Abstract
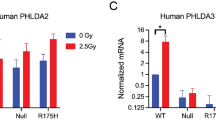
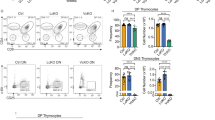
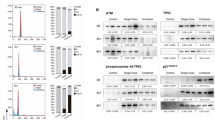
THE p53 tumour suppressor gene is the most widely mutated gene in human tumorigenesis1,2. p53 encodes a transcriptional activator3–7 whose _targets may include genes that regulate genomic stability8,9, the cellular response to DNA damage10,11, and cell-cycle progression12,13. Introduction of wild-type p53 into cell lines that have lost endogenous p53 function can cause growth arrest14–16 or induce a process of cell death known as apoptosis17,18. During normal development, self-reactive thymocytes undergo negative selection by apoptosis19, which can also be induced in immature thymocytes by other stimuli, including exposure to glucocorticoids15 and ionizing radiation16. Although normal negative selection involves signalling through the T-cell receptor14, the induction of apoptosis by other stimuli is poorly understood. We have investigated the requirement for p53 during apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. We report here that immature thymocytes lacking p53 die normally when exposed to compounds that may mimic T-cell receptor engagement and to glucocorticoids but are resistant to the lethal effects of ionizing radiation. These results demonstrate that p53 is required for radiation-induced cell death in the thymus but is not necessary for all forms of apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hollstein, M., Sidransky, D., Vogelstein, B. & Harris, C. C. Science 253, 49–53 (1991).
Levine, A. J., Momand, J. & Finlay, C. A. Nature 352, 453–456 (1991).
Fields, S. & Jang, S. K. Science 249, 1046–1049 (1990).
Raycroft, L., Wu, J. & Lozano, G. Science 249, 1049–1051 (1990).
Farmer, G. et al. Nature 358, 83–86 (1992).
Kern, S. E. et al. Science 256, 827–830 (1992).
Zambetti, G. P., Bargonneti, J., Walker, K., Prives, C. & Levine, A. J. Genes Dev. 6, 1143–1152 (1992).
Livingstone, L. R. et al. Cell 70, 923–935 (1992).
Yin, Y., Tainsky, M. A., Bischoff, F. Z., Strong, L. C. & Wahl, G. M. Cell 70, 937–948 (1992).
Kastan, M. B., Onyekwere, O., Sidransky, D., Vogelstein, B. & Craig, R. W. Cancer Res. 51, 6304–6311 (1991).
Kastan, M. et al. Cell 71, 587–597 (1992).
Michalovitz, D., Halevy, O. & Oren, M. Cell 62, 671–680 (1990).
Martinez, J., Georgoff, I., Martinez, J. & Levine, A. J. Genes Dev. 5, 151–159 (1991).
Mercer, W. E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 6166–6170 (1990).
Diller, L. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 10, 5772–5781 (1990).
Baker, S. J., Markowitz, S., Fearon, E. H., Willson, J. K. V. & Vogelstein, B. Science 249, 912–915 (1990).
Yonish-Rouach, E. et al. Nature 352, 345–347 (1991).
Shaw, P. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 4495–4499 (1992).
MacDonald, H. R. & Lees, R. K. Nature 343, 642–644 (1990).
Wyllie, A. H. Nature 343, 555–559 (1980).
Sellins, K. S. & Cohen, J. J. J. Immun. 139, 3199–3206 (1987).
Crabtree, G. R. Science 243, 335–362 (1989).
Smith, C. A., Williams, G. T., Kingston, R., Jenkinson, E. J. & Owen, J. J. T. Nature 337, 181–184 (1989).
Wyllie, A., Morris, R., Smith, A. & Dunlop, D. J. Pathol 142, 67–77 (1984).
Sentman, C. L., Shutter, J. R., Hockenbery, D., Kanagawa, O. & Korsmeyer, S. Cell 67, 879–888 (1991).
Strasser, A., Harris, A. W. & Cory, S. Cell 67, 889–899 (1991).
Donehower, L. A. et al. Nature 356, 215–221 (1992).
Lane, D. P. Nature 358, 15–16 (1992).
McDonnell, T. J. et al. Cell 57, 79–88 (1989).
Strasser, A., Harris, A. W., Bath, M. L. & Cory, S. Nature 348, 331–333 (1990).
Tsujimoto, Y., Finger, L. R., Yunis, J., Nowell, P. C. & Croce, C. M. Science 226, 1097–1099 (1984).
Gossler, A., Doetschman, T., Korn, R., Serfling, E. & Kernier, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 9065–9069 (1986).
Mori, N. et al. Int. J. Radial. Biol. 62, 153–159 (1991).
Shi, Y. F. et al. J. Immun. 44, 3326–3333 (1990).
Butcher, E. & Ford, W. in Handbook of Experimental Immunology Vol. 2 57.13–57.17 (Blackwell Scientific, Oxford. 1986).
Barry, M. A. & Eastman, A. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 300, 440–450 (1993).
Harlow, E. & Lane, D. Antibodies: a laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1988).
Yewdell, J. W., Gannon, J. V. & Lane, D. P. J. Virol. 59, 444–452 (1986).
Gannon, J. V., Greaves, R., Iggo, R. & Lane, D. P. EMBO J. 9, 1595–1602 (1990).
Guarente, L. & Haldi, M. J. biol. Chem. 264, 17107–17112 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lowe, S., Schmitt, E., Smith, S. et al. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature 362, 847–849 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/362847a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/362847a0