MM, Bierkamp C, Balmer V, Muller E (2001) A central role for the armadillo protein plakoglobin in the autoimmune disease pemphigus vulgaris. J Cell Biol 153(4):823–834
Calkins CC, Setzer SV, Jennings JM, Summers S, Tsunoda K, Amagai M, Kowalczyk AP (2006) Desmoglein endocytosis and desmosome disassembly are coordinated responses to pemphigus autoantibodies. J Biol Chem 281(11):7623–7634. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M512447200
Heupel WM, Zillikens D, Drenckhahn D, Waschke J (2008) Pemphigus vulgaris IgG directly inhibit desmoglein 3-mediated transinteraction. J Immunol 181(3):1825–1834
Jennings JM, Tucker DK, Kottke MD, Saito M, Delva E, Hanakawa Y, Amagai M, Kowalczyk AP (2011) Desmosome disassembly in response to pemphigus vulgaris IgG occurs in distinct phases and can be reversed by expression of exogenous Dsg3. J Invest Dermatol 131(3):706–718. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2010.389
Saito M, Stahley SN, Caughman CY, Mao X, Tucker DK, Payne AS, Amagai M, Kowalczyk AP (2012) Signaling dependent and independent mechanisms in pemphigus vulgaris blister formation. PLoS One 7(12):e50696. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050696
Spindler V, Endlich A, Hartlieb E, Vielmuth F, Schmidt E, Waschke J (2011) The extent of desmoglein 3 depletion in pemphigus vulgaris is dependent on ca(2+)-induced differentiation: a role in suprabasal epidermal skin splitting? Am J Pathol 179(4):1905–1916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.06.043
Spindler V, Rotzer V, Dehner C, Kempf B, Gliem M, Radeva M, Hartlieb E, Harms GS, Schmidt E, Waschke J (2013) Peptide-mediated desmoglein 3 crosslinking prevents pemphigus vulgaris autoantibody-induced skin blistering. J Clin Invest 123(2):800–811. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI60139
Belloni-Fortina A, Faggion D, Pigozzi B, Peserico A, Bordignon M, Baldo V, Alaibac M (2009) Detection of autoantibodies against recombinant desmoglein 1 and 3 molecules in patients with pemphigus vulgaris: correlation with disease extent at the time of diagnosis and during follow-up. Clin Dev Immunol 2009:187864. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/187864
Kamiya K, Aoyama Y, Shirafuji Y, Hamada T, Morizane S, Fujii K, Hisata K, Iwatsuki K (2012) Detection of antibodies against the non-calcium-dependent epitopes of desmoglein 3 in pemphigus vulgaris and their pathogenic significance. Br J Dermatol 167(2):252–261. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.10929.x
Kamiya K, Aoyama Y, Shirafuji Y, Hamada T, Morizane S, Fujii K, Iwatsuki K (2013) A higher correlation of the antibody activities against the calcium-dependent epitopes of desmoglein 3 quantified by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-treated enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with clinical disease activities of pemphigus vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci 70(3):190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.02.011
Payne AS, Ishii K, Kacir S, Lin C, Li H, Hanakawa Y, Tsunoda K, Amagai M, Stanley JR, Siegel DL (2005) Genetic and functional characterization of human pemphigus vulgaris monoclonal autoantibodies isolated by phage display. J Clin Invest 115(4):888–899. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI24185
Tsunoda K, Ota T, Aoki M, Yamada T, Nagai T, Nakagawa T, Koyasu S, Nishikawa T, Amagai M (2003) Induction of pemphigus phenotype by a mouse monoclonal antibody against the amino-terminal adhesive interface of desmoglein 3. J Immunol 170(4):2170–2178
Bhol KC, Ahmed AR (2002) Production of non-pathogenic human monoclonal antibodies to desmoglein 3 from pemphigus vulgaris patient. Autoimmunity 35(2):87–91
Cho MJ, Lo AS, Mao X, Nagler AR, Ellebrecht CT, Mukherjee EM, Hammers CM, Choi EJ, Sharma PM, Uduman M, Li H, Rux AH, Farber SA, Rubin CB, Kleinstein SH, Sachais BS, Posner MR, Cavacini LA, Payne AS (2014) Shared VH1-46 gene usage by pemphigus vulgaris autoantibodies indicates common humoral immune responses among patients. Nat Commun 5:4167. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5167
Di Zenzo G, Di Lullo G, Corti D, Calabresi V, Sinistro A, Vanzetta F, Didona B, Cianchini G, Hertl M, Eming R, Amagai M, Ohyama B, Hashimoto T, Sloostra J, Sallusto F, Zambruno G, Lanzavecchia A (2012) Pemphigus autoantibodies generated through somatic mutations _target the desmoglein-3 cis-interface. J Clin Invest 122(10):3781–3790. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64413
Ishii K, Lin C, Siegel DL, Stanley JR (2008) Isolation of pathogenic monoclonal anti-desmoglein 1 human antibodies by phage display of pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies. J Invest Dermatol 128(4):939–948. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5701132
Yamagami J, Kacir S, Ishii K, Payne AS, Siegel DL, Stanley JR (2009) Antibodies to the desmoglein 1 precursor proprotein but not to the mature cell surface protein cloned from individuals without pemphigus. J Immunol 183(9):5615–5621. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0901691
Yeh SW, Cavacini LA, Bhol KC, Lin MS, Kumar M, Duval M, Posner MR, Ahmed AR (2006) Pathogenic human monoclonal antibody against desmoglein 3. Clin Immunol 120(1):68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2006.03.006
Chan PT, Ohyama B, Nishifuji K, Yoshida K, Ishii K, Hashimoto T, Amagai M (2010) Immune response towards the amino-terminus of desmoglein 1 prevails across different activity stages in nonendemic pemphigus foliaceus. Br J Dermatol 162(6):1242–1250. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09696.x
Futei Y, Amagai M, Sekiguchi M, Nishifuji K, Fujii Y, Nishikawa T (2000) Use of domain-swapped molecules for conformational epitope mapping of desmoglein 3 in pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 115(5):829–834. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00137.x
Ohyama B, Nishifuji K, Chan PT, Kawaguchi A, Yamashita T, Ishii N, Hamada T, Dainichi T, Koga H, Tsuruta D, Amagai M, Hashimoto T (2012) Epitope spreading is rarely found in pemphigus vulgaris by large-scale longitudinal study using desmoglein 2-based swapped molecules. J Invest Dermatol 132(4):1158–1168. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.448
Sekiguchi M, Futei Y, Fujii Y, Iwasaki T, Nishikawa T, Amagai M (2001) Dominant autoimmune epitopes recognized by pemphigus antibodies map to the N-terminal adhesive region of desmogleins. J Immunol 167(9):5439–5448
Sharma PM, Choi EJ, Kuroda K, Hachiya T, Ishii K, Payne AS (2009) Pathogenic anti-desmoglein MAbs show variable ELISA activity because of preferential binding of mature versus proprotein isoforms of desmoglein 3. J Invest Dermatol 129(9):2309–2312. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2009.41
Allen EM, Giudice GJ, Diaz LA (1993) Subclass reactivity of pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies with recombinant human desmoglein. J Invest Dermatol 100(5):685–691
Dmochowski M, Hashimoto T, Nishikawa T (1992) The analysis of IgG subclasses of anti-intercellular antibodies in pemphigus by an immunoblot technique. Arch Dermatol Res 284(5):309–311
Jones CC, Hamilton RG, Jordon RE (1988) Subclass distribution of human IgG autoantibodies in pemphigus. J Clin Immunol 8(1):43–49
Wilson CL, Wojnarowska F, Dean D, Pasricha JS (1993) IgG subclasses in pemphigus in Indian and UK populations. Clin Exp Dermatol 18(3):226–230
Aoki V, Rivitti EA, Diaz LA, Cooperative Group on Fogo Selvagem R (2015) Update on fogo selvagem, an endemic form of pemphigus foliaceus. J Dermatol 42(1):18–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.12675
Lee HE, Berkowitz P, Jolly PS, Diaz LA, Chua MP, Rubenstein DS (2009) Biphasic activation of p38MAPK suggests that apoptosis is a downstream event in pemphigus acantholysis. J Biol Chem 284(18):12524–12532. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M808204200
Warren SJ, Arteaga LA, Rivitti EA, Aoki V, Hans-Filho G, Qaqish BF, Lin MS, Giudice GJ, Diaz LA (2003) The role of subclass switching in the pathogenesis of endemic pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol 120(1):104–108. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12017.x
de Bruin A, Caldelari R, Williamson L, Suter MM, Hunziker T, Wyder M, Muller EJ (2007) Plakoglobin-dependent disruption of the desmosomal plaque in pemphigus vulgaris. Exp Dermatol 16(6):468–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2007.00557.x
Amagai M, Stanley JR (2012) Desmoglein as a _target in skin disease and beyond. J Invest Dermatol 132(3 Pt 2):776–784. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.390
Kitajima Y (2014) 150(th) anniversary series: desmosomes and autoimmune disease, perspective of dynamic desmosome remodeling and its impairments in pemphigus. Cell Commun Adhes 21(6):269–280. https://doi.org/10.3109/15419061.2014.943397
Waschke J, Spindler V (2014) Desmosomes and extradesmosomal adhesive signaling contacts in pemphigus. Med Res Rev 34(6):1127–1145. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21310
Hacker-Foegen MK, Janson M, Amagai M, Fairley JA, Lin MS (2003) Pathogenicity and epitope characteristics of anti-desmoglein-1 from pemphigus foliaceus patients expressing only IgG1 autoantibodies. J Invest Dermatol 121(6):1373–1378. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1747.2003.12608.x
Muller R, Svoboda V, Wenzel E, Gebert S, Hunzelmann N, Muller HH, Hertl M (2006) IgG reactivity against non-conformational NH-terminal epitopes of the desmoglein 3 ectodomain relates to clinical activity and phenotype of pemphigus vulgaris. Exp Dermatol 15(8):606–614. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2006.00451.x
Aoyama Y, Nagai M, Kitajima Y (2010) Binding of pemphigus vulgaris IgG to antigens in desmosome core domains excludes immune complexes rather than directly splitting desmosomes. Br J Dermatol 162(5):1049–1055. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09672.x
Aoyama Y, Owada MK, Kitajima Y (1999) A pathogenic autoantibody, pemphigus vulgaris-IgG, induces phosphorylation of desmoglein 3, and its dissociation from plakoglobin in cultured keratinocytes. Eur J Immunol 29 (7):2233–2240. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199907)29:07&%2360;2233::AID-IMMU2233&%2362;3.0.CO;2-4
Vollner F, Ali J, Kurrle N, Exner Y, Eming R, Hertl M, Banning A, Tikkanen R (2016) Loss of flotillin expression results in weakened desmosomal adhesion and pemphigus vulgaris-like localisation of desmoglein-3 in human keratinocytes. Sci Rep 6:28820. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28820
Berkowitz P, Hu P, Liu Z, Diaz LA, Enghild JJ, Chua MP, Rubenstein DS (2005) Desmosome signaling. Inhibition of p38MAPK prevents pemphigus vulgaris IgG-induced cytoskeleton reorganization. J Biol Chem 280(25):23778–23784. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M501365200
Cirillo N, Lanza A, Prime SS (2010) Induction of hyper-adhesion attenuates autoimmune-induced keratinocyte cell-cell detachment and processing of adhesion molecules via mechanisms that involve PKC. Exp Cell Res 316(4):580–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.10.005
Grando SA (2012) Pemphigus autoimmunity: hypotheses and realities. Autoimmunity 45(1):7–35. https://doi.org/10.3109/08916934.2011.606444
Kawasaki Y, Aoyama Y, Tsunoda K, Amagai M, Kitajima Y (2006) Pathogenic monoclonal antibody against desmoglein 3 augments desmoglein 3 and p38 MAPK phosphorylation in human squamous carcinoma cell line. Autoimmunity 39(7):587–590. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916930600971943
Berkowitz P, Diaz LA, Hall RP, Rubenstein DS (2008) Induction of p38MAPK and HSP27 phosphorylation in pemphigus patient skin. J Invest Dermatol 128(3):738–740. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5701080
Berkowitz P, Hu P, Warren S, Liu Z, Diaz LA, Rubenstein DS (2006) p38MAPK inhibition prevents disease in pemphigus vulgaris mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(34):12855–12860. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602973103
Kitajima Y (2013) New insights into desmosome regulation and pemphigus blistering as a desmosome-remodeling disease. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 29(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2012.08.001
Arredondo J, Chernyavsky AI, Karaouni A, Grando SA (2005) Novel mechanisms of _target cell death and survival and of therapeutic action of IVIg in pemphigus. Am J Pathol 167(6):1531–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61239-4
Frusic-Zlotkin M, Pergamentz R, Michel B, David M, Mimouni D, Bregegere F, Milner Y (2005) The interaction of pemphigus autoimmunoglobulins with epidermal cells: activation of the fas apoptotic pathway and the use of caspase activity for pathogenicity tests of pemphigus patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1050:371–379. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1313.040
Gniadecki R, Jemec GB, Thomsen BM, Hansen M (1998) Relationship between keratinocyte adhesion and death: anoikis in acantholytic diseases. Arch Dermatol Res 290(10):528–532
Pacheco-Tovar MG, Avalos-Diaz E, Vega-Memije E, Bollain-y-Goytia JJ, Lopez-Robles E, Hojyo-Tomoka MT, Dominguez-Soto L, Herrera-Esparza R (2009) The final destiny of acantholytic cells in pemphigus is Fas mediated. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 23(6):697–701. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03162.x
Pelacho B, Natal C, Espana A, Sanchez-Carpintero I, Iraburu MJ, Lopez-Zabalza MJ (2004) Pemphigus vulgaris autoantibodies induce apoptosis in HaCaT keratinocytes. FEBS Lett 566(1–3):6–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2004.03.107
Puviani M, Marconi A, Cozzani E, Pincelli C (2003) Fas ligand in pemphigus sera induces keratinocyte apoptosis through the activation of caspase-8. J Invest Dermatol 120(1):164–167. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12014.x
Kalantari-Dehaghi M, Anhalt GJ, Camilleri MJ, Chernyavsky AI, Chun S, Felgner PL, Jasinskas A, Leiferman KM, Liang L, Marchenko S, Nakajima-Sasaki R, Pittelkow MR, Zone JJ, Grando SA (2013) Pemphigus vulgaris autoantibody profiling by proteomic technique. PLoS One 8(3):e57587. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057587
Marchenko S, Chernyavsky AI, Arredondo J, Gindi V, Grando SA (2010) Antimitochondrial autoantibodies in pemphigus vulgaris: a missing link in disease pathophysiology. J Biol Chem 285(6):3695–3704. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.081570
Evangelista F, Dasher DA, Diaz LA, Prisayanh PS, Li N (2008) E-cadherin is an additional immunological _target for pemphigus autoantibodies. J Invest Dermatol 128(7):1710–1718. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5701260
Kljuic A, Bazzi H, Sundberg JP, Martinez-Mir A, O'Shaughnessy R, Mahoney MG, Levy M, Montagutelli X, Ahmad W, Aita VM, Gordon D, Uitto J, Whiting D, Ott J, Fischer S, Gilliam TC, Jahoda CA, Morris RJ, Panteleyev AA, Nguyen VT, Christiano AM (2003) Desmoglein 4 in hair follicle differentiation and epidermal adhesion: evidence from inherited hypotrichosis and acquired pemphigus vulgaris. Cell 113(2):249–260
Nagasaka T, Nishifuji K, Ota T, Whittock NV, Amagai M (2004) Defining the pathogenic involvement of desmoglein 4 in pemphigus and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. J Clin Invest 114(10):1484–1492. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI20480
Oliveira ME, Culton DA, Prisayanh P, Qaqish BF, Diaz LA (2013) E-cadherin autoantibody profile in patients with pemphigus vulgaris. Br J Dermatol 169(4):812–818. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.12455
Dmochowski M, Hashimoto T, Garrod DR, Nishikawa T (1993) Desmocollins I and II are recognized by certain sera from patients with various types of pemphigus, particularly Brazilian pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol 100(4):380–384
Kim SC, Chung YL, Kim J, Cho NJ, Amagai M (2001) Pemphigus vulgaris with autoantibodies to desmoplakin. Br J Dermatol 145(5):838–840
Nguyen VT, Ndoye A, Grando SA (2000) Pemphigus vulgaris antibody identifies pemphaxin. A novel keratinocyte annexin-like molecule binding acetylcholine. J Biol Chem 275(38):29466–29476. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M003174200
Bhol KC, Rojas AI, Khan IU, Ahmed AR (2000) Presence of interleukin 10 in the serum and blister fluid of patients with pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigoid. Cytokine 12(7):1076–1083. https://doi.org/10.1006/cyto.1999.0642
D'Auria L, Bonifati C, Mussi A, D'Agosto G, De Simone C, Giacalone B, Ferraro C, Ameglio F (1997) Cytokines in the sera of patients with pemphigus vulgaris: interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha levels are significantly increased as compared to healthy subjects and correlate with disease activity. Eur Cytokine Netw 8(4):383–387
Satyam A, Khandpur S, Sharma VK, Sharma A (2009) Involvement of T(H)1/T(H)2 cytokines in the pathogenesis of autoimmune skin disease-pemphigus vulgaris. Immunol Investig 38(6):498–509
Hennerici T, Pollmann R, Schmidt T, Seipelt M, Tackenberg B, Mobs C, Ghoreschi K, Hertl M, Eming R (2016) Increased frequency of T follicular helper cells and elevated Interleukin-27 plasma levels in patients with pemphigus. PLoS One 11(2):e0148919. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148919
Timoteo RP, da Silva MV, Miguel CB, Silva DA, Catarino JD, Rodrigues Junior V, Sales-Campos H, Freire Oliveira CJ (2017) Th1/Th17-related cytokines and chemokines and their implications in the pathogenesis of pemphigus vulgaris. Mediat Inflamm 2017:7151285. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7151285
Zebrowska A, Wozniacka A, Juczynska K, Ociepa K, Waszczykowska E, Szymczak I, Pawliczak R (2017) Correlation between IL36alpha and IL17 and activity of the disease in selected autoimmune blistering diseases. Mediat Inflamm 2017:8980534. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8980534
Cho MJ, Ellebrecht CT, Payne AS (2015) The dual nature of interleukin-10 in pemphigus vulgaris. Cytokine 73(2):335–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2014.11.002
Ameglio F, D'Auria L, Cordiali-Fei P, Trento E, D'Agosto G, Mastroianni A, Giannetti A, Giacalone B (1999) Anti-intercellular substance antibody log titres are correlated with serum concentrations of interleukin-6, interleukin-15 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in patients with pemphigus vulgaris relationships with peripheral blood neutrophil counts, disease severity and duration and patients' age. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 13(4):220–224
Feliciani C, Toto P, Amerio P, Pour SM, Coscione G, Shivji G, Wang B, Sauder DN (2000) In vitro and in vivo expression of interleukin-1alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA in pemphigus vulgaris: interleukin-1alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha are involved in acantholysis. J Invest Dermatol 114(1):71–77. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00835.x
Lopez-Robles E, Avalos-Diaz E, Vega-Memije E, Hojyo-Tomoka T, Villalobos R, Fraire S, Domiguez-Soto L, Herrera-Esparza R (2001) TNFalpha and IL-6 are mediators in the blistering process of pemphigus. Int J Dermatol 40(3):185–188
Lotti R, Marconi A, Pincelli C (2012) Apoptotic pathways in the pathogenesis of pemphigus: _targets for new therapies. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 13(10):1877–1881
Janse IC, van der Wier G, Jonkman MF, Pas HH, Diercks GF (2014) No evidence of apoptotic cells in pemphigus acantholysis. J Invest Dermatol 134(7):2039–2041. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2014.60
Kurzen H, Brenner S (2006) Significance of autoimmunity to non-desmoglein _targets in pemphigus. Autoimmunity 39(7):549–556. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916930600971554
Anhalt GJ, Labib RS, Patel H, Diaz LA (1983) Animal models. Clin Dermatol 1(2):98–105
Takahashi Y, Patel HP, Labib RS, Diaz LA, Anhalt GJ (1985) Experimentally induced pemphigus vulgaris in neonatal BALB/c mice: a time-course study of clinical, immunologic, ultrastructural, and cytochemical changes. J Invest Dermatol 84(1):41–46
Anhalt GJ, Till GO, Diaz LA, Labib RS, Patel HP, Eaglstein NF (1986) Defining the role of complement in experimental pemphigus vulgaris in mice. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 137(9):2835–2840
Amagai M, Klaus-Kovtun V, Stanley JR (1991) Autoantibodies against a novel epithelial cadherin in pemphigus vulgaris, a disease of cell adhesion. Cell 67(5):869–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(91)90360-b
Rock B, Labib RS, Diaz LA (1990) Monovalent Fab' immunoglobulin fragments from endemic pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies reproduce the human disease in neonatal Balb/c mice. J Clin Invest 85(1):296–299. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci114426
Rock B, Martins CR, Theofilopoulos AN, Balderas RS, Anhalt GJ, Labib RS, Futamura S, Rivitti EA, Diaz LA (1989) The pathogenic effect of IgG4 autoantibodies in endemic pemphigus foliaceus (fogo selvagem). N Engl J Med 320(22):1463–1469. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm198906013202206
Koulu L, Kusumi A, Steinberg MS, Klaus-Kovtun V, Stanley JR (1984) Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal core protein in pemphigus foliaceus. J Exp Med 160(5):1509–1518
Koch PJ, Mahoney MG, Ishikawa H, Pulkkinen L, Uitto J, Shultz L, Murphy GF, Whitaker-Menezes D, Stanley JR (1997) _targeted disruption of the pemphigus vulgaris antigen (desmoglein 3) gene in mice causes loss of keratinocyte cell adhesion with a phenotype similar to pemphigus vulgaris. J Cell Biol 137(5):1091–1102
Amagai M (2008) Pemphigus vulgaris and its active disease mouse model. Curr Dir Autoimmun 10:167–181. https://doi.org/10.1159/000131453
Ohyama M, Amagai M, Tsunoda K, Ota T, Koyasu S, J-i H, Umezawa A, Nishikawa T (2002) Immunologic and histopathologic characterization of an active disease mouse model for pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 118(1):199–204. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0022-202x.2001.01643.x
Shimizu A, Ishiko A, Ota T, Tsunoda K, Koyasu S, Amagai M, Nishikawa T (2002) Ultrastructural changes in mice actively producing antibodies to desmoglein 3 parallel those in patients with pemphigus vulgaris. Arch Dermatol Res 294(7):318–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-002-0341-z
Tsunoda K, Ota T, Aoki M, Yamada T, Nagai T, Nakagawa T, Koyasu S, Nishikawa T, Amagai M (2003) Induction of pemphigus phenotype by a mouse monoclonal antibody against the amino-terminal adhesive interface of desmoglein 3. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 170(4):2170–2178
Shimizu A, Ishiko A, Ota T, Saito H, Oka H, Tsunoda K, Amagai M, Nishikawa T (2005) In vivo ultrastructural localization of the desmoglein 3 adhesive interface to the desmosome mid-line. J Invest Dermatol 124(5):984–989. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23706.x
Shimizu A, Ishiko A, Ota T, Tsunoda K, Amagai M, Nishikawa T (2004) IgG binds to desmoglein 3 in desmosomes and causes a desmosomal split without keratin retraction in a pemphigus mouse model. J Invest Dermatol 122(5):1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22426.x
Takahashi H, Amagai M, Nishikawa T, Fujii Y, Kawakami Y, Kuwana M (2008) Novel system evaluating in vivo pathogenicity of desmoglein 3-reactive T cell clones using murine pemphigus vulgaris. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 181(2):1526–1535
Takahashi H, Kuwana M, Amagai M (2009) A single helper T cell clone is sufficient to commit polyclonal naive B cells to produce pathogenic IgG in experimental pemphigus vulgaris. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 182(3):1740–1745
Aoki-Ota M, Kinoshita M, Ota T, Tsunoda K, Iwasaki T, Tanaka S, Koyasu S, Nishikawa T, Amagai M (2006) Tolerance induction by the blockade of CD40/CD154 interaction in pemphigus vulgaris mouse model. J Invest Dermatol 126(1):105–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5700016
YOKOYAMA T, Matsuda S, Takae Y, Wada N, Nishikawa T, Amagai M, Koyasu S (2011) Antigen-independent development of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells suppressing autoantibody production in experimental pemphigus vulgaris. Int Immunol 23(6):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxr020
Aoki-Ota M, Tsunoda K, Ota T, Iwasaki T, Koyasu S, Amagai M, Nishikawa T (2004) A mouse model of pemphigus vulgaris by adoptive transfer of naive splenocytes from desmoglein 3 knockout mice. Br J Dermatol 151(2):346–354. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06056.x
Kawasaki H, Tsunoda K, Hata T, Ishii K, Yamada T, Amagai M (2006) Synergistic pathogenic effects of combined mouse monoclonal anti-desmoglein 3 IgG antibodies on pemphigus vulgaris blister formation. J Invest Dermatol 126(12):2621–2630. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5700450
Fan JL, Memar O, McCormick DJ, Prabhakar BS (1999) BALB/c mice produce blister-causing antibodies upon immunization with a recombinant human desmoglein 3. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 163(11):6228–6235
Kaithamana S, Fan J-L, Memar O, Li K, Uitto J, Seetharamaiah GS, Prabhakar BS (2003) Relevance of differential immunogenicity of human and mouse recombinant desmoglein-3 for the induction of acantholytic autoantibodies in mice. Clin Exp Immunol 132(1):16–23
Ishikawa H, Li K, Tamai K, Sawamura D, Uitto J (2000) Cloning of the mouse desmoglein 3 gene (Dsg3): interspecies conservation within the cadherin superfamily. Exp Dermatol 9(4):229–239
CULTON DA, McCray SK, Park M, Roberts JC, Li N, Zedek DC, Anhalt GJ, Cowley DO, Liu Z, Diaz LA (2015) Mucosal pemphigus vulgaris anti-Dsg3 IgG is pathogenic to the oral mucosa of humanized Dsg3 mice. J Invest Dermatol 135(6):1590–1597. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2015.54
Loiseau P, Lecleach L, Prost C, Lepage V, Busson M, Bastuji-Garin S, Roujeau JC, Charron D (2000) HLA class II polymorphism contributes to specify desmoglein derived peptides in pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. J Autoimmun 15(1):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaut.2000.0388
Svecova D, Parnicka Z, Pastyrikova L, Urbancek S, Luha J, Buc M (2015) HLA DRB1* and DQB1* alleles are associated with disease severity in patients with pemphigus vulgaris. Int J Dermatol 54(2):168–173. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.12418
Lee E, Lendas KA, Chow S, Pirani Y, Gordon D, Dionisio R, Nguyen D, Spizuoco A, Fotino M, Zhang Y, Sinha AA (2006) Disease relevant HLA class II alleles isolated by genotypic, haplotypic, and sequence analysis in north American Caucasians with pemphigus vulgaris. Hum Immunol 67(1–2):125–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2005.09.003
Wucherpfennig KW, Strominger JL (1995) Selective binding of self peptides to disease-associated major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules: a mechanism for MHC-linked susceptibility to human autoimmune diseases. J Exp Med 181(5):1597–1601
Wucherpfennig KW, Yu B, Bhol K, Monos DS, Argyris E, Karr RW, Ahmed AR, Strominger JL (1995) Structural basis for major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-linked susceptibility to autoimmunity: charged residues of a single MHC binding pocket confer selective presentation of self-peptides in pemphigus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(25):11935–11939
Hertl M, Eming R, Veldman C (2006) T cell control in autoimmune bullous skin disorders. J Clin Invest 116(5):1159–1166. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci28547
Eming R, Hennerici T, Bäcklund J, Feliciani C, Visconti KC, Willenborg S, Wohde J, Holmdahl R, Sønderstrup G, Hertl M (2014) Pathogenic IgG antibodies against desmoglein 3 in pemphigus vulgaris are regulated by HLA-DRB1*04:02-restricted T cells. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 193(9):4391–4399. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1401081
Schmidt T, Willenborg S, Hünig T, Deeg CA, Sonderstrup G, Hertl M, Eming R (2016) Induction of T regulatory cells by the superagonistic anti-CD28 antibody D665 leads to decreased pathogenic IgG autoantibodies against desmoglein 3 in a HLA-transgenic mouse model of pemphigus vulgaris. Exp Dermatol 25(4):293–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.12919
Zhao CY, Murrell DF (2015) Pemphigus vulgaris: an evidence-based treatment update. Drugs 75(3):271–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0353-6
Beissert S, Werfel T, Frieling U, Bohm M, Sticherling M, Stadler R, Zillikens D, Rzany B, Hunzelmann N, Meurer M, Gollnick H, Ruzicka T, Pillekamp H, Junghans V, Luger TA (2006) A comparison of oral methylprednisolone plus azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil for the treatment of pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 142(11):1447–1454. https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.142.11.1447
Beissert S, Mimouni D, Kanwar AJ, Solomons N, Kalia V, Anhalt GJ (2010) Treating pemphigus vulgaris with prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Invest Dermatol 130(8):2041–2048. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2010.91
Chams-Davatchi C, Mortazavizadeh A, Daneshpazhooh M, Davatchi F, Balighi K, Esmaili N, Akhyani M, Hallaji Z, Seirafi H, Mortazavi H (2013) Randomized double blind trial of prednisolone and azathioprine, vs. prednisolone and placebo, in the treatment of pemphigus vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27(10):1285–1292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04717.x
Enk AH, Hadaschik EN, Eming R, Fierlbeck G, French LE, Girolomoni G, Hertl M, Jolles S, Karpati S, Steinbrink K, Stingl G, Volc-Platzer B, Zillikens D (2016) European guidelines (S1) on the use of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in dermatology. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 30(10):1657–1669. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.13725
Eming R, Hertl M (2006) Immunoadsorption in pemphigus. Autoimmunity 39(7):609–616. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916930600972040
Kasperkiewicz M, Eming R, Behzad M, Hunzelmann N, Meurer M, Schulze-Koops H, von Wussow P, Hertl M, Zillikens D, Freivogel K, Dorner T, Schmidt E (2012) Efficacy and safety of rituximab in pemphigus: experience of the German registry of autoimmune diseases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 10(10):727–732. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1610-0387.2012.07931.x
Joly P, Maho-Vaillant M, Prost-Squarcioni C, Hebert V, Houivet E, Calbo S, Caillot F, Golinski ML, Labeille B, Picard-Dahan C, Paul C, Richard MA, Bouaziz JD, Duvert-Lehembre S, Bernard P, Caux F, Alexandre M, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Vabres P, Delaporte E, Quereux G, Dupuy A, Debarbieux S, Avenel-Audran M, D'Incan M, Bedane C, Beneton N, Jullien D, Dupin N, Misery L, Machet L, Beylot-Barry M, Dereure O, Sassolas B, Vermeulin T, Benichou J, Musette P, French study group on autoimmune bullous skin d (2017) First-line rituximab combined with short-term prednisone versus prednisone alone for the treatment of pemphigus (Ritux 3): a prospective, multicentre, parallel-group, open-label randomised trial. Lancet 389 (10083):2031–2040. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30070-3
Hammers CM, Stanley JR (2016) Mechanisms of disease: pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Annu Rev Pathol 11:175–197. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-012615-044313
Kasperkiewicz M, Ellebrecht CT, Takahashi H, Yamagami J, Zillikens D, Payne AS, Amagai M (2017) Pemphigus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17026. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.26
Amber KT, Staropoli P, Shiman MI, Elgart GW, Hertl M (2013) Autoreactive T cells in the immune pathogenesis of pemphigus vulgaris. Exp Dermatol 22(11):699–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.12229
Hertl M, Karr RW, Amagai M, Katz SI (1998) Heterogeneous MHC II restriction pattern of autoreactive desmoglein 3 specific T cell responses in pemphigus vulgaris patients and normals. J Invest Dermatol 110(4):388–392. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00156.x
Veldman CM, Gebhard KL, Uter W, Wassmuth R, Grotzinger J, Schultz E, Hertl M (2004) T cell recognition of desmoglein 3 peptides in patients with pemphigus vulgaris and healthy individuals. J Immunol 172(6):3883–3892
Beutner EH, Jordon RE (1964) Demonstration of skin antibodies in sera of pemphigus vulgaris patients by indirect immunofluorescent staining. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 117:505–510
Colliou N, Picard D, Caillot F, Calbo S, Le Corre S, Lim A, Lemercier B, Le Mauff B, Maho-Vaillant M, Jacquot S, Bedane C, Bernard P, Caux F, Prost C, Delaporte E, Doutre MS, Dreno B, Franck N, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Chosidow O, Pauwels C, Picard C, Roujeau JC, Sigal M, Tancrede-Bohin E, Templier I, Eming R, Hertl M, D'Incan M, Joly P, Musette P (2013) Long-term remissions of severe pemphigus after rituximab therapy are associated with prolonged failure of desmoglein B cell response. Sci Transl Med 5 (175):175ra130. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3005166
Eming R, Nagel A, Wolff-Franke S, Podstawa E, Debus D, Hertl M (2008) Rituximab exerts a dual effect in pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 128(12):2850–2858. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2008.172
Hammers CM, Chen J, Lin C, Kacir S, Siegel DL, Payne AS, Stanley JR (2015) Persistence of anti-desmoglein 3 IgG(+) B-cell clones in pemphigus patients over years. J Invest Dermatol 135(3):742–749. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2014.291
Alexander T, Sarfert R, Klotsche J, Kuhl AA, Rubbert-Roth A, Lorenz HM, Rech J, Hoyer BF, Cheng Q, Waka A, Taddeo A, Wiesener M, Schett G, Burmester GR, Radbruch A, Hiepe F, Voll RE (2015) The proteasome inhibitior bortezomib depletes plasma cells and ameliorates clinical manifestations of refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 74(7):1474–1478. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206016
Ichikawa HT, Conley T, Muchamuel T, Jiang J, Lee S, Owen T, Barnard J, Nevarez S, Goldman BI, Kirk CJ, Looney RJ, Anolik JH (2012) Beneficial effect of novel proteasome inhibitors in murine lupus via dual inhibition of type I interferon and autoantibody-secreting cells. Arthritis Rheum 64(2):493–503. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.33333
Taddeo A, Khodadadi L, Voigt C, Mumtaz IM, Cheng Q, Moser K, Alexander T, Manz RA, Radbruch A, Hiepe F, Hoyer BF (2015) Long-lived plasma cells are early and constantly generated in New Zealand black/New Zealand white F1 mice and their therapeutic depletion requires a combined _targeting of autoreactive plasma cells and their precursors. Arthritis Res Ther 17:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-015-0551-3
Hiepe F, Radbruch A (2016) Plasma cells as an innovative _target in autoimmune disease with renal manifestations. Nat Rev Nephrol 12(4):232–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2016.20
Ellebrecht CT, Choi EJ, Allman DM, Tsai DE, Wegener WA, Goldenberg DM, Payne AS (2014) Subcutaneous veltuzumab, a humanized anti-CD20 antibody, in the treatment of refractory pemphigus vulgaris. JAMA Dermatol 150(12):1331–1335. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1939
Huang A, Madan RK, Levitt J (2016) Future therapies for pemphigus vulgaris: rituximab and beyond. J Am Acad Dermatol 74(4):746–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.008
Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z, Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Hughes G (2016) Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16039. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.39
Stohl W (2017) Inhibition of B cell activating factor (BAFF) in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Expert Rev Clin Immunol 13(6):623–633. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666X.2017.1291343
Ellebrecht CT, Bhoj VG, Nace A, Choi EJ, Mao X, Cho MJ, Di Zenzo G, Lanzavecchia A, Seykora JT, Cotsarelis G, Milone MC, Payne AS (2016) Reengineering chimeric antigen receptor T cells for _targeted therapy of autoimmune disease. Science 353(6295):179–184. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf6756
Kochenderfer JN, Dudley ME, Kassim SH, Somerville RP, Carpenter RO, Stetler-Stevenson M, Yang JC, Phan GQ, Hughes MS, Sherry RM, Raffeld M, Feldman S, Lu L, Li YF, Ngo LT, Goy A, Feldman T, Spaner DE, Wang ML, Chen CC, Kranick SM, Nath A, Nathan DA, Morton KE, Toomey MA, Rosenberg SA (2015) Chemotherapy-refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and indolent B-cell malignancies can be effectively treated with autologous T cells expressing an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor. J Clin Oncol 33(6):540–549. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.56.2025
Lee DW, Kochenderfer JN, Stetler-Stevenson M, Cui YK, Delbrook C, Feldman SA, Fry TJ, Orentas R, Sabatino M, Shah NN, Steinberg SM, Stroncek D, Tschernia N, Yuan C, Zhang H, Zhang L, Rosenberg SA, Wayne AS, Mackall CL (2015) T cells expressing CD19 chimeric antigen receptors for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children and young adults: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet 385(9967):517–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61403-3
Maude SL, Frey N, Shaw PA, Aplenc R, Barrett DM, Bunin NJ, Chew A, Gonzalez VE, Zheng Z, Lacey SF, Mahnke YD, Melenhorst JJ, Rheingold SR, Shen A, Teachey DT, Levine BL, June CH, Porter DL, Grupp SA (2014) Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in leukemia. N Engl J Med 371(16):1507–1517. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1407222
Eming R, Hennerici T, Backlund J, Feliciani C, Visconti KC, Willenborg S, Wohde J, Holmdahl R, Sonderstrup G, Hertl M (2014) Pathogenic IgG antibodies against desmoglein 3 in pemphigus vulgaris are regulated by HLA-DRB1*04:02-restricted T cells. J Immunol 193(9):4391–4399. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1401081
Bhol K, Natarajan K, Nagarwalla N, Mohimen A, Aoki V, Ahmed AR (1995) Correlation of peptide specificity and IgG subclass with pathogenic and nonpathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus vulgaris: a model for autoimmunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(11):5239–5243
Lo AS, Mao X, Mukherjee EM, Ellebrecht CT, Yu X, Posner MR, Payne AS, Cavacini LA (2016) Pathogenicity and epitope characteristics do not differ in IgG subclass-switched anti-desmoglein 3 IgG1 and IgG4 autoantibodies in pemphigus vulgaris. PLoS One 11(6):e0156800. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156800
Spaeth S, Riechers R, Borradori L, Zillikens D, Budinger L, Hertl M (2001) IgG, IgA and IgE autoantibodies against the ectodomain of desmoglein 3 in active pemphigus vulgaris. Br J Dermatol 144(6):1183–1188
Nagel A, Lang A, Engel D, Podstawa E, Hunzelmann N, de Pita O, Borradori L, Uter W, Hertl M (2010) Clinical activity of pemphigus vulgaris relates to IgE autoantibodies against desmoglein 3. Clin Immunol 134(3):320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2009.11.006
Xu RC, Zhu HQ, Li WP, Zhao XQ, Yuan HJ, Zheng J, Pan M (2013) The imbalance of Th17 and regulatory T cells in pemphigus patients. Eur J Dermatol 23(6):795–802. https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2013.2177
Asothai R, Anand V, Das D, Antil PS, Khandpur S, Sharma VK, Sharma A (2015) Distinctive Treg associated CCR4-CCL22 expression profile with altered frequency of Th17/Treg cell in the immunopathogenesis of pemphigus vulgaris. Immunobiology 220(10):1129–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2015.06.008
Miller SD, Turley DM, Podojil JR (2007) Antigen-specific tolerance strategies for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol 7(9):665–677. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2153
Pearson RM, Casey LM, Hughes KR, Miller SD, Shea LD (2017) In vivo reprogramming of immune cells: technologies for induction of antigen-specific tolerance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2017.04.005
Prasad S, Kohm AP, McMahon JS, Luo X, Miller SD (2012) Pathogenesis of NOD diabetes is initiated by reactivity to the insulin B chain 9-23 epitope and involves functional epitope spreading. J Autoimmun 39(4):347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2012.04.005
Turley DM, Miller SD (2007) Peripheral tolerance induction using ethylenecarbodiimide-fixed APCs uses both direct and indirect mechanisms of antigen presentation for prevention of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 178(4):2212–2220
Lutterotti A, Yousef S, Sputtek A, Sturner KH, Stellmann JP, Breiden P, Reinhardt S, Schulze C, Bester M, Heesen C, Schippling S, Miller SD, Sospedra M, Martin R (2013) Antigen-specific tolerance by autologous myelin peptide-coupled cells: a phase 1 trial in multiple sclerosis. Sci Transl Med 5 (188):188ra175. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3006168
Getts DR, Martin AJ, McCarthy DP, Terry RL, Hunter ZN, Yap WT, Getts MT, Pleiss M, Luo X, King NJ, Shea LD, Miller SD (2012) Microparticles bearing encephalitogenic peptides induce T-cell tolerance and ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat Biotechnol 30(12):1217–1224. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2434
Pearson RM, Casey LM, Hughes KR, Wang LZ, North MG, Getts DR, Miller SD, Shea LD (2017) Controlled delivery of single or multiple antigens in tolerogenic nanoparticles using peptide-polymer bioconjugates. Mol Ther 25(7):1655–1664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.04.015
Serra P, Santamaria P (2015) Nanoparticle-based autoimmune disease therapy. Clin Immunol 160(1):3–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2015.02.003
Veldman C, Pahl A, Beissert S, Hansen W, Buer J, Dieckmann D, Schuler G, Hertl M (2006) Inhibition of the transcription factor Foxp3 converts desmoglein 3-specific type 1 regulatory T cells into Th2-like cells. J Immunol 176(5):3215–3222
Klatzmann D, Abbas AK (2015) The promise of low-dose interleukin-2 therapy for autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 15(5):283–294. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3823
Saadoun D, Rosenzwajg M, Joly F, Six A, Carrat F, Thibault V, Sene D, Cacoub P, Klatzmann D (2011) Regulatory T-cell responses to low-dose interleukin-2 in HCV-induced vasculitis. N Engl J Med 365(22):2067–2077. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1105143
Koreth J, Matsuoka K, Kim HT, McDonough SM, Bindra B, Alyea EP 3rd, Armand P, Cutler C, Ho VT, Treister NS, Bienfang DC, Prasad S, Tzachanis D, Joyce RM, Avigan DE, Antin JH, Ritz J, Soiffer RJ (2011) Interleukin-2 and regulatory T cells in graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med 365(22):2055–2066. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1108188
He J, Zhang X, Wei Y, Sun X, Chen Y, Deng J, Jin Y, Gan Y, Hu X, Jia R, Xu C, Hou Z, Leong YA, Zhu L, Feng J, An Y, Jia Y, Li C, Liu X, Ye H, Ren L, Li R, Yao H, Li Y, Chen S, Zhang X, Su Y, Guo J, Shen N, Morand EF, Yu D, Li Z (2016) Low-dose interleukin-2 treatment selectively modulates CD4(+) T cell subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Med 22(9):991–993. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4148
Sawaf M, Dumortier H, Monneaux F (2016) Follicular helper T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: why should they be considered as interesting therapeutic _targets? J Immunol Res 2016:5767106. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5767106
Elwood F, Witter DJ, Piesvaux J, Kraybill B, Bays N, Alpert C, Goldenblatt P, Qu Y, Ivanovska I, Lee HH, Chiu CS, Tang H, Scott ME, Deshmukh SV, Zielstorff M, Byford A, Chakravarthy K, Dorosh L, Rivkin A, Klappenbach J, Pan BS, Kariv I, Dinsmore C, Slipetz D, Dandliker PJ (2017) Evaluation of JAK3 biology in autoimmune disease using a highly selective, irreversible JAK3 inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 361(2):229–244. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.116.239723
Winthrop KL (2017) The emerging safety profile of JAK inhibitors in rheumatic disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol 13(5):320. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2017.51
Eming R, Rech J, Barth S, Kalden JR, Schuler G, Harrer T, Hertl M (2006) Prolonged clinical remission of patients with severe pemphigus upon rapid removal of desmoglein-reactive autoantibodies by immunoadsorption. Dermatology 212(2):177–187. https://doi.org/10.1159/000090659
Langenhan J, Dworschak J, Saschenbrecker S, Komorowski L, Schlumberger W, Stocker W, Westermann J, Recke A, Zillikens D, Schmidt E, Probst C (2014) Specific immunoadsorption of pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus requires the entire ectodomains of desmogleins. Exp Dermatol 23(4):253–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.12355
Schmidt E, Spindler V, Eming R, Amagai M, Antonicelli F, Baines JF, Belheouane M, Bernard P, Borradori L, Caproni M, Di Zenzo G, Grando S, Harman K, Jonkman MF, Koga H, Ludwig RJ, Kowalczyk AP, Muller EJ, Nishie W, Pas H, Payne AS, Sadik CD, Seppanen A, Setterfield J, Shimizu H, Sinha AA, Sprecher E, Sticherling M, Ujiie H, Zillikens D, Hertl M, Waschke J (2017) Meeting report of the pathogenesis of pemphigus and pemphigoid meeting in Munich, September 2016. J Invest Dermatol 137(6):1199–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2017.01.028
Galichet A, Borradori L, Muller EJ (2014) A new light on an old disease: adhesion signaling in pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 134(1):8–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.439
Walter E, Vielmuth F, Rotkopf L, Sardy M, Horvath ON, Goebeler M, Schmidt E, Eming R, Hertl M, Spindler V, Waschke J (2017) Different signaling patterns contribute to loss of keratinocyte cohesion dependent on autoantibody profile in pemphigus. Sci Rep 7(1):3579. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03697-7
Egu DT, Walter E, Spindler V, Waschke J (2017) Inhibition of p38MAPK signaling prevents epidermal blistering and alterations of desmosome structure induced by pemphigus autoantibodies in human epidermis. Br J Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.15721
Sweeney SE (2009) The as-yet unfulfilled promise of p38 MAPK inhibitors. Nat Rev Rheumatol 5(9):475–477. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2009.171
Schultz HY, Diaz LA, Sirois DA, Werth VP, Grando SA (2011) Generating consensus research goals and treatment strategies for pemphigus and pemphigoid: the 2010 JC Bystryn pemphigus and pemphigoid meeting. J Invest Dermatol 131(7):1395–1399. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.120
Pacheco-Tovar D, Lopez-Luna A, Herrera-Esparza R, Avalos-Diaz E (2011) The caspase pathway as a possible therapeutic _target in experimental pemphigus. Autoimmune Dis 2011:563091. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/563091
Li N, Zhao M, Wang J, Liu Z, Diaz LA (2009) Involvement of the apoptotic mechanism in pemphigus foliaceus autoimmune injury of the skin. J Immunol 182(1):711–717
Schmidt-Hieber M, Dabrowski R, Aicher B, Lohneis P, Busse A, Tietze-Buerger C, Reufi B, Thiel E, Blau IW (2012) In vitro effects of perifosine, bortezomib and lenalidomide against hematopoietic progenitor cells from healthy donors. Investig New Drugs 30(4):1396–1403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9705-6
van der Helm LH, Bosman MC, Schuringa JJ, Vellenga E (2015) Effective _targeting of primitive AML CD34+ cells by the second-generation proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib. Br J Haematol 171(4):652–655. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13418
Kaur K, Kalra S, Kaushal S (2014) Systematic review of tofacitinib: a new drug for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther 36(7):1074–1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.06.018
Xing L, Dai Z, Jabbari A, Cerise JE, Higgins CA, Gong W, de Jong A, Harel S, DeStefano GM, Rothman L, Singh P, Petukhova L, Mackay-Wiggan J, Christiano AM, Clynes R (2014) Alopecia areata is driven by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and is reversed by JAK inhibition. Nat Med 20(9):1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3645
Merrill JT, Burgos-Vargas R, Westhovens R, Chalmers A, D'Cruz D, Wallace DJ, Bae SC, Sigal L, Becker JC, Kelly S, Raghupathi K, Li T, Peng Y, Kinaszczuk M, Nash P (2010) The efficacy and safety of abatacept in patients with non-life-threatening manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a twelve-month, multicenter, exploratory, phase IIb, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 62(10):3077–3087. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27601
de Paoli FV, Nielsen BD, Rasmussen F, Deleuran B, Sondergaard K (2014) Abatacept induces clinical improvement in patients with severe systemic sclerosis. Scand J Rheumatol 43(4):342–345. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009742.2013.812238
Emery P, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Combe BG, Furst DE, Barre E, Karyekar CS, Wong DA, Huizinga TW (2015) Evaluating drug-free remission with abatacept in early rheumatoid arthritis: results from the phase 3b, multicentre, randomised, active-controlled AVERT study of 24 months, with a 12-month, double-blind treatment period. Ann Rheum Dis 74(1):19–26. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206106
Mease PJ, Gottlieb AB, van der Heijde D, FitzGerald O, Johnsen A, Nys M, Banerjee S, Gladman DD (2017) Efficacy and safety of abatacept, a T-cell modulator, in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 76(9):1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210724
Narbutt J, Lukamowicz J, Bogaczewicz J, Sysa-Jedrzejowska A, Torzecka JD, Lesiak A (2008) Serum concentration of interleukin-6 is increased both in active and remission stages of pemphigus vulgaris. Mediat Inflamm 2008:875394. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/875394
Elhai M, Meunier M, Matucci-Cerinic M, Maurer B, Riemekasten G, Leturcq T, Pellerito R, Von Muhlen CA, Vacca A, Airo P, Bartoli F, Fiori G, Bokarewa M, Riccieri V, Becker M, Avouac J, Muller-Ladner U, Distler O, Allanore Y, Eustar (2013) Outcomes of patients with systemic sclerosis-associated polyarthritis and myopathy treated with tocilizumab or abatacept: a EUSTAR observational study. Ann Rheum Dis 72 (7):1217–1220. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202657
Khanna D, Denton CP, Merkel PA, Krieg T, Le Brun FO, Marr A, Papadakis K, Pope J, Matucci-Cerinic M, Furst DE, Investigators D, Investigators D (2016) Effect of Macitentan on the development of new ischemic digital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis: DUAL-1 and DUAL-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA 315(18):1975–1988. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.5258
Acknowledgements
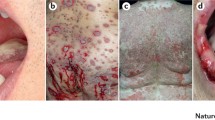
We are grateful to Günther Henkel and Irina Nuhn for the clinical photographs. This review was supported by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation-FOR 2497) to TS, RE and MH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
When necessary, informed consent has been collected from patients.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollmann, R., Schmidt, T., Eming, R. et al. Pemphigus: a Comprehensive Review on Pathogenesis, Clinical Presentation and Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 54, 1–25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8662-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-017-8662-z