Abstract
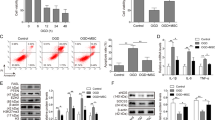
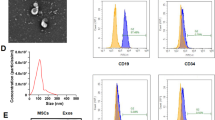
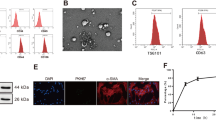
Exosomes-related microRNAs (miRNAs) have been considered to be the significant biomarkers contributing to the development of atrial fibrillation (AF). We observed the implicit mechanism of exosomes-miR-148a derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) in AF. The AF cell and mice models were established firstly. QRT-PCR and Western blot analysis were applied to detect the expression of miR-148a, SPARC-associated modular calcium-binding protein 2 (SMOC2), Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase-3. BMSCs were separated from healthy mice and exosomes were obtained from BMSCs. BMSCs were transfected with mimics and inhibitor, and HL-1 cells were treated with mimics and pcDNA3.1. MTT assay were used to detect cell viability of cells. Flow cytometric analysis and TUNEL analysis were used for detecting cell apoptosis of cells. In our study, exosomes derived from BMSCs inhibited the development of AF, and miR-148a acted a vital role in this segment. SMOC2 was a _target gene of miR-148a and promoted apoptosis of HL-1 cells. Additionally, miR-148a mimics decreased cellular apoptosis, eliminated SMOC2 expression, and elevated Bcl-2 expression in AF-treated cells. Collectively, miR-148a overexpressed in BMSC-exosomes restrained cardiomyocytes apoptosis by inhibiting SMOC2.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- BMSCs:
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- SPARC:
-
Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine
- SMOC2:
-
SPARC-associated modular calcium-binding protein 2
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2
- Bax:
-
BCL2-associated X protein
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5)-Dimethylthiahiazo(-z-y1)-3,5-di- phenytetrazoliumromide
- mRNAs:
-
Messenger RNAs
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- RIP:
-
RNA immunoprecipitation
References
Xiao, J., Zhang, Y., Tang, Y., Dai, H., OuYang, Y., Li, C., & Yu, M. (2021). hsa-miR-4443 inhibits myocardial fibroblast proliferation by _targeting THBS1 to regulate TGF-beta1/alpha-SMA/collagen signaling in atrial fibrillation. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 54(4), e10692. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431X202010692
Shen, N. N., Zhang, C., Li, Z., Kong, L. C., Wang, X. H., Gu, Z. C., & Wang, J. L. (2020). MicroRNA expression signatures of atrial fibrillation: The critical systematic review and bioinformatics analysis. Experimental Biology and Medicine (Maywood, N.J.), 245(1), 42–53. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370219890303
Komal, S., Yin, J. J., Wang, S. H., Huang, C. Z., Tao, H. L., Dong, J. Z., Han, S. N., & Zhang, L. R. (2019). MicroRNAs: Emerging biomarkers for atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiology, 74(6), 475–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjcc.2019.05.018
Jiang, M., Zhang, X., Wang, X., Xu, F., Zhang, J., Li, L., Xie, X., Wang, L., Yang, Y., & Xu, J. T. (2021). MicroRNA-124-3p attenuates the development of nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain by _targeting early growth response 1 in the dorsal root ganglia and spinal dorsal horn. Journal of Neurochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15433
Miao, C., Wang, X., Zhou, W., & Huang, J. (2021). The emerging roles of exosomes in autoimmune diseases, with special emphasis on microRNAs in exosomes. Pharmacological Research, 169, 105680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105680
Huang, Y. (2018). The novel regulatory role of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 22(12), 5768–5775. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13866
Acunzo, M., Romano, G., Wernicke, D., & Croce, C. M. (2015). MicroRNA and cancer–a brief overview. Advances in Biological Regulation, 57, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.013
Wojciechowska, A., Braniewska, A., & Kozar-Kaminska, K. (2017). MicroRNA in cardiovascular biology and disease. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 26(5), 865–874. https://doi.org/10.17219/acem/62915
Zhao, Y., Samal, E., & Srivastava, D. (2005). Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that _targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature, 436(7048), 214–220. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03817
Gao, F., Kataoka, M., Liu, N., Liang, T., Huang, Z.-P., Gu, F., Ding, J., Liu, J., Zhang, F., Ma, Q., Wang, Y., Zhang, M., Hu, X., Kyselovic, J., Hu, X., Pu, W. T., Ja, W., Chen, J., & Wang, D.-Z. (2019). Therapeutic role of miR-19a/19b in cardiac regeneration and protection from myocardial infarction. Nature Communications, 10(1), 1802–1802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09530-1
Natsume, Y., Oaku, K., Takahashi, K., Nakamura, W., Oono, A., Hamada, S., Yamazoe, M., Ihara, K., Sasaki, T., Goya, M., Hirao, K., Furukawa, T., & Sasano, T. (2018). Combined analysis of human and experimental murine samples identified novel circulating MicroRNAs as biomarkers for atrial fibrillation. Circulation Journal, 82(4), 965–973. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-17-1194
da Silva, A. M. G., de Araujo, J. N. G., de Oliveira, K. M., Novaes, A. E. M., Lopes, M. B., de Sousa, J. C. V., Filho, A. A. A., Luchessi, A. D., de Rezende, A. A., Hirata, M. H., & Silbiger, V. N. (2018). Circulating miRNAs in acute new-onset atrial fibrillation and their _target mRNA network. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 29(8), 1159–1166. https://doi.org/10.1111/jce.13612
Chiang, D. Y., Zhang, M., Voigt, N., Alsina, K. M., Jakob, H., Martin, J. F., Dobrev, D., Wehrens, X. H. T., & Li, N. (2015). Identification of microRNA-mRNA dysregulations in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. International Journal of Cardiology, 184, 190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.01.075
Lo Sicco, C., Reverberi, D., Balbi, C., Ulivi, V., Principi, E., Pascucci, L., Becherini, P., Bosco, M. C., Varesio, L., Franzin, C., Pozzobon, M., Cancedda, R., & Tasso, R. (2017). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as mediators of anti-inflammatory effects: endorsement of macrophage polarization. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 6(3), 1018–1028. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.16-0363
Nguyen, H. P., Simpson, R. J., Salamonsen, L. A., & Greening, D. W. (2016). Extracellular vesicles in the intrauterine environment: challenges and potential functions. Biology of Reproduction, 95(5), 109. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.116.143503
Yang, J., Liu, X. X., Fan, H., Tang, Q., Shou, Z. X., Zuo, D. M., Zou, Z., Xu, M., Chen, Q. Y., Peng, Y., Deng, S. J., & Liu, Y. J. (2015). Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against experimental colitis via attenuating colon inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. PLoS ONE, 10(10), e0140551. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140551
Yang, M., Lin, L., Sha, C., Li, T., Zhao, D., Wei, H., Chen, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, X., Xu, W., Li, Y., & Zhu, X. (2020). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-144-5p improves rat ovarian function after chemotherapy-induced ovarian failure by _targeting PTEN. Laboratory Investigation, 100(3), 342–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-019-0321-y
Liao, W., Ning, Y., Xu, H.-J., Zou, W.-Z., Hu, J., Liu, X.-Z., Yang, Y., & Li, Z.-H. (2019). BMSC-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-122-5p promote proliferation of osteoblasts in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clinical Science, 133(18), 1955–1975. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20181064
Huang, S., Li, Y., Wu, P., Xiao, Y., Duan, N., Quan, J., & Du, W. (2020). microRNA-148a-3p in extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppresses SMURF1 to prevent osteonecrosis of femoral head. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(19), 11512–11523. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15766
Jiang, C. K., & Gong, F. (2017). Regulation and mechanism of miR-148a on cardiomyocyte differentiation induced by 5-aza in mesenchymal stem cells. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology, 33(6), 514–518. https://doi.org/10.12047/j.cjap.5601.2017.122
Lu, M., Huang, L., Tang, Y., Sun, T., Li, J., Xiao, S., Zheng, X., Christopher, O., & Mao, H. (2020). ARNTL2 knockdown suppressed the invasion and migration of colon carcinoma: Decreased SMOC2-EMT expression through inactivation of PI3K/AKT pathway. American Journal of Translational Research, 12(4), 1293–1308.
Liu, P., Lu, J., Cardoso, W. V., & Vaziri, C. (2008). The SPARC-related factor SMOC-2 promotes growth factor-induced cyclin D1 expression and DNA synthesis via integrin-linked kinase. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 19(1), 248–261. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0510
Luo, L., Wang, C.-C., Song, X.-P., Wang, H.-M., Zhou, H., Sun, Y., Wang, X.-K., Hou, S., & Pei, F.-Y. (2018). Suppression of SMOC2 reduces bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibition of TGF-β1/SMADs pathway. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 105, 841–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.058
Peeters, T., Monteagudo, S., Tylzanowski, P., Luyten, F. P., Lories, R., & Cailotto, F. (2018). SMOC2 inhibits calcification of osteoprogenitor and endothelial cells. PLoS ONE, 13(6), e0198104–e0198104. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198104
Rocnik, E. F., Liu, P., Sato, K., Walsh, K., & Vaziri, C. (2006). The novel SPARC family member SMOC-2 potentiates angiogenic growth factor activity *. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(32), 22855–22864. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M513463200
Zomer, A., Vendrig, T., Hopmans, E. S., van Eijndhoven, M., Middeldorp, J. M., & Pegtel, D. M. (2010). Exosomes: Fit to deliver small RNA. Communicative & Integrative Biology, 3(5), 447–450. https://doi.org/10.4161/cib.3.5.12339
Raso, A., Dirkx, E., Philippen, L. E., Fernandez-Celis, A., De Majo, F., Sampaio-Pinto, V., Sansonetti, M., Juni, R., El Azzouzi, H., Calore, M., Bitsch, N., Olieslagers, S., Oerlemans, M. I. F. J., Huibers, M. M., de Weger, R. A., Reckman, Y. J., Pinto, Y. M., Zentilin, L., Zacchigna, S., … De Windt, L. J. (2019). Therapeutic delivery of miR-148a suppresses ventricular dilation in heart failure. Molecular Therapy, 27(3), 584–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.11.011
Witwer, K. W., Buzás, E. I., Bemis, L. T., Bora, A., Lässer, C., Lötvall, J., Nolte-’t Hoen, E. N., Piper, M. G., Sivaraman, S., Skog, J., Théry, C., Wauben, M. H., & Hochberg, F. (2013). Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3402i3400.20360
Stoorvogel, W. (2012). Functional transfer of microRNA by exosomes. Blood, 119(3), 646–648. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-11-389478
Kuse, N., Kamio, K., Azuma, A., Matsuda, K., Inomata, M., Usuki, J., Morinaga, A., Tanaka, T., Kashiwada, T., Atsumi, K., Hayashi, H., Saito, Y., Seike, M., & Gemma, A. (2020). Exosome-derived microRNA-22 ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by regulating fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Nippon Medical School, 87(3), 118–128. https://doi.org/10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2020_87-302
Zhu, J., Liu, B., Wang, Z., Wang, D., Ni, H., Zhang, L., & Wang, Y. (2019). Exosomes from nicotine-stimulated macrophages accelerate atherosclerosis through miR-21-3p/PTEN-mediated VSMC migration and proliferation. Theranostics, 9(23), 6901–6919. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.37357
Dai, Y., Wang, S., Chang, S., Ren, D., Shali, S., Li, C., Yang, H., Huang, Z., & Ge, J. (2020). M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry microRNA-148a to alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TXNIP and the TLR4/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 142, 65–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.02.007
Lu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, N., Pan, Z., Gao, X., Zhang, F., Zhang, Y., Shan, H., Luo, X., Bai, Y., Sun, L., Song, W., Xu, C., Wang, Z., & Yang, B. (2010). MicroRNA-328 contributes to adverse electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 122(23), 2378–2387. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.958967
Ling, T. Y., Wang, X. L., Chai, Q., Lu, T., Stulak, J. M., Joyce, L. D., Daly, R. C., Greason, K. L., Wu, L. Q., Shen, W. K., Cha, Y. M., & Lee, H. C. (2017). Regulation of cardiac CACNB2 by microRNA-499: Potential role in atrial fibrillation. BBA Clin, 7, 78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbacli.2017.02.002
Yuan, J., Chen, H., Ge, D., Xu, Y., Xu, H., Yang, Y., Gu, M., Zhou, Y., Zhu, J., Ge, T., Chen, Q., Gao, Y., Wang, Y., Li, X., & Zhao, Y. (2017). Mir-21 promotes cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction Via _targeting Smad7. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 42(6), 2207–2219. https://doi.org/10.1159/000479995
Fang, Z., Weng, Y., Xiao, F., & Yu, J. (2021). LncRNA RP11–390F4.3 inhibits invasion and migration of glioblastoma cells by downregulating ROCK1. NeuroReport. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000001676
Kumar, S., Sharawat, S. K., Ali, A., Gaur, V., Malik, P. S., Kumar, S., Mohan, A., & Guleria, R. (2020). Identification of differentially expressed circulating serum microRNA for the diagnosis and prognosis of Indian non-small cell lung cancer patients. Current Problems in Cancer, 44(4), 100540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100540
Zhang, H., Liu, W., Ge, H., & Li, K. (2021). Aberrant expression of miR-148a-3p in Alzheimer’s disease and its protective role against amyloid-beta induced neurotoxicity. Neuroscience Letters, 756, 135953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135953
Zhao, X., Chen, X., Wu, X., Zhu, L., Long, J., Su, L., & Gu, L. (2021). Machine learning analysis of MicroRNA expression data reveals novel diagnostic biomarker for ischemic stroke. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 30(8), 105825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105825
Jiang, K., Yang, J., Yang, C., Zhang, T., Shaukat, A., Yang, X., Dai, A., Wu, H., & Deng, G. (2020). miR-148a suppresses inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced endometritis. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(1), 405–417. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14744
Xiong, J., Ni, J., Chen, C., & Wang, K. (2020). miR-148a-3p regulates alcoholic liver fibrosis through _targeting ERBB3. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 46(3), 1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2020.4655
Miao, B., Qi, W.-j, Zhang, S.-w, Wang, H., Wang, C., Hu, L., Huang, G.-w, Li, S.-r, & Wang, H. (2019). miR-148a suppresses autophagy by down-regulation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology, 19(4), 557–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2019.04.014
Gerarduzzi, C., Kumar, R. K., Trivedi, P., Ajay, A. K., Iyer, A., Boswell, S., Hutchinson, J. N., Waikar, S. S., & Vaidya, V. S. (2017). Silencing SMOC2 ameliorates kidney fibrosis by inhibiting fibroblast to myofibroblast transformation. JCI Insight, 2(8), e90299. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90299
Xu, M., Yi, M., & Li, N. (2021). MicroRNA-17-5p restrains the dysfunction of Ang-II induced podocytes by suppressing secreted modular calcium-binding protein 2 via NF-κB and TGFβ signaling. Environmental Toxicology, 36(7), 1402–1411. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.23136
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
We did not accept funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZ contributed to conception, design, and manuscript writing; WZ and YM performed the research; ZC involved in data analysis and interpretation; and all authors contributed to the final approval of the manuscript:
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The experimental protocol of our study was performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by Xi’an No.3 Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital Northwest University. The protocol of this research has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Xi’an No.3 Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital Northwest University. All patients have signed written informed consent. (IECAF20200501).
Consent to Participate
All patients have signed written informed consent.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Man, Y. & Chen, Z. microRNA-148a in Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviates Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Atrial Fibrillation by Inhibiting SMOC2. Mol Biotechnol 64, 1076–1087 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00487-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00487-z